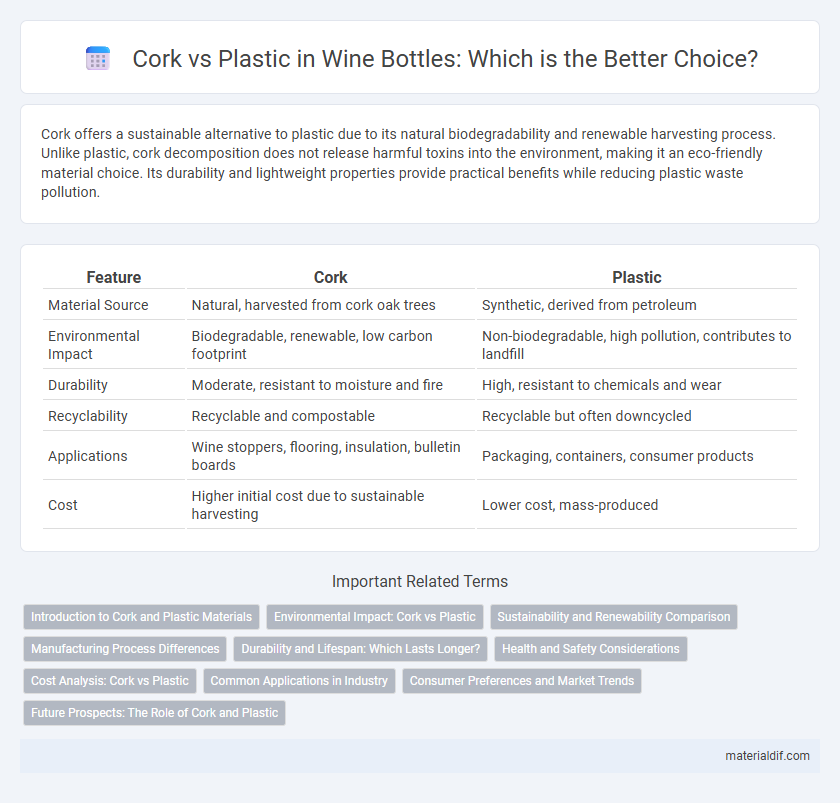
Cork offers a sustainable alternative to plastic due to its natural biodegradability and renewable harvesting process. Unlike plastic, cork decomposition does not release harmful toxins into the environment, making it an eco-friendly material choice. Its durability and lightweight properties provide practical benefits while reducing plastic waste pollution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cork | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural, harvested from cork oak trees | Synthetic, derived from petroleum |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high pollution, contributes to landfill |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to moisture and fire | High, resistant to chemicals and wear |
| Recyclability | Recyclable and compostable | Recyclable but often downcycled |
| Applications | Wine stoppers, flooring, insulation, bulletin boards | Packaging, containers, consumer products |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to sustainable harvesting | Lower cost, mass-produced |
Introduction to Cork and Plastic Materials
Cork, a natural, renewable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, offers exceptional sustainability and biodegradability compared to synthetic plastics derived from petrochemicals. Cork's unique cellular structure provides lightweight insulation, moisture resistance, and durability without harmful environmental impact, unlike conventional plastic materials that contribute significantly to pollution and landfill accumulation. The growing preference for cork in various applications highlights its eco-friendly advantages and potential to reduce reliance on non-biodegradable plastics.
Environmental Impact: Cork vs Plastic
Cork is a sustainable and biodegradable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without harming the tree, promoting forest conservation and carbon sequestration. In contrast, plastic production relies on fossil fuels, generating greenhouse gas emissions and contributing significantly to pollution and landfill waste. Cork's natural decomposition reduces environmental footprint, whereas plastic persists for centuries, causing microplastic contamination in ecosystems.
Sustainability and Renewability Comparison
Cork, harvested from the bark of cork oak trees, offers a sustainable and renewable alternative to plastic due to its natural biodegradability and ability to regenerate after harvesting without harming the tree. Unlike plastic, which is derived from fossil fuels and contributes to long-term environmental pollution, cork production supports biodiversity and carbon sequestration in cork oak forests. This makes cork a highly eco-friendly material for packaging, flooring, and insulation applications, promoting circular economy principles.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Cork manufacturing involves harvesting the bark from cork oak trees without cutting them down, allowing natural regeneration and sustainability. Plastic production relies on petrochemical processes, including polymerization and molding, which consume non-renewable fossil fuels and generate higher carbon emissions. Cork processing is energy-efficient with minimal chemical use, while plastic manufacturing entails complex refining and significant environmental pollutants.
Durability and Lifespan: Which Lasts Longer?
Cork offers impressive durability due to its natural cellular structure, resisting wear, moisture, and decay better than many synthetic materials. Plastic, while often resistant to certain types of damage, tends to degrade over time through cracking, UV exposure, and chemical breakdown. The lifespan of cork products can extend for decades with minimal maintenance, whereas plastic items frequently require replacement due to brittleness and environmental stress.
Health and Safety Considerations
Cork, a natural and hypoallergenic material, offers superior breathability and resistance to mold and mildew compared to plastic, reducing potential health risks in indoor environments. Plastic materials often contain harmful chemicals such as phthalates and BPA, which can off-gas toxic substances impacting respiratory health. Choosing cork for flooring, insulation, or household products enhances safety by minimizing exposure to allergens and toxic compounds commonly associated with plastics.
Cost Analysis: Cork vs Plastic
Cork offers a cost-effective alternative to plastic, with lower long-term expenses due to its durability and biodegradability. While plastic may have a lower initial purchase price, cork reduces costs associated with environmental impact and disposal fees. Businesses in Cork benefit from investing in cork products, as they align with sustainable practices and decreasing regulatory costs tied to plastic waste management.
Common Applications in Industry
Cork is extensively used in the construction industry for insulation and acoustic panels due to its natural thermal and sound-resistant properties, offering an eco-friendly alternative to plastic-based materials. In packaging, cork provides sustainable cushioning and sealing solutions for wine bottles, replacing synthetic plastic stoppers. The automotive sector incorporates cork in gaskets and vibration dampening components, benefiting from its lightweight and biodegradability compared to plastic counterparts.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences in Cork show a strong shift towards sustainable materials, with cork being favored over plastic due to its eco-friendly properties, biodegradability, and renewable sourcing. Market trends indicate a rising demand for cork products in sectors such as packaging, fashion, and home decor, driven by increasing environmental awareness and government regulations targeting plastic reduction. Cork's durability, lightweight nature, and unique aesthetic appeal further enhance its market position as a preferred alternative to plastic among environmentally conscious consumers.
Future Prospects: The Role of Cork and Plastic
Cork offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative to plastic, making it a vital material in sustainable packaging and construction industries as global demand for eco-friendly solutions rises. Advances in cork harvesting techniques and increased investment in cork oak forest management enhance its availability and economic viability, positioning cork as a key player in reducing plastic pollution. Plastic, while versatile and cost-effective, faces growing regulatory restrictions and environmental challenges, driving innovation toward bioplastics and recycled materials that may coexist with cork in a circular economy.
Cork vs Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com