Nickel silver, often mistaken for genuine silver, is an alloy made primarily of nickel, copper, and zinc, lacking any actual silver content. Genuine silver, such as sterling silver, contains at least 92.5% pure silver, ensuring superior luster, value, and hypoallergenic properties. While nickel silver offers durability and affordability, genuine silver remains preferred for its authentic appearance and intrinsic worth in fine jewelry and silverware.
Table of Comparison
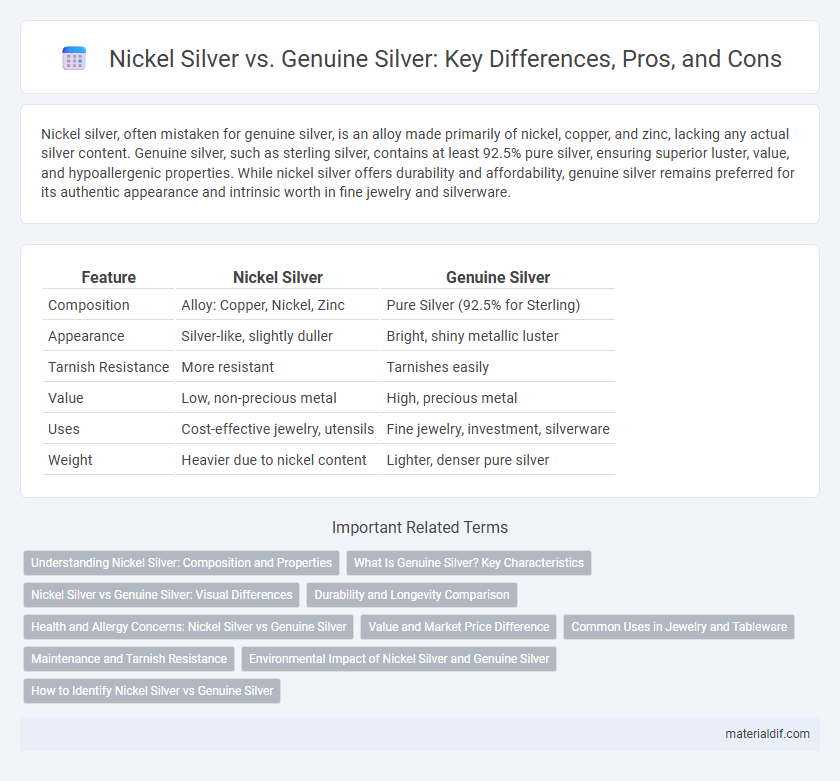
| Feature | Nickel Silver | Genuine Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alloy: Copper, Nickel, Zinc | Pure Silver (92.5% for Sterling) |
| Appearance | Silver-like, slightly duller | Bright, shiny metallic luster |
| Tarnish Resistance | More resistant | Tarnishes easily |
| Value | Low, non-precious metal | High, precious metal |
| Uses | Cost-effective jewelry, utensils | Fine jewelry, investment, silverware |
| Weight | Heavier due to nickel content | Lighter, denser pure silver |
Understanding Nickel Silver: Composition and Properties
Nickel silver, also known as German silver, is an alloy composed primarily of copper, nickel, and zinc, with no actual silver content, distinguishing it from genuine silver which is mainly pure silver or sterling silver (92.5% silver). The properties of nickel silver include high corrosion resistance, durability, and a silvery appearance that mimics genuine silver but with a harder texture and lower cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for identifying authentic silver items and selecting materials based on desired aesthetic and functional properties.
What Is Genuine Silver? Key Characteristics
Genuine silver, also known as fine silver, consists of 99.9% pure silver, offering exceptional luster and superior conductivity compared to nickel silver, which contains no actual silver and is an alloy of nickel, copper, and zinc. Key characteristics of genuine silver include its soft malleability, high reflectivity, and natural resistance to corrosion, while nickel silver often exhibits a duller finish and lower durability. Jewelry, tableware, and coins frequently utilize genuine silver for its value, authenticity, and classic appearance.
Nickel Silver vs Genuine Silver: Visual Differences
Nickel silver, also known as German silver, contains a mix of nickel, copper, and zinc, giving it a duller, grayish appearance compared to the bright, reflective shine of genuine silver, which is composed of 92.5% pure silver in sterling form. Genuine silver tends to develop a natural patina and tarnish over time, enhancing its classic look, whereas nickel silver maintains a consistent color but can appear less lustrous and more muted. Close inspection reveals that genuine silver often features hallmark stamps indicating purity, while nickel silver typically lacks such markings, making visual identification crucial for distinguishing between the two metals.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Nickel silver, an alloy composed of copper, nickel, and zinc, offers superior durability and resistance to tarnish compared to genuine silver, making it less prone to scratches and corrosion. Genuine silver, primarily made of 92.5% silver (sterling silver), is softer and more susceptible to dents and wear over time despite its higher intrinsic value. For items requiring long-lasting strength and frequent use, nickel silver provides enhanced longevity, whereas genuine silver requires more maintenance to preserve its pristine appearance.
Health and Allergy Concerns: Nickel Silver vs Genuine Silver
Nickel silver, an alloy containing nickel, often triggers allergic reactions such as skin irritation and rashes in sensitive individuals due to nickel sensitivity, whereas genuine silver, especially sterling silver (92.5% pure silver), is hypoallergenic and safer for prolonged skin contact. Genuine silver's antibacterial properties further reduce the risk of skin infections, making it a preferable choice for jewelry and other items worn directly against the skin. Those with metal allergies should opt for genuine silver over nickel silver to avoid adverse health effects associated with nickel exposure.
Value and Market Price Difference
Nickel silver contains no actual silver and is primarily composed of copper, nickel, and zinc, making it significantly less valuable than genuine silver, which is approximately 92.5% pure in sterling silver form. Market prices for genuine silver fluctuate based on precious metal demand and supply, typically trading above $25 per ounce, while nickel silver has negligible intrinsic market value and is often priced based on its metal alloy components. The stark price difference impacts investment potential and resale value, with genuine silver recognized as a tradable precious metal and nickel silver largely regarded as a costume or utility material.
Common Uses in Jewelry and Tableware
Nickel silver, also known as German silver, is a durable alloy commonly used in costume jewelry, flatware, and decorative tableware due to its affordability and resistance to tarnishing. Genuine silver, primarily sterling silver composed of 92.5% pure silver, is preferred for high-end jewelry and fine dining utensils because of its lustrous finish and hypoallergenic properties. Both metals play significant roles in jewelry and tableware, with nickel silver favored for budget-friendly and practical items and genuine silver chosen for luxury and heirloom-quality pieces.
Maintenance and Tarnish Resistance
Nickel silver, an alloy containing copper, nickel, and zinc, offers superior tarnish resistance compared to genuine silver, reducing the need for frequent polishing and maintenance. Genuine silver, primarily composed of 92.5% silver in sterling forms, requires regular cleaning to prevent tarnish caused by sulfur compounds in air. The durability of nickel silver makes it ideal for items exposed to moisture and frequent handling, while genuine silver demands more careful upkeep to maintain its luster.
Environmental Impact of Nickel Silver and Genuine Silver
Nickel silver, composed of copper, nickel, and zinc, has a significant environmental footprint due to intensive mining and energy consumption associated with nickel extraction, which often leads to habitat destruction and water pollution. Genuine silver mining, while also environmentally demanding, generally results in higher levels of toxic waste and heavy metal contamination, particularly from mercury and cyanide used in refining processes. Sustainable practices and recycling efforts in both materials can mitigate environmental damage, but genuine silver's extraction remains more ecologically challenging than nickel silver production.
How to Identify Nickel Silver vs Genuine Silver
Nickel silver can be identified by its lack of the sterling silver hallmark, with markings such as "Nickel," "Nickel silver," or "800" indicating base metal alloys, whereas genuine silver usually features the "925" stamp denoting 92.5% pure silver. Magnetic tests help differentiate them since nickel silver is often attracted to magnets due to its nickel content, while genuine silver is non-magnetic. Additionally, the color tone of nickel silver tends to be more yellowish compared to the bright white luster of genuine sterling silver.
Nickel silver vs Genuine silver Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com