Acid-etched glass offers a smooth, frosted finish achieved through chemical treatment, resulting in a consistent and elegant appearance ideal for privacy and decorative applications. Sandblasted glass is created by blasting abrasive materials onto the surface, producing a textured and slightly rough finish that enhances grip and visual depth. Both techniques obscure visibility while allowing light transmission, but acid-etched glass provides a more uniform and delicate look compared to the coarser texture of sandblasted glass.
Table of Comparison
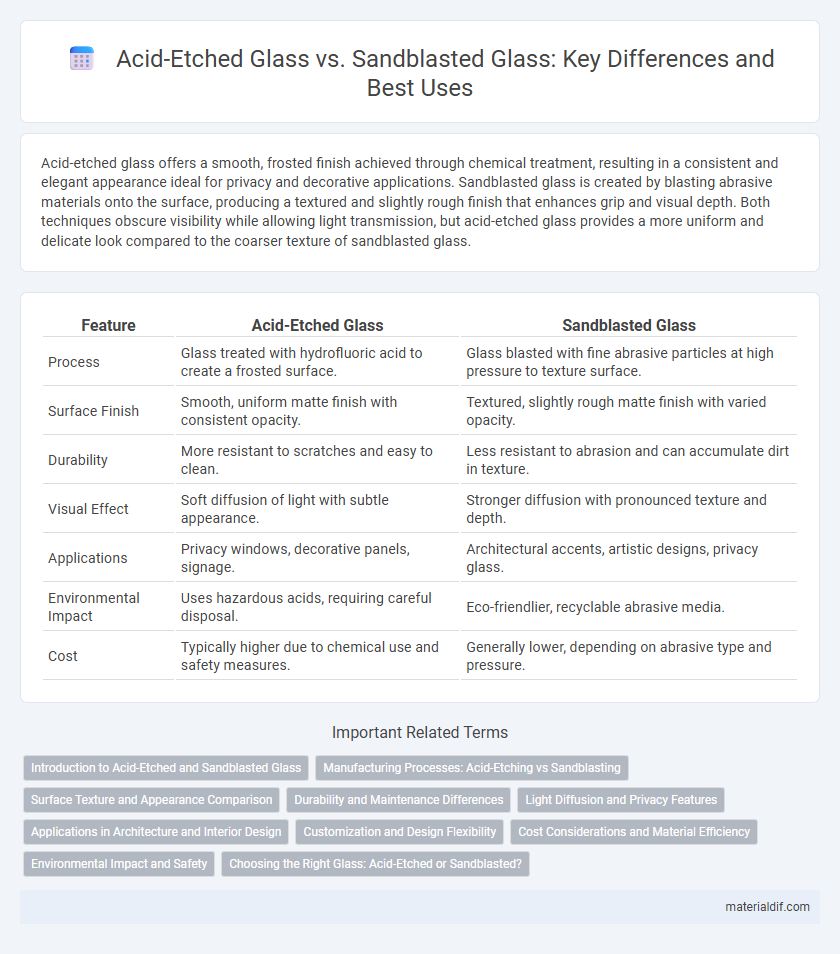
| Feature | Acid-Etched Glass | Sandblasted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Glass treated with hydrofluoric acid to create a frosted surface. | Glass blasted with fine abrasive particles at high pressure to texture surface. |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform matte finish with consistent opacity. | Textured, slightly rough matte finish with varied opacity. |
| Durability | More resistant to scratches and easy to clean. | Less resistant to abrasion and can accumulate dirt in texture. |
| Visual Effect | Soft diffusion of light with subtle appearance. | Stronger diffusion with pronounced texture and depth. |
| Applications | Privacy windows, decorative panels, signage. | Architectural accents, artistic designs, privacy glass. |
| Environmental Impact | Uses hazardous acids, requiring careful disposal. | Eco-friendlier, recyclable abrasive media. |
| Cost | Typically higher due to chemical use and safety measures. | Generally lower, depending on abrasive type and pressure. |
Introduction to Acid-Etched and Sandblasted Glass
Acid-etched glass is created by applying acidic chemicals to the glass surface, producing a smooth, uniform matte finish that offers privacy while allowing light transmission. Sandblasted glass results from propelling abrasive materials at high pressure onto the glass, creating a textured, frosted appearance with customizable patterns and depths. Both techniques enhance glass aesthetics and functionality but differ in texture, durability, and application precision.
Manufacturing Processes: Acid-Etching vs Sandblasting
Acid-etched glass is created by applying hydrofluoric acid to the surface, which chemically reacts to produce a smooth, frosted appearance with consistent opacity. Sandblasted glass involves propelling fine abrasive particles at high pressure to physically abrade the surface, resulting in a textured, matte finish with variable depth and pattern control. The acid-etching process offers precision for detailed designs and smoother finishes, while sandblasting provides more versatility for intricate textures and artistic effects.
Surface Texture and Appearance Comparison
Acid-etched glass features a smoother, matte surface created through chemical treatment that produces a uniform, frosted appearance. Sandblasted glass has a more textured and rough finish due to abrasive blasting, resulting in a varied, tactile surface with a slightly opaque look. Both methods diffuse light softly but acid-etched glass offers a more consistent translucency compared to the granular texture of sandblasted glass.
Durability and Maintenance Differences
Acid-etched glass features a chemical process that creates a smooth, frosted surface with enhanced resistance to scratches and stains, making it highly durable and easy to maintain. Sandblasted glass undergoes a high-pressure abrasive treatment that produces a textured finish but can be more prone to micro-abrasions and requires more frequent cleaning to prevent buildup in the rough surface. Overall, acid-etched glass offers superior longevity and lower maintenance needs compared to sandblasted glass in commercial and residential applications.
Light Diffusion and Privacy Features
Acid-etched glass provides a smooth, frosted surface that diffuses light softly while maintaining moderate privacy by obscuring detailed images. Sandblasted glass creates a textured finish that offers enhanced privacy through a more pronounced diffusion effect, effectively scattering light to reduce glare and visibility. Both techniques improve light diffusion, but sandblasted glass delivers superior privacy due to its deeper surface etching.
Applications in Architecture and Interior Design
Acid-etched glass offers a smooth, uniform frosted appearance ideal for privacy in office partitions, bathroom windows, and decorative panels, enhancing light diffusion without compromising translucency. Sandblasted glass provides a textured, matte finish that creates more pronounced patterns and depth, making it suitable for feature walls, signage, and artistic installations in modern architectural and interior design projects. Both techniques improve aesthetics and functionality by controlling light transmission and adding tactile interest to various structural and decorative elements.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Acid-etched glass offers precise control over texture and opacity, allowing intricate patterns and detailed designs through chemical treatments, which enhances customization for artistic and architectural applications. Sandblasted glass provides versatile design flexibility with its ability to create varied depths and textures by adjusting blasting pressure and masking techniques, enabling both subtle and bold visual effects. Both methods support tailored aesthetics, but acid-etching suits fine, delicate motifs while sandblasting excels in creating dynamic, tactile surfaces for bespoke glass projects.
Cost Considerations and Material Efficiency
Acid-etched glass generally incurs higher production costs due to the chemical processes and safety measures required, while sandblasted glass tends to be more cost-effective with quicker turnaround times. Sandblasting also allows for greater material efficiency by minimizing waste, as the abrasive treatment can be precisely controlled compared to the broad application of acid etching. In large-scale projects, sandblasted glass offers superior scalability without significantly impacting material or labor expenses.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Acid-etched glass involves using hydrofluoric acid, which poses significant environmental hazards due to toxic waste disposal challenges and potential chemical exposure, making it less eco-friendly compared to sandblasted glass. Sandblasting employs abrasive materials like silica or aluminum oxide without harmful chemicals, resulting in more sustainable waste management and lower environmental risk. In terms of safety, sandblasted glass often has a more uniform texture that reduces surface imperfections, while acid-etching may weaken glass if not controlled properly, increasing breakage risk.
Choosing the Right Glass: Acid-Etched or Sandblasted?
Acid-etched glass offers a smooth, frosted appearance with precise patterns created through chemical erosion, ideal for decorative and privacy applications requiring subtle elegance. Sandblasted glass features a more textured, matte finish produced by abrasive blasting, providing a durable surface with a distinct tactile quality suitable for high-traffic areas. Selecting the right glass depends on the desired aesthetic, durability, and level of opacity, with acid etching favored for intricate designs and sandblasting preferred for rugged, uniform finishes.
Acid-etched glass vs Sandblasted glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com