Gravel mulch provides superior drainage and long-lasting durability, making it ideal for pathways and areas prone to moisture retention, while organic mulch improves soil fertility by decomposing and enriching the ground with nutrients. Unlike organic mulch, gravel does not attract pests or need frequent replacement, offering a low-maintenance landscaping option. However, organic mulch better supports plant growth by maintaining soil moisture and temperature, crucial for garden beds and sensitive plants.
Table of Comparison
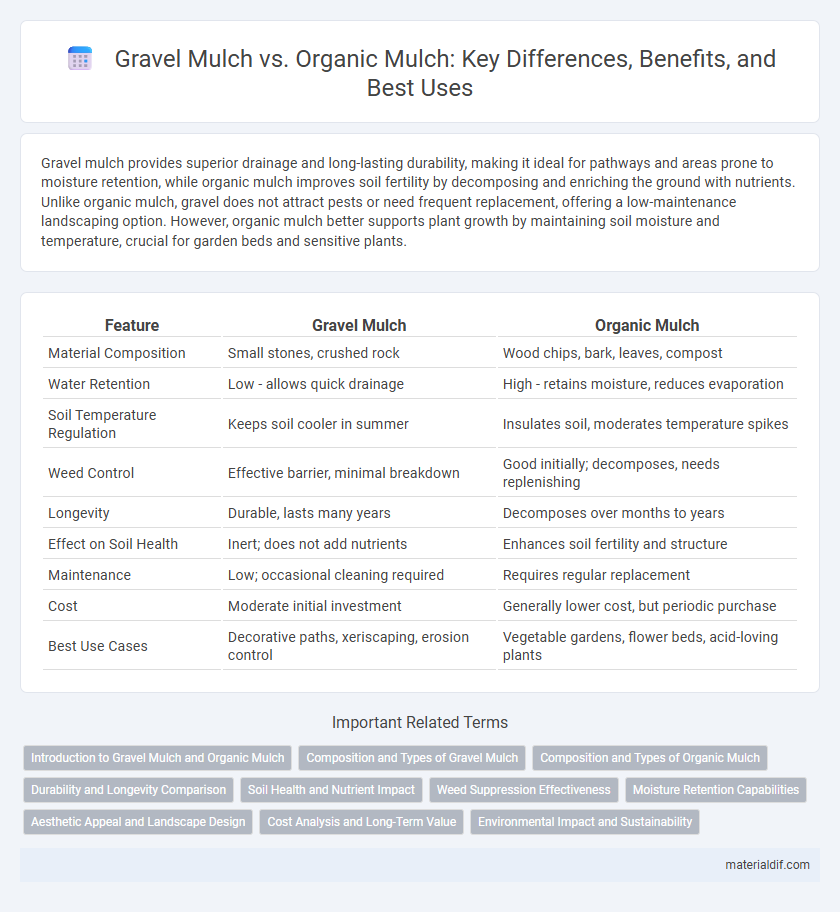
| Feature | Gravel Mulch | Organic Mulch |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Small stones, crushed rock | Wood chips, bark, leaves, compost |
| Water Retention | Low - allows quick drainage | High - retains moisture, reduces evaporation |
| Soil Temperature Regulation | Keeps soil cooler in summer | Insulates soil, moderates temperature spikes |
| Weed Control | Effective barrier, minimal breakdown | Good initially; decomposes, needs replenishing |
| Longevity | Durable, lasts many years | Decomposes over months to years |
| Effect on Soil Health | Inert; does not add nutrients | Enhances soil fertility and structure |
| Maintenance | Low; occasional cleaning required | Requires regular replacement |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Generally lower cost, but periodic purchase |
| Best Use Cases | Decorative paths, xeriscaping, erosion control | Vegetable gardens, flower beds, acid-loving plants |
Introduction to Gravel Mulch and Organic Mulch
Gravel mulch consists of small stones or pebbles used as a ground cover to improve drainage, reduce weed growth, and provide a decorative landscape element. Organic mulch, made from natural materials like bark, wood chips, or compost, enhances soil fertility by decomposing and adding nutrients. Choosing between gravel and organic mulch depends on factors such as soil improvement needs, moisture retention, and aesthetic preferences.
Composition and Types of Gravel Mulch
Gravel mulch consists primarily of inorganic materials such as crushed stones, pebbles, and decorative rocks, offering durability and excellent drainage compared to organic mulch made from bark, leaves, and composted plant material. Common types of gravel mulch include pea gravel, limestone, river rock, and decomposed granite, each varying in size, color, and texture to suit different landscaping needs. Unlike organic mulch that decomposes over time, gravel mulch remains stable, reducing soil erosion and suppressing weeds without altering soil nutrient content.
Composition and Types of Organic Mulch
Gravel mulch consists primarily of small stones or pebbles, offering excellent drainage and durability, while organic mulch includes materials such as wood chips, bark, straw, and composted leaves that decompose to enrich soil fertility. The composition of organic mulches varies, with hardwood bark providing long-lasting coverage, straw promoting moisture retention, and composted leaves enhancing nutrient content for plant growth. Choosing between gravel and organic mulch depends on landscape needs, soil improvement goals, and maintenance preferences.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Gravel mulch offers superior durability and longevity compared to organic mulch, lasting several years without decomposing or needing replacement. Unlike organic mulch, which breaks down over time and requires regular replenishing every 1-2 years, gravel mulch maintains its structure and effectiveness in weed suppression. This makes gravel mulch a cost-effective, low-maintenance choice for long-term landscaping projects.
Soil Health and Nutrient Impact
Gravel mulch improves soil drainage and prevents erosion but does not contribute nutrients or organic matter, which can limit long-term soil fertility. Organic mulch, such as wood chips or compost, enhances soil health by adding vital nutrients and improving microbial activity, leading to richer, more fertile soil. Over time, organic mulch supports nutrient cycling and moisture retention, promoting sustainable plant growth compared to inert gravel.
Weed Suppression Effectiveness
Gravel mulch provides superior weed suppression by creating a solid barrier that blocks sunlight and prevents seed germination, reducing weed growth over time. Organic mulch, while beneficial for soil health and moisture retention, tends to decompose and require more frequent replenishment, which can allow weeds to emerge more easily. The durability and density of gravel mulch make it a long-lasting solution for minimizing weed problems in landscaping.
Moisture Retention Capabilities
Gravel mulch offers superior drainage but holds less moisture compared to organic mulch, which retains water effectively by absorbing and slowly releasing it into the soil. Organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark, enhances soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation and maintaining consistent soil temperature. Choosing between gravel and organic mulch depends on plant water needs and soil conditions, with organic mulch typically providing better moisture conservation for drought-sensitive plants.
Aesthetic Appeal and Landscape Design
Gravel mulch offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with clean lines and a variety of color options that complement contemporary landscape designs, providing durability and low maintenance appeal. Organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark, enhances natural landscapes with its rich, earthy tones and texture, promoting soil health and moisture retention. Selecting between gravel and organic mulch depends on the desired visual style and maintenance preferences for the garden environment.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Gravel mulch typically involves higher upfront costs due to material and installation but offers low maintenance and durability with a lifespan of 20+ years, providing significant long-term value. Organic mulch, while initially cheaper, requires annual replacement and may incur additional costs related to pest control and soil health management. When evaluating cost-effectiveness over time, gravel mulch is often more economical because it reduces recurring expenses and supports consistent soil moisture retention.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gravel mulch reduces water evaporation and prevents soil erosion, making it a sustainable option for long-term landscaping with minimal maintenance and no need for frequent replacement. Organic mulch, while supporting soil health by adding nutrients and promoting microbial activity, decomposes over time and requires regular replenishment, which can contribute to carbon emissions through repeated transport and processing. Choosing gravel mulch benefits arid environments by conserving water and limiting organic waste, whereas organic mulch enhances soil fertility but may demand more resources to maintain ecological balance.
Gravel Mulch vs Organic Mulch Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com