Bamboo yarn offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to synthetic yarn, making it ideal for comfortable and eco-friendly textiles. It is naturally antibacterial and biodegradable, reducing environmental impact, while synthetic yarns often rely on petrochemicals and can contribute to microplastic pollution. The softness and durability of bamboo yarn provide a sustainable alternative without compromising fabric quality.
Table of Comparison
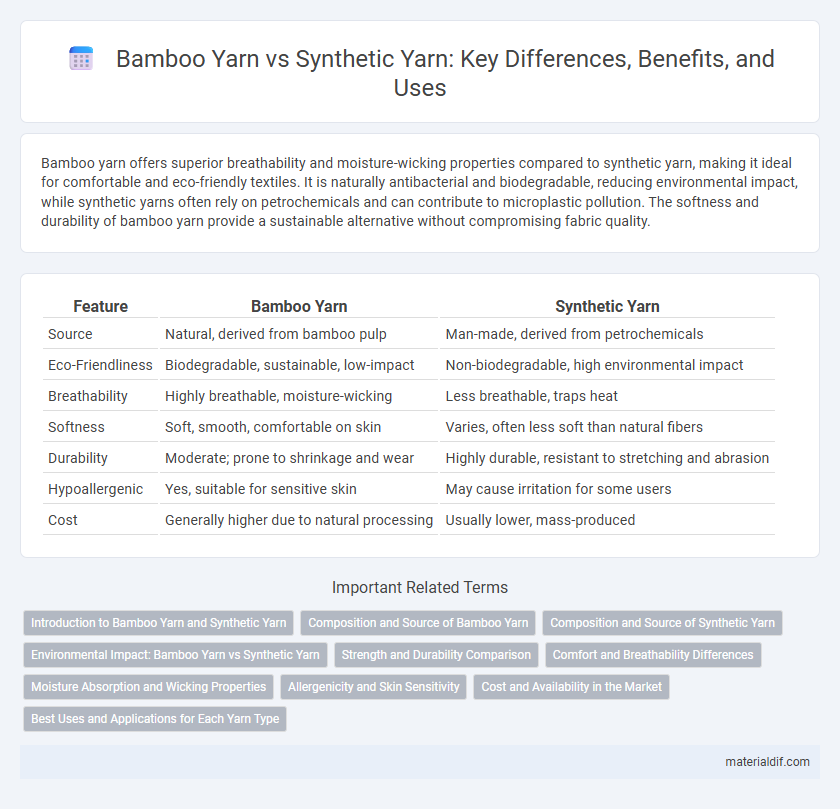
| Feature | Bamboo Yarn | Synthetic Yarn |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from bamboo pulp | Man-made, derived from petrochemicals |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable, low-impact | Non-biodegradable, high environmental impact |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Less breathable, traps heat |
| Softness | Soft, smooth, comfortable on skin | Varies, often less soft than natural fibers |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to shrinkage and wear | Highly durable, resistant to stretching and abrasion |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, suitable for sensitive skin | May cause irritation for some users |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural processing | Usually lower, mass-produced |
Introduction to Bamboo Yarn and Synthetic Yarn
Bamboo yarn is derived from the cellulose fibers of bamboo plants, offering natural antibacterial properties, breathability, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic yarns. Synthetic yarns, commonly produced from petrochemical-based materials like polyester and nylon, provide durability, elasticity, and moisture resistance but lack the environmental benefits and softness of bamboo yarn. The choice between bamboo and synthetic yarns depends on priorities such as sustainability, texture, and performance in textile applications.
Composition and Source of Bamboo Yarn
Bamboo yarn is composed primarily of natural cellulose fibers extracted from bamboo plants, making it a renewable and biodegradable textile option. Unlike synthetic yarns derived from petrochemicals such as polyester or nylon, bamboo yarn retains the inherent antimicrobial and moisture-wicking properties of its botanical origin. The sustainable cultivation of bamboo, requiring minimal pesticides and water, distinguishes bamboo yarn as an eco-friendly alternative in the textile industry.
Composition and Source of Synthetic Yarn
Bamboo yarn is composed of natural fibers derived from bamboo plants through a mechanical or chemical process, offering biodegradability and breathability. Synthetic yarn, commonly made from petrochemical-based polymers such as polyester, nylon, or acrylic, is produced through chemical synthesis and relies heavily on non-renewable fossil fuels. The environmental impact of synthetic yarns arises from their petroleum origin and non-biodegradable nature, contrasting with bamboo yarn's renewable plant-based source.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo Yarn vs Synthetic Yarn
Bamboo yarn is biodegradable and produced from sustainable bamboo plants that require minimal water and pesticides, significantly reducing environmental pollution compared to synthetic yarn. Synthetic yarns, usually derived from petroleum-based polymers like polyester and nylon, contribute to microplastic pollution and consume substantial non-renewable resources during production. The renewable nature and lower carbon footprint of bamboo yarn make it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable textile manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Bamboo yarn exhibits superior strength due to its natural cellulose fibers, which provide resistance to tension and wear over time. Unlike synthetic yarns made from petrochemical polymers, bamboo fibers maintain durability without significant fiber degradation or pilling after multiple washes. This natural resilience makes bamboo yarn an eco-friendly yet robust alternative to synthetic yarns in textile production.
Comfort and Breathability Differences
Bamboo yarn offers superior comfort and breathability compared to synthetic yarn due to its natural moisture-wicking and thermoregulating properties, keeping the skin cool and dry. Its fibers are softer and more hypoallergenic, reducing irritation and enhancing wearability for sensitive skin. Synthetic yarns often trap heat and moisture, leading to less ventilation and a higher risk of discomfort and sweat buildup.
Moisture Absorption and Wicking Properties
Bamboo yarn exhibits superior moisture absorption and wicking properties compared to synthetic yarn, thanks to its natural cellulose fibers that can absorb up to 40% of their weight in moisture. This enhances breathability and keeps the skin dry by efficiently drawing sweat away from the body. Synthetic yarns, often made from petrochemicals like polyester or nylon, tend to trap moisture, leading to reduced comfort during prolonged wear.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Bamboo yarn is naturally hypoallergenic and possesses antibacterial properties, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies, as it resists irritation and reduces the risk of allergic reactions. Synthetic yarns, often made from petrochemicals, can trap heat and moisture, which may exacerbate skin sensitivity and cause rashes or itching in sensitive individuals. The breathable, moisture-wicking nature of bamboo yarn enhances comfort and minimizes skin irritation compared to many synthetic fibers.
Cost and Availability in the Market
Bamboo yarn tends to have a higher price point compared to synthetic yarn due to its eco-friendly production processes and natural origin, which increases manufacturing costs. Synthetic yarn is widely available in the market at lower prices owing to large-scale production and the use of petroleum-based raw materials. Market availability favors synthetic yarn, making it a cost-effective option for mass production and budget-conscious consumers.
Best Uses and Applications for Each Yarn Type
Bamboo yarn excels in breathable, moisture-wicking applications such as summer garments, baby clothes, and eco-friendly textiles due to its softness, antibacterial properties, and biodegradability. Synthetic yarns like polyester and nylon offer superior durability, elasticity, and resistance to wear, making them ideal for activewear, outdoor gear, and industrial fabrics. Choosing between bamboo and synthetic yarn depends on the desired balance of comfort, environmental impact, and performance requirements in the final product.
Bamboo yarn vs Synthetic yarn Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com