Brown gravel offers rich, earthy tones that blend seamlessly with natural landscapes, making it ideal for garden paths and rustic settings. Gray gravel provides a sleek, modern appearance with versatile neutral shades, complementing contemporary driveways and patios. Both types offer excellent drainage and durability but differ primarily in aesthetic appeal and color coordination with surrounding environments.
Table of Comparison
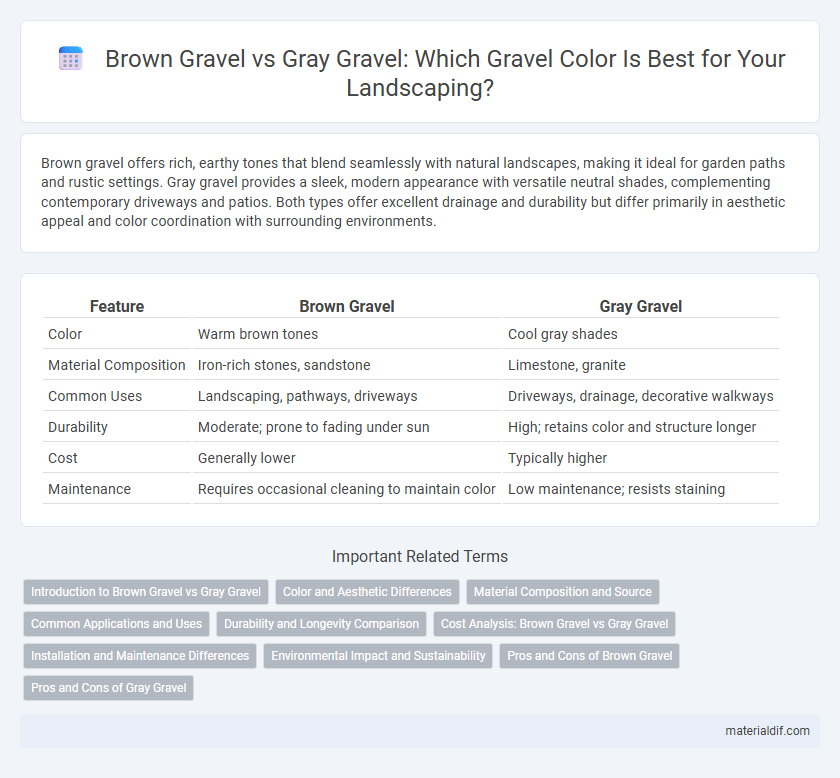
| Feature | Brown Gravel | Gray Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Warm brown tones | Cool gray shades |
| Material Composition | Iron-rich stones, sandstone | Limestone, granite |
| Common Uses | Landscaping, pathways, driveways | Driveways, drainage, decorative walkways |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to fading under sun | High; retains color and structure longer |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Maintenance | Requires occasional cleaning to maintain color | Low maintenance; resists staining |
Introduction to Brown Gravel vs Gray Gravel
Brown gravel features warm, earth-toned hues ranging from light tan to deep chocolate, ideal for landscaping projects aiming to create a natural, rustic ambiance. Gray gravel offers a cooler, neutral palette with shades from light silver to charcoal, often preferred for modern driveways and urban garden designs. Choosing between brown and gray gravel depends on the desired aesthetic, climate compatibility, and surrounding architecture.
Color and Aesthetic Differences
Brown gravel features warm, earthy tones that blend seamlessly with natural landscapes, enhancing garden beds and pathways with a rustic appeal. Gray gravel offers a cooler, modern aesthetic that complements contemporary designs and adds a sleek, neutral backdrop to driveways and patios. The choice between brown and gray gravel significantly impacts the overall visual harmony and style of outdoor spaces, making color a key factor in landscape design decisions.
Material Composition and Source
Brown gravel typically originates from riverbeds and consists mainly of sedimentary rocks such as sandstone and shale, giving it a rich, earthy hue. Gray gravel is commonly derived from crushed granite or limestone, characterized by its dense composition and neutral coloration. Both types offer unique aesthetic and functional qualities depending on their mineral content and geological source.
Common Applications and Uses
Brown gravel, characterized by its warm, earthy tones, is frequently used in landscaping projects such as garden pathways, driveways, and decorative borders due to its natural aesthetic appeal and ability to complement various soil types. Gray gravel, known for its neutral and versatile color, is preferred for construction applications like concrete aggregate, road base, and drainage systems, offering durability and a clean, modern look. Both types serve functional purposes, but brown gravel is favored for visual appeal in outdoor spaces, while gray gravel is often chosen for its strength and practicality in heavy-duty uses.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Brown gravel typically contains higher iron oxide content, which can enhance its durability by providing natural resistance to weathering and erosion. Gray gravel, often composed of limestone or granite, tends to have greater hardness and density, contributing to superior longevity under heavy traffic conditions. The choice between brown and gray gravel should consider the specific environmental exposure and load requirements to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Cost Analysis: Brown Gravel vs Gray Gravel
Brown gravel typically costs between $30 and $50 per ton, making it a budget-friendly option for landscaping and driveways, while gray gravel ranges from $40 to $70 per ton, reflecting its popularity and widespread use in construction projects. The availability and source location heavily influence the price difference, with brown gravel often sourced locally and gray gravel sometimes imported or processed for specific uses. Maintenance and longevity factors also impact overall cost, as gray gravel tends to compact better and resist dirt accumulation, potentially reducing long-term replacement expenses.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Brown gravel, composed primarily of sandstone and iron oxide, offers easier installation due to its angular shape that locks firmly, reducing shifting during use, whereas gray gravel, often made from granite or limestone, may require more compaction to stabilize because of its smoother, rounded edges. Maintenance for brown gravel involves less frequent replenishment as its heavier particles resist displacement, while gray gravel may need regular raking and topping to maintain an even surface and prevent weed growth. Both types benefit from proper drainage installation, but brown gravel's natural moisture resistance can reduce erosion issues commonly observed with gray gravel in wet climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Brown gravel typically has a lower environmental impact due to its local sourcing, reducing transportation emissions compared to gray gravel often sourced from distant quarries. Both types affect ecosystems, but brown gravel's extraction sites generally show better restoration practices that support biodiversity. Sustainable gravel use prioritizes recycling materials and minimizing habitat disruption regardless of color.
Pros and Cons of Brown Gravel
Brown gravel offers excellent aesthetic warmth and blends naturally with landscaping, enhancing garden paths and driveways with its earthy tones. It provides good drainage and durability, making it suitable for outdoor applications, but its darker color may show dirt more prominently and can heat up more in direct sunlight. Compared to gray gravel, brown gravel may require more maintenance to keep its vibrant look but contributes to a softer, more organic appearance in various settings.
Pros and Cons of Gray Gravel
Gray gravel offers superior versatility and aesthetic appeal for landscaping and construction projects, with its neutral color complementing various design schemes. It provides excellent drainage and durability, making it ideal for driveways and pathways, but it may show dirt and stains more readily than darker gravels. While generally cost-effective, gray gravel can have a higher initial price compared to brown gravel due to its popularity and sourcing.
Brown Gravel vs Gray Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com