Bamboo charcoal is produced by slow-burning bamboo at high temperatures without oxygen, resulting in porous charcoal that absorbs impurities and odors. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes further processing with steam or chemicals to increase its surface area and adsorption capacity, making it more effective for air and water purification. The enhanced microporous structure of activated bamboo carbon provides superior filtration compared to regular bamboo charcoal.
Table of Comparison
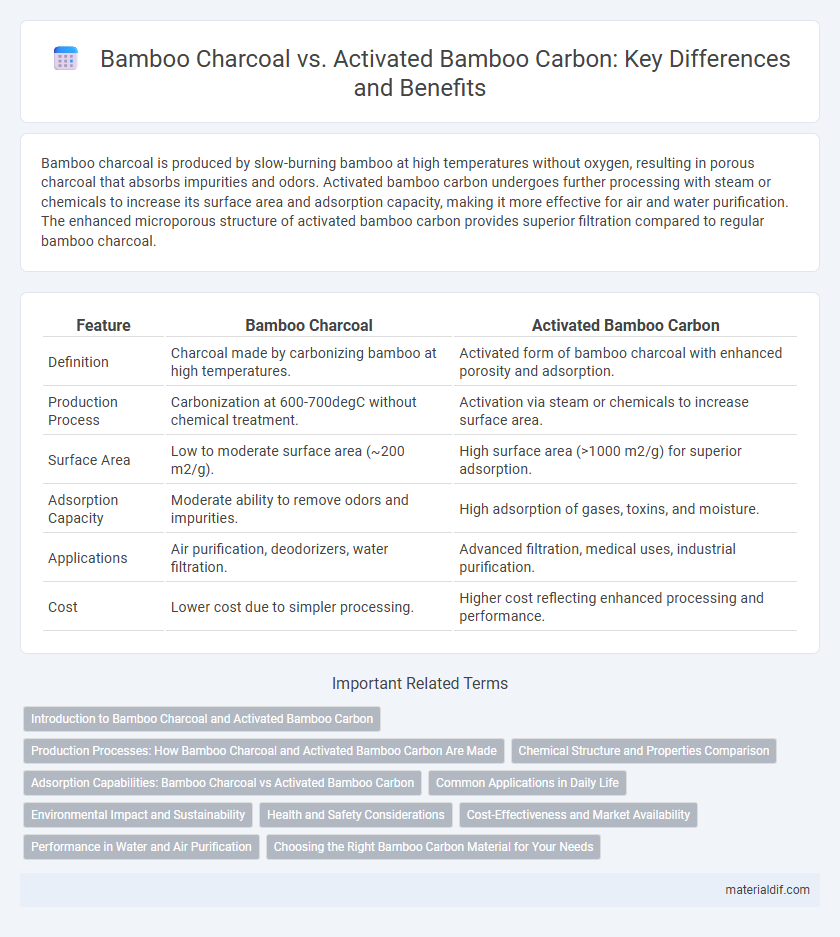
| Feature | Bamboo Charcoal | Activated Bamboo Carbon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Charcoal made by carbonizing bamboo at high temperatures. | Activated form of bamboo charcoal with enhanced porosity and adsorption. |
| Production Process | Carbonization at 600-700degC without chemical treatment. | Activation via steam or chemicals to increase surface area. |
| Surface Area | Low to moderate surface area (~200 m2/g). | High surface area (>1000 m2/g) for superior adsorption. |
| Adsorption Capacity | Moderate ability to remove odors and impurities. | High adsorption of gases, toxins, and moisture. |
| Applications | Air purification, deodorizers, water filtration. | Advanced filtration, medical uses, industrial purification. |
| Cost | Lower cost due to simpler processing. | Higher cost reflecting enhanced processing and performance. |
Introduction to Bamboo Charcoal and Activated Bamboo Carbon
Bamboo charcoal is a natural carbon material produced by pyrolyzing bamboo at high temperatures, known for its porous structure and excellent adsorption properties. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes further activation through steam or chemical treatment, significantly increasing its surface area and enhancing its capacity to trap toxins, odors, and moisture. These distinctions make activated bamboo carbon more effective in applications like air purification, water filtration, and cosmetics compared to standard bamboo charcoal.
Production Processes: How Bamboo Charcoal and Activated Bamboo Carbon Are Made
Bamboo charcoal is produced by slow pyrolysis of bamboo at temperatures around 600-700degC in a low-oxygen environment, resulting in a porous black material used for filtration and deodorization. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes further treatment, typically steam or chemical activation at higher temperatures (800-900degC), increasing its surface area and enhancing adsorption properties. These distinct production processes create significant differences in porosity and functionality between bamboo charcoal and activated bamboo carbon.
Chemical Structure and Properties Comparison
Bamboo charcoal consists primarily of carbon with a porous structure formed through pyrolysis, exhibiting moderate adsorption capacity and natural impurities like ash. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes further chemical or physical activation, increasing surface area and pore volume, resulting in enhanced adsorption efficiency and higher purity levels. The activation process introduces functional groups such as hydroxyl and carboxyl, boosting chemical reactivity and making activated bamboo carbon more suitable for filtration and catalytic applications.
Adsorption Capabilities: Bamboo Charcoal vs Activated Bamboo Carbon
Bamboo charcoal exhibits moderate adsorption capabilities due to its porous structure, effectively trapping moisture and odors in household environments. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes a rigorous activation process, significantly enhancing its surface area and pore volume, which enables superior adsorption of toxins, pollutants, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Studies indicate activated bamboo carbon can adsorb up to 10 times more contaminants compared to regular bamboo charcoal.
Common Applications in Daily Life
Bamboo charcoal is commonly used in air purification, odor absorption, and moisture control due to its natural porous structure, making it ideal for home dehumidifiers and refrigerator deodorizing bags. Activated bamboo carbon, which undergoes a chemical activation process to enhance its surface area, is widely applied in water filtration, skincare products, and toxin removal in medical devices. Both forms exploit bamboo's sustainable properties but serve distinct roles in daily life based on their adsorption capabilities and activation levels.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo charcoal and activated bamboo carbon differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability; bamboo charcoal is produced through a simple pyrolysis process that releases fewer pollutants, making it a more eco-friendly carbon source. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes an energy-intensive activation process, often involving chemical agents, which increases its environmental footprint despite enhanced adsorption capabilities. Both materials benefit from bamboo's rapid growth and renewability, but bamboo charcoal's lower processing requirements position it as a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious applications.
Health and Safety Considerations
Bamboo charcoal and activated bamboo carbon differ significantly in health and safety aspects, with activated bamboo carbon offering enhanced adsorption properties that improve air and water purification, reducing harmful toxins more effectively. Bamboo charcoal is generally safe but can release impurities if not properly processed, whereas activated bamboo carbon undergoes rigorous activation to ensure higher purity and safety for medical, cosmetic, and environmental applications. Proper handling and usage of activated bamboo carbon minimize risks of respiratory irritation and promote safer use in health-related products.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Bamboo charcoal is generally more cost-effective due to lower processing expenses, making it widely accessible for household and industrial uses. Activated bamboo carbon, which undergoes additional activation processes to enhance adsorption properties, commands a higher price but offers superior performance in air and water purification applications. Market availability of bamboo charcoal is broader, while activated bamboo carbon is more niche, catering primarily to specialized environmental and health-related sectors.
Performance in Water and Air Purification
Bamboo charcoal exhibits high porosity and strong adsorption capacity, making it effective in removing impurities like chlorine, heavy metals, and odors from water and air. Activated bamboo carbon undergoes an additional activation process, significantly enhancing its surface area and pore structure, which boosts its adsorption efficiency for volatile organic compounds, harmful gases, and moisture. Performance tests reveal that activated bamboo carbon consistently outperforms bamboo charcoal in both water filtration systems and air purifiers, offering superior contaminant removal and longer-lasting effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Bamboo Carbon Material for Your Needs
Bamboo charcoal offers natural odor absorption and moisture control, ideal for air purification and skincare applications, while activated bamboo carbon undergoes a high-temperature activation process that enhances its porous surface area, making it more effective for water filtration and toxin adsorption. Selecting the right bamboo carbon depends on the intended use: opt for regular bamboo charcoal for general deodorizing and humidity regulation, and choose activated bamboo carbon when requiring superior filtration or chemical absorption capabilities. Understanding the specific properties and functionalities ensures optimal performance and efficiency in environmental or health-related applications.
Bamboo charcoal vs Activated bamboo carbon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com