Limestone gravel offers a smooth texture and a light color, making it ideal for decorative landscaping and driveways, while its alkaline properties help neutralize acidic soils. Granite gravel is harder and more durable, providing excellent drainage and resistance to erosion, which is perfect for heavy-duty construction and road base applications. Choosing between limestone and granite gravel depends on the specific project requirements, including aesthetic preferences and functional durability.
Table of Comparison
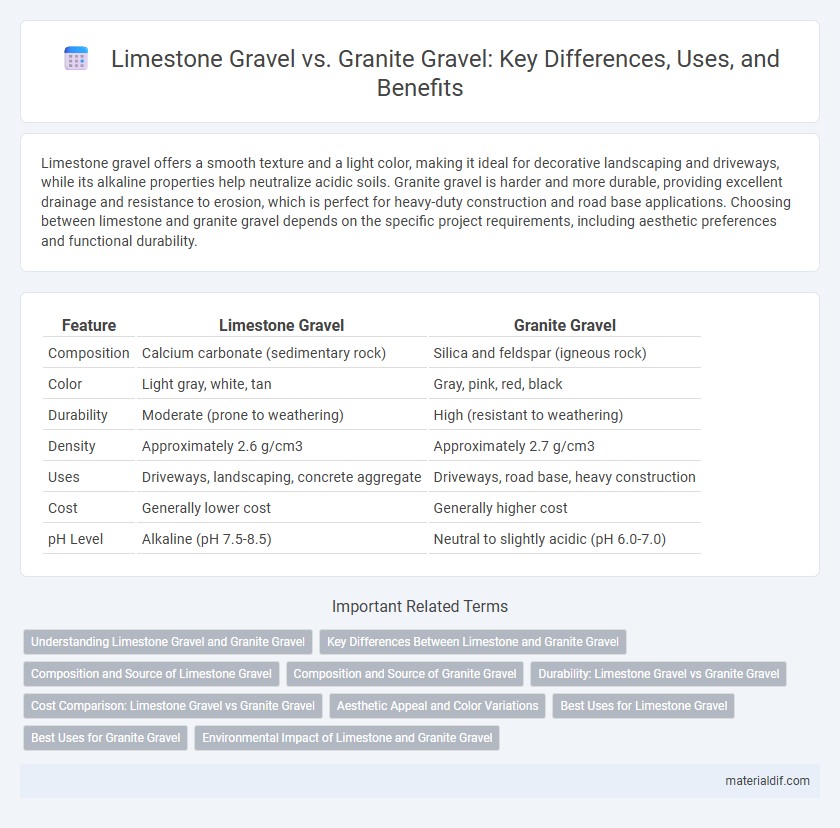
| Feature | Limestone Gravel | Granite Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Calcium carbonate (sedimentary rock) | Silica and feldspar (igneous rock) |
| Color | Light gray, white, tan | Gray, pink, red, black |
| Durability | Moderate (prone to weathering) | High (resistant to weathering) |
| Density | Approximately 2.6 g/cm3 | Approximately 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Uses | Driveways, landscaping, concrete aggregate | Driveways, road base, heavy construction |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Generally higher cost |
| pH Level | Alkaline (pH 7.5-8.5) | Neutral to slightly acidic (pH 6.0-7.0) |
Understanding Limestone Gravel and Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel, composed primarily of calcium carbonate, offers excellent drainage and compacts well for stable surfaces, making it ideal for driveways and landscaping. Granite gravel, known for its durability and angular shape, provides superior traction and resists weathering, making it preferred for heavy-duty construction and road base applications. Understanding the mineral composition and physical properties of limestone and granite gravel helps in selecting the appropriate material based on project requirements.
Key Differences Between Limestone and Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel is primarily composed of sedimentary rock rich in calcium carbonate, offering a softer, more porous texture that enhances drainage but may degrade faster over time. Granite gravel consists of igneous rock with high durability and density, providing superior strength and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Key differences include limestone gravel's alkaline pH which can affect soil chemistry, compared to granite gravel's neutral pH and greater longevity in diverse environmental conditions.
Composition and Source of Limestone Gravel
Limestone gravel is primarily composed of calcium carbonate derived from sedimentary rock formed mainly in marine environments, often sourced from quarrying crushed limestone deposits. Granite gravel consists mostly of quartz, feldspar, and mica crystals from igneous rock, originating from the natural weathering and fragmentation of granite outcrops. Limestone gravel offers a more reactive surface due to its carbonate content, while granite gravel provides greater durability and hardness from its silicate minerals.
Composition and Source of Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel primarily consists of calcium carbonate derived from sedimentary rock formations, while granite gravel is composed of interlocking crystals of quartz, feldspar, and mica from igneous rock sources. Granite gravel originates from the natural weathering and crushing of granite rocks found in mountainous and volcanic regions, providing a dense and durable aggregate. Its mineral composition offers high resistance to abrasion, making granite gravel ideal for heavy-duty construction applications.
Durability: Limestone Gravel vs Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel offers moderate durability, often preferred for landscaping where aesthetic appeal is important but heavy load-bearing is minimal. Granite gravel exhibits superior durability due to its hardness and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and construction projects requiring long-lasting materials. The mineral composition of granite, primarily quartz and feldspar, contributes significantly to its strength compared to the softer calcium carbonate in limestone.
Cost Comparison: Limestone Gravel vs Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel generally costs less than granite gravel due to its abundant availability and easier extraction process. Granite gravel tends to be more expensive because of its durability and higher crushing costs associated with mining harder rock. When selecting between limestone and granite gravel, budget considerations can significantly influence project decisions based on their price differences.
Aesthetic Appeal and Color Variations
Limestone gravel offers a warm, neutral palette with creamy beige and off-white tones that blend seamlessly into natural landscapes, enhancing curb appeal with its subtle elegance. Granite gravel provides a more dynamic and diverse aesthetic, featuring speckled patterns and colors ranging from pink and red to gray and black, adding texture and visual interest to driveways and pathways. Both gravels support different design preferences, but granite's wider color spectrum makes it more versatile for contemporary and bold landscaping projects.
Best Uses for Limestone Gravel
Limestone gravel is highly valued for its durability and excellent compaction, making it ideal for driveways, pathways, and construction base layers where stability is crucial. Its natural calcium carbonate content enhances soil pH, benefiting agricultural applications and landscaping projects requiring improved drainage and support. Compared to granite gravel, limestone gravel provides a smoother, more cohesive surface, making it preferable for decorative and functional uses in residential and commercial settings.
Best Uses for Granite Gravel
Granite gravel is highly durable and offers excellent drainage, making it ideal for driveways, walkways, and construction base layers where strength and stability are essential. Its angular shape allows for better compaction compared to limestone gravel, which can be more prone to washing away in heavy rains. Granite gravel also resists wear and weathering, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-traffic areas and outdoor landscaping projects.
Environmental Impact of Limestone and Granite Gravel
Limestone gravel, primarily composed of calcium carbonate, has a lower environmental footprint due to its natural abundance and ease of recycling, reducing quarrying demands. Granite gravel, containing silicate minerals, is more energy-intensive to extract and process, leading to higher carbon emissions and habitat disruption. The biodegradable nature of limestone supports soil health, while granite's hardness extends material lifespan but contributes more to ecological disturbance during extraction.
Limestone Gravel vs Granite Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com