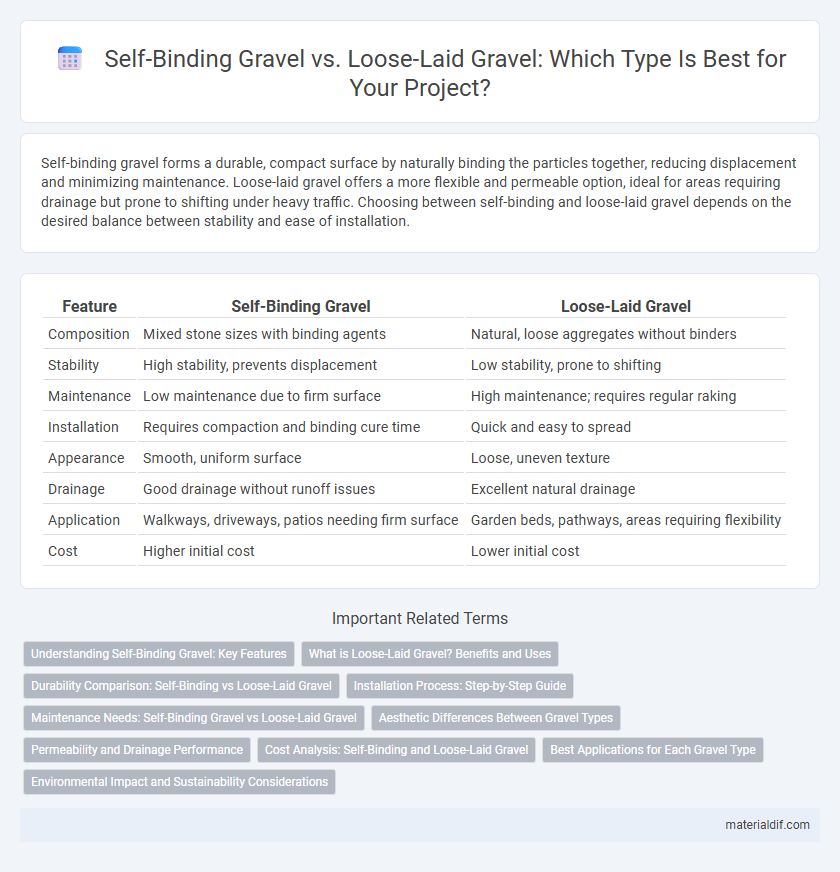
Self-binding gravel forms a durable, compact surface by naturally binding the particles together, reducing displacement and minimizing maintenance. Loose-laid gravel offers a more flexible and permeable option, ideal for areas requiring drainage but prone to shifting under heavy traffic. Choosing between self-binding and loose-laid gravel depends on the desired balance between stability and ease of installation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Binding Gravel | Loose-Laid Gravel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Mixed stone sizes with binding agents | Natural, loose aggregates without binders |
| Stability | High stability, prevents displacement | Low stability, prone to shifting |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to firm surface | High maintenance; requires regular raking |
| Installation | Requires compaction and binding cure time | Quick and easy to spread |
| Appearance | Smooth, uniform surface | Loose, uneven texture |
| Drainage | Good drainage without runoff issues | Excellent natural drainage |
| Application | Walkways, driveways, patios needing firm surface | Garden beds, pathways, areas requiring flexibility |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Understanding Self-Binding Gravel: Key Features
Self-binding gravel consists of naturally occurring fine particles that, when compacted, create a firm and stable surface ideal for pathways and driveways. Unlike loose-laid gravel, it reduces migration and erosion by forming a semi-solid layer that enhances durability and requires less maintenance. Its key features include improved load-bearing capacity, enhanced drainage, and resistance to displacement under traffic.
What is Loose-Laid Gravel? Benefits and Uses
Loose-laid gravel refers to small, unbound stones spread loosely over a surface without any adhesive or binding material. This type of gravel offers excellent drainage, is easy to install and maintain, and provides a flexible, permeable ground cover ideal for pathways, driveways, and garden beds. Its natural look and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice for landscaping projects requiring quick installation and water runoff control.
Durability Comparison: Self-Binding vs Loose-Laid Gravel
Self-binding gravel offers superior durability compared to loose-laid gravel due to its compacted, interlocking structure that resists displacement and erosion. Its cohesive properties reduce the need for frequent maintenance, making it ideal for high-traffic pathways and driveways. Loose-laid gravel, while easier to install, tends to scatter and degrade faster under heavy use and environmental stress.
Installation Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Self-binding gravel requires a compacted sub-base followed by spreading and compacting the gravel mixture to activate the binding agents, creating a solid surface. Loose-laid gravel involves leveling the ground, spreading the gravel evenly, and lightly compacting without binding materials, allowing for flexibility and easier repairs. Proper preparation and compaction are essential for both types to ensure durability and performance in driveways or pathways.
Maintenance Needs: Self-Binding Gravel vs Loose-Laid Gravel
Self-binding gravel requires less frequent maintenance due to its compact and stable surface, reducing weed growth and erosion compared to loose-laid gravel. Loose-laid gravel often demands regular raking, topping up, and weed control to maintain a tidy and safe surface. Choosing self-binding gravel minimizes upkeep efforts and enhances long-term durability for pathways and driveways.
Aesthetic Differences Between Gravel Types
Self-binding gravel creates a smooth, compact surface with a uniform appearance, ideal for pathways and driveways requiring a polished look. Loose-laid gravel offers a more natural, textured aesthetic with visible individual stones, enhancing garden beds and informal landscaping. Color consistency and stone size in self-binding gravel provide a clean, modern finish, while loose-laid gravel emphasizes rustic charm and organic variation.
Permeability and Drainage Performance
Self-binding gravel offers moderate permeability with better structural integrity, reducing water runoff and enhancing drainage performance compared to loose-laid gravel. Loose-laid gravel has higher permeability due to its loose structure, allowing rapid water infiltration but often causing instability and potential erosion. Optimizing drainage systems requires balancing permeability with surface firmness, where self-binding gravel excels in erosion control and loose-laid gravel favors maximum water absorption.
Cost Analysis: Self-Binding and Loose-Laid Gravel
Self-binding gravel typically costs more upfront due to the binding agents and installation complexity, averaging between $3 to $7 per square foot, while loose-laid gravel ranges from $1 to $3 per square foot, reflecting simpler installation and material costs. Maintenance expenses for self-binding gravel are generally lower, as the compacted surface reduces displacement and weed growth, whereas loose-laid gravel often requires periodic replenishment and weed control treatments. Considering long-term durability, self-binding gravel offers cost efficiency over time despite higher initial investment, making it suitable for high-traffic areas or driveways.
Best Applications for Each Gravel Type
Self-binding gravel is ideal for driveways, pathways, and areas with moderate foot traffic because its compact surface resists displacement and reduces dust. Loose-laid gravel suits landscaping, decorative garden beds, and drainage solutions due to its easy installation and better water permeability. Selecting the right gravel type depends on factors such as load-bearing needs, maintenance preferences, and environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Self-binding gravel reduces soil erosion and limits sediment runoff by creating a stable surface, promoting water infiltration and minimizing environmental degradation compared to loose-laid gravel. Loose-laid gravel often requires frequent replenishment and can contribute to increased dust and sediment pollution, impacting local ecosystems negatively. Choosing self-binding gravel enhances sustainability by reducing maintenance needs and preserving natural habitats through improved ground stabilization.
Self-Binding Gravel vs Loose-Laid Gravel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com