Wool felt is a dense, non-woven fabric created by matting and compressing wool fibers, offering excellent insulation and a firm texture ideal for crafts and industrial uses. Wool knit, on the other hand, is made by interlocking loops of wool yarn, providing stretchiness, breathability, and softness perfect for clothing and accessories. Choosing between wool felt and wool knit depends on the desired flexibility, durability, and application of the wool fabric.
Table of Comparison
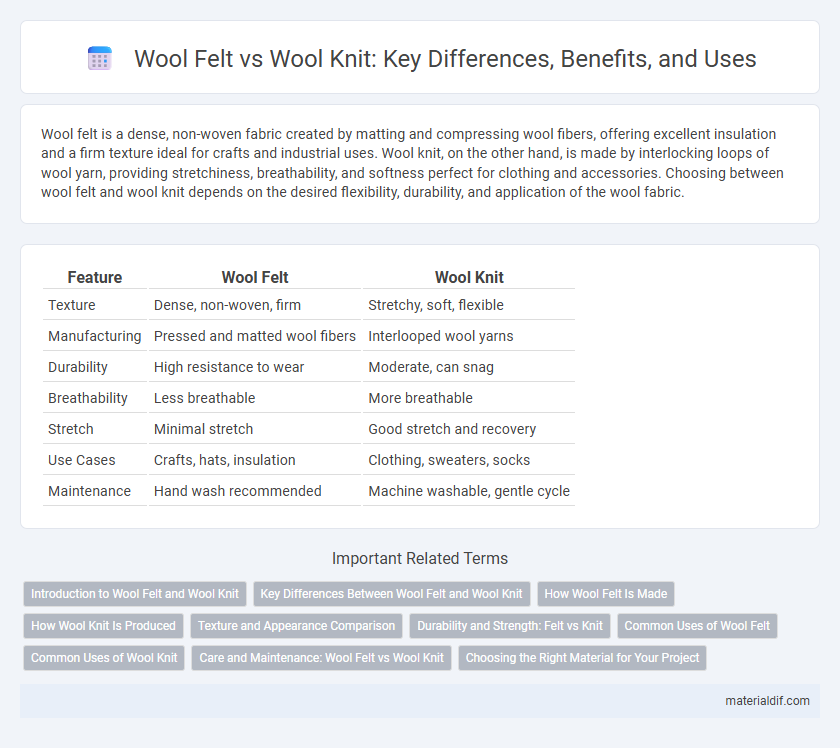
| Feature | Wool Felt | Wool Knit |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Dense, non-woven, firm | Stretchy, soft, flexible |
| Manufacturing | Pressed and matted wool fibers | Interlooped wool yarns |
| Durability | High resistance to wear | Moderate, can snag |
| Breathability | Less breathable | More breathable |
| Stretch | Minimal stretch | Good stretch and recovery |
| Use Cases | Crafts, hats, insulation | Clothing, sweaters, socks |
| Maintenance | Hand wash recommended | Machine washable, gentle cycle |
Introduction to Wool Felt and Wool Knit
Wool felt is a dense, non-woven fabric created by matting and compressing wool fibers, known for its firmness and insulation properties. Wool knit, on the other hand, is made by interlooping yarns to create a stretchy, breathable fabric ideal for flexible clothing applications. These distinct manufacturing processes result in wool felt being more rigid and durable, while wool knit offers softness and elasticity.
Key Differences Between Wool Felt and Wool Knit
Wool felt is a dense, non-woven fabric created by matting and compressing wool fibers, resulting in a stiff and durable material ideal for crafts and insulation. Wool knit is produced through interlocking loops of yarn, offering stretchability, softness, and flexibility suitable for garments and activewear. Key differences include texture, elasticity, and manufacturing processes, with wool felt being rigid and structured, while wool knit provides comfort and shape retention.
How Wool Felt Is Made
Wool felt is made through a process called wet felting, where wool fibers are exposed to heat, moisture, and agitation, causing them to mat and compress into a dense, non-woven fabric. Unlike wool knit, which is produced by interlocking loops of yarn, wool felt involves bonding fibers together without any knitting or weaving. This method results in a thick, sturdy material commonly used for insulation, crafts, and industrial applications.
How Wool Knit Is Produced
Wool knit is produced by interlocking loops of wool yarn using knitting needles or machines, creating a flexible and stretchy fabric. This method contrasts with wool felt, which is made by matting and compressing wool fibers together through heat, moisture, and agitation. The knitting process preserves wool's natural elasticity and breathability, making wool knit ideal for garments requiring comfort and flexibility.
Texture and Appearance Comparison
Wool felt features a dense, firm texture created by matting and pressing wool fibers together, resulting in a smooth, uniform surface ideal for structured projects. Wool knit showcases a flexible, stretchy texture formed by interlooping yarns, offering a softer, more breathable appearance with natural drape. The distinct tactile qualities and visual patterns between wool felt and wool knit influence their suitability for different garment styles and functional uses.
Durability and Strength: Felt vs Knit
Wool felt offers superior durability and strength due to its dense, non-woven structure that resists stretching and abrasion, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Wool knit, while providing flexibility and breathability, tends to be less robust and more prone to pilling and wear over time. The compact fibers in wool felt create a firmer material, whereas the looped construction of wool knit sacrifices some strength for elasticity and comfort.
Common Uses of Wool Felt
Wool felt is widely used in crafting, fashion accessories, and home decor due to its dense, non-woven texture that provides durability and structure. It is ideal for making hats, slippers, and protective padding, offering excellent insulation and softness. Unlike wool knit, which is stretchy and flexible, wool felt excels in applications requiring firmness and shape retention.
Common Uses of Wool Knit
Wool knit fabric is widely used in apparel such as sweaters, scarves, and gloves due to its stretchability and insulating properties. Its breathable yet warm nature makes it ideal for activewear and layering pieces in cold climates. Unlike wool felt, which is dense and stiff, wool knit provides flexibility and comfort, enhancing its suitability for everyday and performance wear.
Care and Maintenance: Wool Felt vs Wool Knit
Wool felt requires gentle handling and spot cleaning to maintain its dense structure, as it is prone to shrinking and distortion when exposed to water and heat. Wool knit, being more elastic and flexible, benefits from hand washing with cold water and mild detergents, followed by flat drying to prevent stretching and pilling. Proper storage in a cool, dry place and avoiding exposure to moths are essential for prolonging the lifespan of both wool felt and wool knit garments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Wool felt offers a dense, non-woven texture ideal for structured crafts and insulation, while wool knit provides stretch and breathability suitable for apparel and flexible designs. Selecting wool felt benefits projects requiring rigidity and durability, whereas wool knit is optimal for comfort and elasticity. Understanding the distinct properties of wool felt and wool knit ensures the right material choice tailored to your project's functional and aesthetic needs.
Wool Felt vs Wool Knit Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com