Polyester resin is a synthetic polymer primarily used in composites, coatings, and adhesives due to its strong bonding properties and chemical resistance. Polyester fiber, on the other hand, is a versatile textile material known for its durability, moisture-wicking ability, and ease of care in clothing and upholstery applications. Understanding the distinct functions of polyester resin and polyester fiber helps optimize their use in industrial manufacturing and fabric production.
Table of Comparison
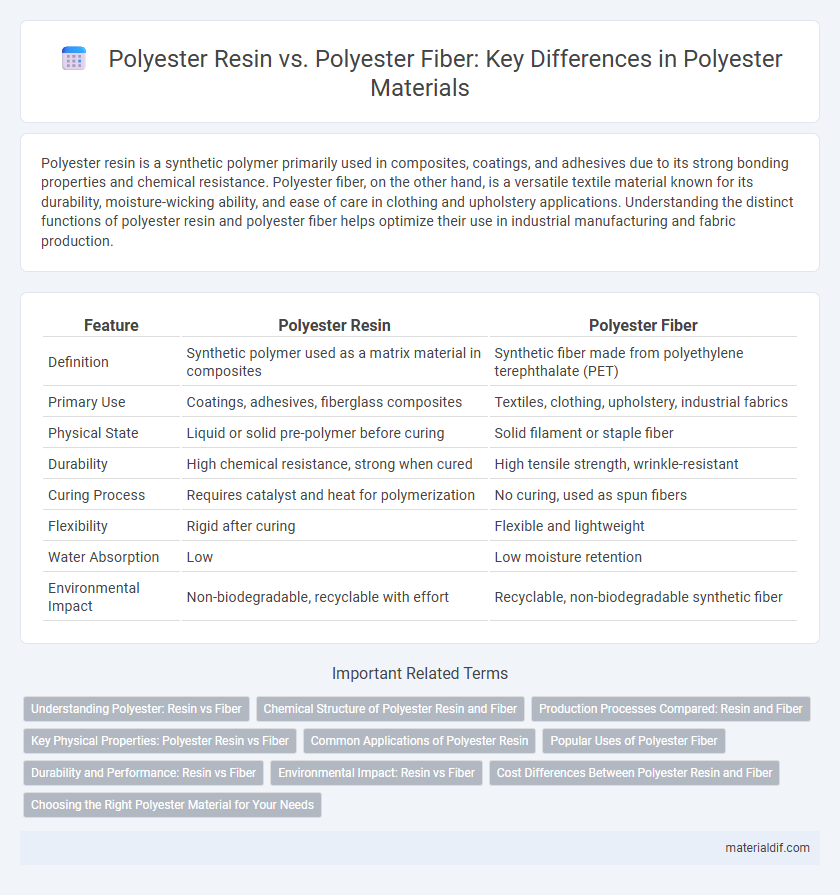
| Feature | Polyester Resin | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Synthetic polymer used as a matrix material in composites | Synthetic fiber made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |
| Primary Use | Coatings, adhesives, fiberglass composites | Textiles, clothing, upholstery, industrial fabrics |
| Physical State | Liquid or solid pre-polymer before curing | Solid filament or staple fiber |
| Durability | High chemical resistance, strong when cured | High tensile strength, wrinkle-resistant |
| Curing Process | Requires catalyst and heat for polymerization | No curing, used as spun fibers |
| Flexibility | Rigid after curing | Flexible and lightweight |
| Water Absorption | Low | Low moisture retention |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable with effort | Recyclable, non-biodegradable synthetic fiber |
Understanding Polyester: Resin vs Fiber
Polyester resin, a synthetic polymer primarily used in composite materials and coatings, offers high strength and chemical resistance for industrial applications. Polyester fiber, derived from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is widely utilized in textiles due to its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and ease of care. Understanding the distinct composition and functionalities of polyester resin versus polyester fiber is essential for selecting the appropriate material in manufacturing and consumer products.
Chemical Structure of Polyester Resin and Fiber
Polyester resin is a thermosetting polymer primarily composed of unsaturated polyester chains cross-linked through styrene monomers, forming a rigid, three-dimensional network ideal for composites and coatings. Polyester fiber consists of long, linear polymer chains of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with ester functional groups, providing flexibility and durability in textiles. The chemical structure of polyester resin involves reactive double bonds enabling curing, while polyester fiber's stable ester linkages result in high tensile strength and resistance to environmental degradation.
Production Processes Compared: Resin and Fiber
Polyester resin is produced through the polycondensation of dicarboxylic acids and diols, involving esterification followed by polymerization to create a viscous liquid used in composite materials and coatings. Polyester fiber production involves melt spinning or solution spinning of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymers to form continuous filaments for textiles and industrial applications. The resin production emphasizes chemical synthesis and curing, while fiber production focuses on polymer extrusion and fiber drawing for tensile strength and texture control.
Key Physical Properties: Polyester Resin vs Fiber
Polyester resin exhibits high strength, excellent chemical resistance, and a rigid, thermosetting structure ideal for composite materials, while polyester fiber features flexibility, durability, and moisture-wicking abilities suitable for textiles. The resin's hardness and dimensional stability contrast with the fiber's tensile strength and elasticity, making each suited for distinct industrial applications. Thermal resistance and moisture absorption rates also differ significantly, with resin showing superior heat tolerance and fiber offering greater breathability.
Common Applications of Polyester Resin
Polyester resin is widely used in marine, automotive, and construction industries due to its excellent adhesive properties and durability in composite materials. It serves as a key component in fiberglass laminates, boat hulls, and automotive body panels, providing corrosion resistance and structural strength. Unlike polyester fiber, which is primarily utilized in textiles and apparel, polyester resin's primary applications revolve around molding and reinforcement purposes in industrial manufacturing.
Popular Uses of Polyester Fiber
Polyester fiber is widely used in textiles for clothing, upholstery, and home furnishings due to its durability, resistance to wrinkles, and ability to retain shape. It is also popular in industrial applications, including conveyor belts, safety belts, and tire reinforcements, because of its high tensile strength and resistance to stretching. Polyester resin, on the other hand, primarily finds applications in composite materials, coatings, and adhesives rather than textiles.
Durability and Performance: Resin vs Fiber
Polyester resin exhibits high chemical resistance and structural durability, making it ideal for composite materials and coatings that require toughness and long-term performance under stress. Polyester fiber, on the other hand, offers excellent tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, which contribute to its widespread use in textiles and reinforcing applications. While resin provides rigidity and protection, the fiber ensures flexibility and resilience, each optimized for different durability and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact: Resin vs Fiber
Polyester resin production involves significant emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and relies heavily on petrochemical sources, contributing to air pollution and non-renewable resource depletion. Polyester fiber, especially when recycled, presents a lower environmental footprint by reducing landfill waste and energy consumption compared to virgin fiber manufacturing. However, both materials pose challenges related to microplastic pollution during their lifecycle and end-of-use disposal.
Cost Differences Between Polyester Resin and Fiber
Polyester resin typically incurs higher production costs due to complex chemical synthesis and curing processes, while polyester fiber offers more economical manufacturing through melt spinning techniques. The price disparity also reflects polyester resin's application in high-performance composites versus polyester fiber's widespread use in textiles and apparel. Cost efficiency of polyester fiber makes it a preferred choice for large-scale fabric production, whereas polyester resin justifies its premium price in structural and industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Polyester Material for Your Needs
Polyester resin and polyester fiber serve different applications based on their properties; polyester resin is a durable thermosetting polymer ideal for coatings, adhesives, and composite materials, while polyester fiber offers flexibility, strength, and moisture resistance primarily for textiles and upholstery. Selecting the right polyester material depends on the desired function: choose polyester resin for structural or protective purposes requiring hardness and chemical resistance, and opt for polyester fiber for clothing, home furnishings, or industrial fabrics demanding softness and resilience. Understanding the specific requirements such as durability, texture, and environmental exposure ensures optimal material performance in construction, fashion, or manufacturing projects.
Polyester resin vs Polyester fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com