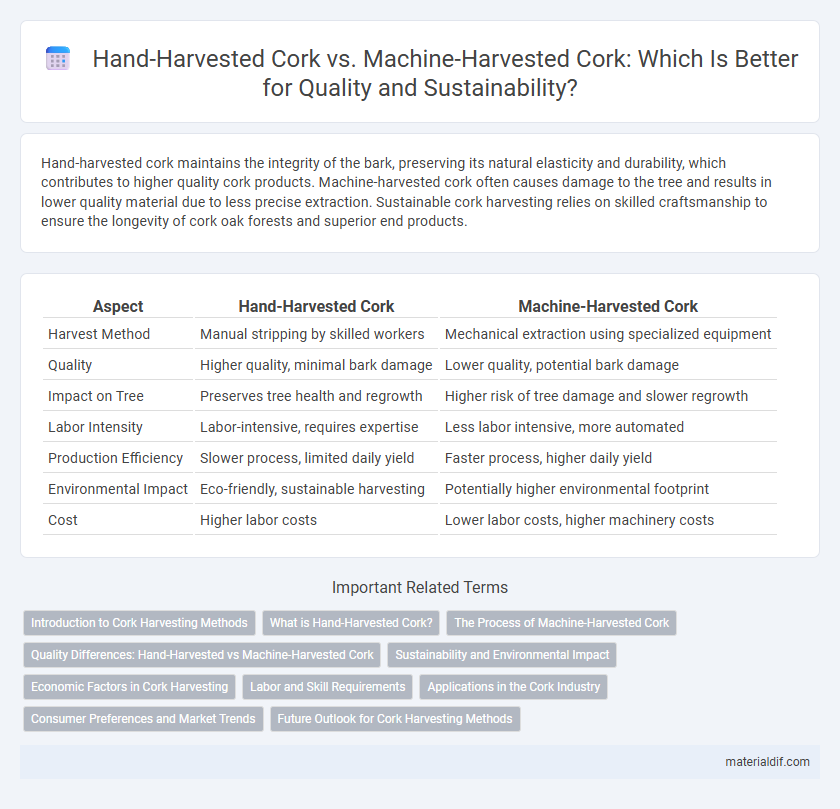
Hand-harvested cork maintains the integrity of the bark, preserving its natural elasticity and durability, which contributes to higher quality cork products. Machine-harvested cork often causes damage to the tree and results in lower quality material due to less precise extraction. Sustainable cork harvesting relies on skilled craftsmanship to ensure the longevity of cork oak forests and superior end products.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hand-Harvested Cork | Machine-Harvested Cork |
|---|---|---|
| Harvest Method | Manual stripping by skilled workers | Mechanical extraction using specialized equipment |
| Quality | Higher quality, minimal bark damage | Lower quality, potential bark damage |
| Impact on Tree | Preserves tree health and regrowth | Higher risk of tree damage and slower regrowth |
| Labor Intensity | Labor-intensive, requires expertise | Less labor intensive, more automated |
| Production Efficiency | Slower process, limited daily yield | Faster process, higher daily yield |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable harvesting | Potentially higher environmental footprint |
| Cost | Higher labor costs | Lower labor costs, higher machinery costs |
Introduction to Cork Harvesting Methods
Hand-harvested cork involves skilled laborers carefully peeling the bark from cork oak trees, preserving the tree's health and ensuring a high-quality, sustainable product. Machine-harvested cork offers increased efficiency and speed but can risk damaging the trees and reducing cork quality due to less precise extraction. The choice between methods impacts the ecological balance, cork texture, and industry standards in cork production regions like Portugal and Spain.
What is Hand-Harvested Cork?
Hand-harvested cork is carefully extracted from the bark of cork oak trees (Quercus suber) using traditional manual tools, preserving the tree's health and ensuring sustainable harvesting. This method allows workers to selectively strip the bark without damaging the tree, which can then regenerate its cork layer over approximately nine years. Hand-harvesting maintains the cork's natural quality, resulting in higher-grade cork used in products like premium wine stoppers and artisanal crafts.
The Process of Machine-Harvested Cork
Machine-harvested cork involves using specialized mechanical equipment to strip bark from cork oak trees efficiently, allowing for faster collection compared to traditional hand-harvesting methods. This process minimizes labor intensity but may risk damaging the tree's outer layers if not carefully managed, potentially affecting future cork quality. Advances in machine technology focus on precision and sustainability to preserve cork oak health while increasing production scalability.
Quality Differences: Hand-Harvested vs Machine-Harvested Cork
Hand-harvested cork from Cork oak trees maintains superior quality due to careful stripping techniques that preserve the bark's cellular integrity, resulting in fewer defects and greater elasticity. Machine-harvested cork often suffers from increased damage to the bark layers, leading to lower density and compromised durability. The meticulous process of hand-harvesting ensures premium cork stoppers with enhanced sealing properties, essential for high-end wine preservation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hand-harvested cork preserves the cork oak trees by ensuring careful stripping that promotes tree health and long-term growth, minimizing environmental disruption. Machine-harvested cork, although faster, risks damaging the bark and reducing tree lifespan, leading to greater ecological stress and potential biodiversity loss. Sustainable cork production prioritizes manual harvesting techniques to maintain carbon sequestration rates and support Mediterranean ecosystems.
Economic Factors in Cork Harvesting
Hand-harvested cork supports local economies by creating jobs and preserving traditional skills in rural areas, contributing to community stability. Machine-harvested cork increases efficiency and lowers production costs, enhancing competitiveness in global markets while reducing labor expenses. Balancing economic factors involves weighing the higher labor costs and cultural value of hand-harvesting against the cost savings and scalability offered by mechanization.
Labor and Skill Requirements
Hand-harvested cork demands highly skilled laborers who use specialized techniques to carefully extract the bark without damaging the trees, preserving their health and productivity over decades. Machine-harvested cork requires less manual expertise but often results in lower-quality bark due to less precision and potential tree damage. The artisanal skill involved in hand-harvesting ensures sustainable cork production and maintains the material's premium value in the market.
Applications in the Cork Industry
Hand-harvested cork preserves the bark's quality and structural integrity, making it ideal for premium wine stoppers and luxury flooring. Machine-harvested cork increases efficiency but may compromise the cellular structure, limiting its use primarily to insulation and agglomerated cork products. The choice between methods directly impacts the end product's durability, texture, and market value within the cork industry.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor hand-harvested cork due to its sustainability and superior quality, driving demand in premium wine and luxury goods markets. Market trends reveal a growing preference for artisanal craftsmanship, with hand-harvested corks perceived as eco-friendly and contributing to product authenticity. Machine-harvested cork remains cost-effective but faces challenges in consumer perception and market positioning compared to the artisanal appeal of traditional hand-harvesting methods.
Future Outlook for Cork Harvesting Methods
Hand-harvested cork maintains superior bark quality and fosters sustainable forest ecosystems through selective and careful stripping techniques essential for cork oak health. Machine-harvested cork offers increased efficiency and lower labor costs but risks damaging trees and reducing long-term cork quality, impacting the premium cork market. Future outlooks favor integrating advanced mechanization with traditional practices to balance productivity, environmental sustainability, and product excellence in cork harvesting.
hand-harvested cork vs machine-harvested cork Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com