Harvested cork, obtained directly from the bark of cork oak trees without harming them, offers a natural and sustainable material with superior durability and elasticity compared to recycled cork. Recycled cork, sourced from repurposed cork products, provides an eco-friendly alternative by reducing waste and conserving resources while potentially lacking the same texture and longevity. Both forms contribute to environmental sustainability, but harvested cork remains the preferred choice for premium quality applications.
Table of Comparison
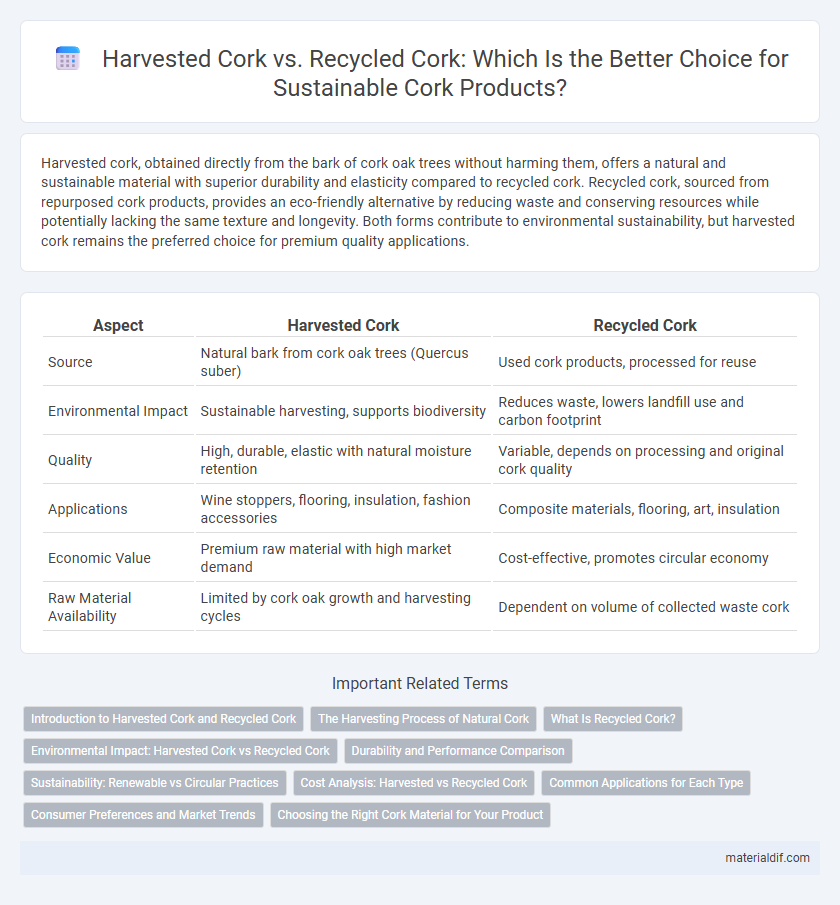
| Aspect | Harvested Cork | Recycled Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural bark from cork oak trees (Quercus suber) | Used cork products, processed for reuse |
| Environmental Impact | Sustainable harvesting, supports biodiversity | Reduces waste, lowers landfill use and carbon footprint |
| Quality | High, durable, elastic with natural moisture retention | Variable, depends on processing and original cork quality |
| Applications | Wine stoppers, flooring, insulation, fashion accessories | Composite materials, flooring, art, insulation |
| Economic Value | Premium raw material with high market demand | Cost-effective, promotes circular economy |
| Raw Material Availability | Limited by cork oak growth and harvesting cycles | Dependent on volume of collected waste cork |
Introduction to Harvested Cork and Recycled Cork
Harvested cork is obtained from the bark of cork oak trees, primarily grown in Portugal and Spain, where sustainable stripping methods allow regeneration without harming the tree. Recycled cork, derived from used wine stoppers and cork products, is processed and repurposed to reduce environmental waste and conserve natural resources. Both harvested and recycled cork contribute to eco-friendly industries by promoting sustainable production and minimizing carbon footprints in materials like flooring, insulation, and fashion.
The Harvesting Process of Natural Cork
The harvesting process of natural cork involves carefully stripping the bark from cork oak trees (Quercus suber) without damaging the tree, allowing it to regenerate every 9 to 12 years. This sustainable method preserves the tree's health and ensures high-quality cork material, which is stronger and more breathable compared to recycled cork products derived from processing used cork items. Natural cork harvesting supports biodiversity in cork oak forests and provides raw material essential for premium wine stoppers, insulation panels, and flooring solutions.
What Is Recycled Cork?
Recycled cork is made from used cork materials collected from wine stoppers, flooring, and other cork products, reducing environmental waste by repurposing these components instead of using new bark. Harvested cork, in contrast, comes directly from the bark of cork oak trees, which is carefully stripped every 9 to 12 years without harming the trees, supporting sustainable forest management. Using recycled cork conserves natural cork forests and minimizes production energy and emissions, making it an eco-friendly alternative in industries such as construction, fashion, and packaging.
Environmental Impact: Harvested Cork vs Recycled Cork
Harvested cork comes from the bark of cork oak trees, which can be sustainably stripped without harming the tree, promoting forest conservation and carbon sequestration. Recycled cork reduces demand for new cork extraction, lowering energy consumption and waste in production processes, but may involve additional processing stages that generate emissions. Both methods contribute to circular economy goals, yet harvested cork directly supports biodiversity and ecosystem health in cork oak landscapes.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Harvested cork exhibits superior durability due to its natural cellular structure, providing excellent compression resistance and elasticity for long-term performance. Recycled cork, while eco-friendly, may show reduced structural integrity as the granulated material can weaken bonds, affecting resilience and lifespan. Optimal applications for recycled cork often involve less demanding uses where sustainability outweighs maximum durability requirements.
Sustainability: Renewable vs Circular Practices
Harvested cork, sourced from the bark of cork oak trees, exemplifies a renewable practice as the bark regenerates every 9 to 12 years without harming the tree, ensuring a continuous supply. Recycled cork, on the other hand, supports circular economy principles by repurposing used cork products, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Both processes contribute significantly to sustainability, with harvested cork promoting natural resource renewal and recycled cork enhancing material lifecycle efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Harvested vs Recycled Cork
Harvested cork typically involves higher initial costs due to manual labor and sustainable tree management but offers premium quality raw material for various industries. Recycled cork reduces expenses by minimizing raw material extraction and waste, making it a cost-effective option for manufacturing cork-based products. Evaluating long-term savings, recycled cork supports circular economy principles while harvested cork ensures material integrity and supply stability.
Common Applications for Each Type
Harvested cork, sourced directly from cork oak trees, is widely used in wine stoppers, flooring, and insulation due to its natural elasticity and durability. Recycled cork, derived from repurposed cork products, finds common applications in eco-friendly accessories, such as coasters, bulletin boards, and footwear components, promoting sustainability. Both types contribute to reducing environmental impact but serve distinct market needs based on their origin and processing.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor harvested cork due to its natural origin and eco-friendly harvesting process, which aligns with sustainable values. Market trends show a growing demand for recycled cork products driven by cost-efficiency and circular economy principles, particularly in fashion and construction industries. Data from recent studies reveal that consumers are more willing to pay a premium for harvested cork in premium products, while recycled cork gains traction in mass-market applications.
Choosing the Right Cork Material for Your Product
Harvested cork, sourced directly from the bark of cork oak trees, offers natural durability and superior elasticity, making it ideal for high-quality wine stoppers and insulation products. Recycled cork, produced from reclaimed cork waste, supports sustainability by reducing environmental impact and is perfect for eco-friendly flooring and fashion accessories. Selecting between harvested and recycled cork depends on product requirements, balancing performance needs with environmental considerations.
harvested cork vs recycled cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com