Translucent porcelain offers a delicate, light-permeable quality that enhances the visual depth and realism of ceramic pets, making them appear more lifelike and refined. Opaque porcelain, on the other hand, provides a solid, matte finish that emphasizes durability and a classic, traditional aesthetic. Choosing between translucent and opaque porcelain depends on whether you prioritize intricate detail and luminosity or a sturdy, timeless ceramic pet.
Table of Comparison
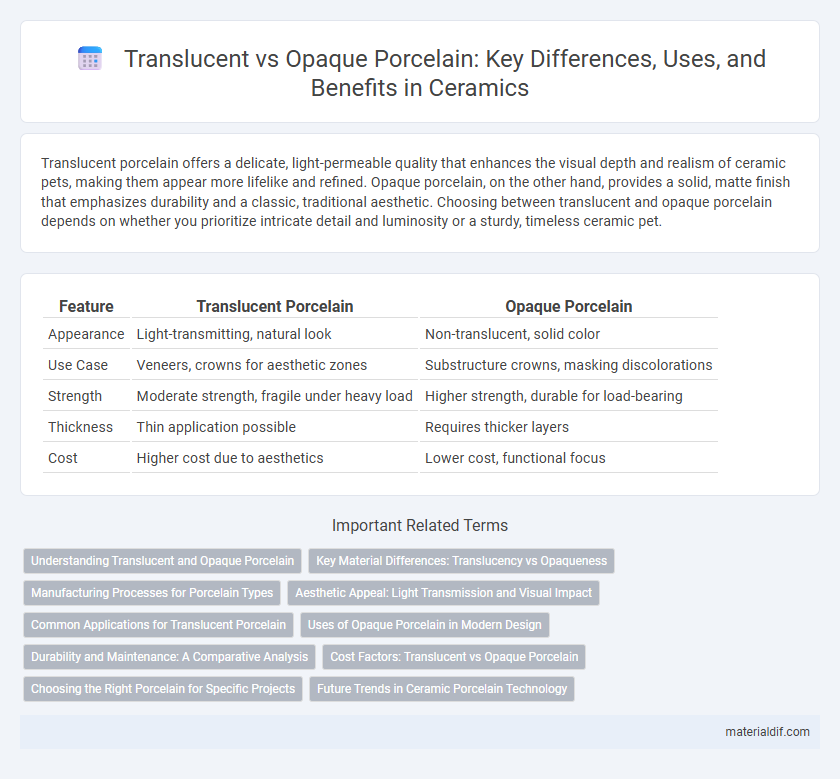
| Feature | Translucent Porcelain | Opaque Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Light-transmitting, natural look | Non-translucent, solid color |
| Use Case | Veneers, crowns for aesthetic zones | Substructure crowns, masking discolorations |
| Strength | Moderate strength, fragile under heavy load | Higher strength, durable for load-bearing |
| Thickness | Thin application possible | Requires thicker layers |
| Cost | Higher cost due to aesthetics | Lower cost, functional focus |
Understanding Translucent and Opaque Porcelain
Translucent porcelain exhibits a higher degree of light transmission due to its refined microstructure and minimal opacity, making it ideal for applications requiring aesthetic appeal and natural light diffusion. Opaque porcelain contains added opacifiers like feldspar or zirconium silicate that block light, providing enhanced durability and resistance to stains and scratches. Selecting between translucent and opaque porcelain depends on balancing visual transparency with functional strength and maintenance needs.
Key Material Differences: Translucency vs Opaqueness
Translucent porcelain exhibits a higher degree of light transmission due to its refined particle size and lower porosity, allowing for a lifelike depth and subtle glow ideal for artistic and restorative applications. Opaque porcelain, characterized by its dense particle composition and higher alumina content, prevents light passage, resulting in a solid, non-translucent appearance suited for structural and masking purposes. These material differences in translucency versus opaqueness directly influence the aesthetic outcomes and functional roles of porcelain in ceramics and dental restorations.
Manufacturing Processes for Porcelain Types
Translucent porcelain is manufactured using refined kaolin clay and feldspar, fired at higher temperatures to achieve a denser, glass-like structure that allows light to pass through. Opaque porcelain utilizes a different blend of clays, including higher amounts of feldspar and quartz, and undergoes a firing process at slightly lower temperatures to produce a more solid, non-transparent texture. The controlled firing conditions and precise raw material compositions are critical in creating the distinct translucency or opacity characteristics of each porcelain type.
Aesthetic Appeal: Light Transmission and Visual Impact
Translucent porcelain offers superior light transmission, creating a natural, lifelike appearance that enhances smile aesthetics by mimicking the subtle depth of natural teeth. Opaque porcelain, with its limited light permeability, provides better masking of underlying discolorations but results in a less vibrant visual impact. The choice between translucent and opaque porcelain significantly influences the restoration's ability to blend seamlessly with surrounding dentition.
Common Applications for Translucent Porcelain
Translucent porcelain is commonly used in dental restorations such as veneers, crowns, and bridges due to its ability to mimic the natural translucency of tooth enamel. It is also preferred for fine art ceramics and decorative tiles where aesthetic appeal and light diffusion are crucial. The material's strength combined with its translucency makes it ideal for applications requiring both durability and visual elegance.
Uses of Opaque Porcelain in Modern Design
Opaque porcelain is widely used in modern design for creating durable and visually striking surfaces such as kitchen countertops, bathroom tiles, and wall claddings. Its ability to block light makes it ideal for applications requiring privacy or hiding imperfections, while offering a solid, uniform appearance. The material's resistance to stains, scratches, and heat ensures longevity and low maintenance in both residential and commercial spaces.
Durability and Maintenance: A Comparative Analysis
Translucent porcelain offers a delicate, glass-like appearance while maintaining high durability suitable for moderate use, but it may require more careful handling to prevent chipping compared to opaque porcelain. Opaque porcelain is renowned for its robust strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-duty applications with minimal maintenance. Both types resist staining and moisture, yet opaque porcelain generally demands less frequent upkeep due to its density and inherent toughness.
Cost Factors: Translucent vs Opaque Porcelain
Translucent porcelain often incurs higher material and manufacturing costs due to its refined composition and complex firing process, which enhances light transmission and aesthetic appeal. Opaque porcelain, with a denser structure and less intricate production requirements, generally offers a more cost-effective solution. Price differences are influenced by raw material purity, production techniques, and market demand for visual effects in ceramics.
Choosing the Right Porcelain for Specific Projects
Translucent porcelain offers a luminous finish ideal for decorative applications like lighting fixtures and fine tableware, where subtle light diffusion enhances aesthetics. Opaque porcelain provides robust durability and resistance to wear, making it suitable for utilitarian items such as tiles, sanitary ware, and industrial components. Selecting the right porcelain hinges on balancing visual appeal with functional demands specific to project requirements.
Future Trends in Ceramic Porcelain Technology
Translucent porcelain is poised to dominate future ceramic trends due to advancements in nano-crystalline technology that enhance light transmission without compromising strength. Innovations in material composition are enabling manufacturers to produce porcelain with superior translucency and durability, meeting increasing demands for aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Research in bio-compatible, sustainable raw materials also suggests a growing shift toward eco-friendly porcelain products in architectural and dental applications.
Translucent Porcelain vs Opaque Porcelain Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com