Polymer-coated gravel offers enhanced durability and improved resistance to erosion compared to uncoated gravel, making it ideal for landscaping and construction projects. The polymer coating binds the gravel particles together, reducing dust and preventing displacement under heavy traffic or weather conditions. Uncoated gravel, while more affordable, lacks these protective benefits and may require more frequent maintenance or replenishment.
Table of Comparison
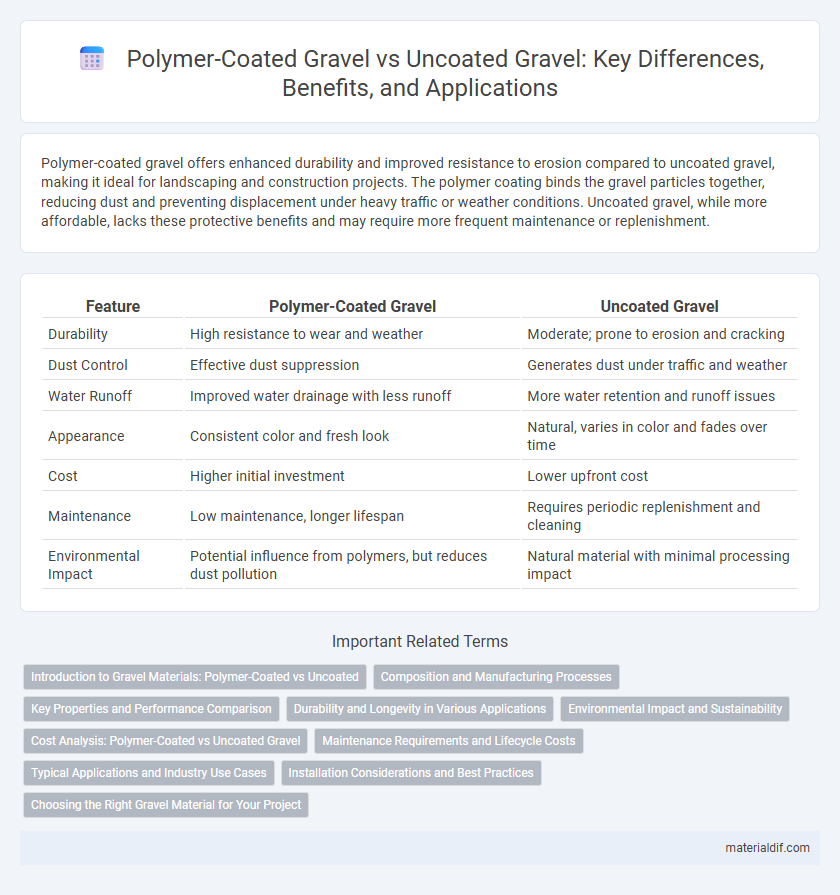
| Feature | Polymer-Coated Gravel | Uncoated Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to wear and weather | Moderate; prone to erosion and cracking |
| Dust Control | Effective dust suppression | Generates dust under traffic and weather |
| Water Runoff | Improved water drainage with less runoff | More water retention and runoff issues |
| Appearance | Consistent color and fresh look | Natural, varies in color and fades over time |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, longer lifespan | Requires periodic replenishment and cleaning |
| Environmental Impact | Potential influence from polymers, but reduces dust pollution | Natural material with minimal processing impact |
Introduction to Gravel Materials: Polymer-Coated vs Uncoated
Polymer-coated gravel offers enhanced durability and resistance to weathering compared to uncoated gravel, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and landscaping projects requiring long-lasting stability. Uncoated gravel, composed of natural aggregates, provides excellent drainage and cost-efficiency but lacks the protective layer that prevents erosion and fragmentation. The polymer coating binds gravel particles, reducing dust and maintaining structural integrity under varying environmental conditions.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polymer-coated gravel consists of natural stones bound with a durable polymer resin, enhancing water resistance and structural integrity compared to uncoated gravel, which is purely natural aggregate without additives. The manufacturing process of polymer-coated gravel involves cleaning raw gravel followed by spraying or mixing it with a polymer binder, then curing to form a hard, protective layer that improves longevity and reduces dust and erosion. Uncoated gravel is produced by crushing and sorting natural stones with minimal processing, maintaining its raw mineral composition but lacking the enhanced properties provided by polymer coatings.
Key Properties and Performance Comparison
Polymer-coated gravel offers enhanced durability and water resistance compared to uncoated gravel, resulting in improved structural integrity and reduced erosion. The polymer coating provides better adhesion and stability, which is especially beneficial in construction and landscaping applications requiring long-lasting performance. Uncoated gravel, while cost-effective and natural, lacks the protective layer, making it more susceptible to wear and environmental degradation over time.
Durability and Longevity in Various Applications
Polymer-coated gravel exhibits superior durability by resisting wear, washout, and chemical degradation compared to uncoated gravel, making it ideal for high-traffic and industrial applications. The polymer coating acts as a protective barrier, significantly extending the gravel's longevity in landscaping, road construction, and drainage systems. Uncoated gravel tends to degrade faster under harsh environmental conditions, leading to increased maintenance and replacement costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer-coated gravel significantly reduces dust generation and runoff pollution compared to uncoated gravel, enhancing environmental protection in construction and landscaping projects. The coated gravel's longer durability decreases the frequency of replacement, minimizing resource consumption and landfill waste. However, uncoated gravel remains more biodegradable and easier to recycle, making it a more sustainable choice in natural ecosystems.
Cost Analysis: Polymer-Coated vs Uncoated Gravel
Polymer-coated gravel typically incurs higher initial costs due to the additional coating process, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance expenses over time. Uncoated gravel offers lower upfront investment but may require more frequent replacement and generate higher dust levels, increasing overall lifecycle costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that polymer-coated gravel can provide better long-term value in infrastructure and landscaping projects despite its premium price.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Costs
Polymer-coated gravel offers significantly reduced maintenance requirements due to its enhanced resistance to erosion, dust, and weed growth compared to uncoated gravel. This coating extends the gravel's lifecycle by preventing displacement and degradation, resulting in lower long-term replacement and repair costs. Consequently, polymer-coated gravel delivers greater cost efficiency over time despite a higher initial investment.
Typical Applications and Industry Use Cases
Polymer-coated gravel is extensively used in civil engineering projects such as road construction, erosion control, and drainage systems, providing enhanced durability and reduced dust emissions compared to uncoated gravel. Uncoated gravel remains prevalent in landscaping, garden paths, and driveways due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. The petrochemical and construction industries favor polymer-coated gravel for heavy traffic zones and infrastructure projects requiring longevity and environmental compliance.
Installation Considerations and Best Practices
Polymer-coated gravel offers enhanced adhesion and reduced dust during installation compared to uncoated gravel, leading to quicker stabilization and less maintenance. Best practices for polymer-coated gravel include ensuring a dry surface for optimal bonding and using appropriate compaction equipment to maximize aggregate interlock. In contrast, uncoated gravel requires thorough grading and consistent moisture control to prevent displacement and erosion over time.
Choosing the Right Gravel Material for Your Project
Polymer-coated gravel offers enhanced durability and resistance to erosion compared to uncoated gravel, making it ideal for high-traffic areas or projects requiring long-term stability. Uncoated gravel is more cost-effective and provides better drainage, suitable for landscaping or projects where water permeability is crucial. Selecting the right gravel material depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Polymer-coated gravel vs uncoated gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com