Polyester PET offers higher tensile strength and excellent chemical resistance compared to Polyester PBT, making it ideal for durable textile applications and food packaging. Polyester PBT provides superior flexibility, impact resistance, and better dimensional stability, which benefits automotive parts and electrical components. The choice between PET and PBT depends on the specific mechanical and thermal requirements of the intended application.
Table of Comparison
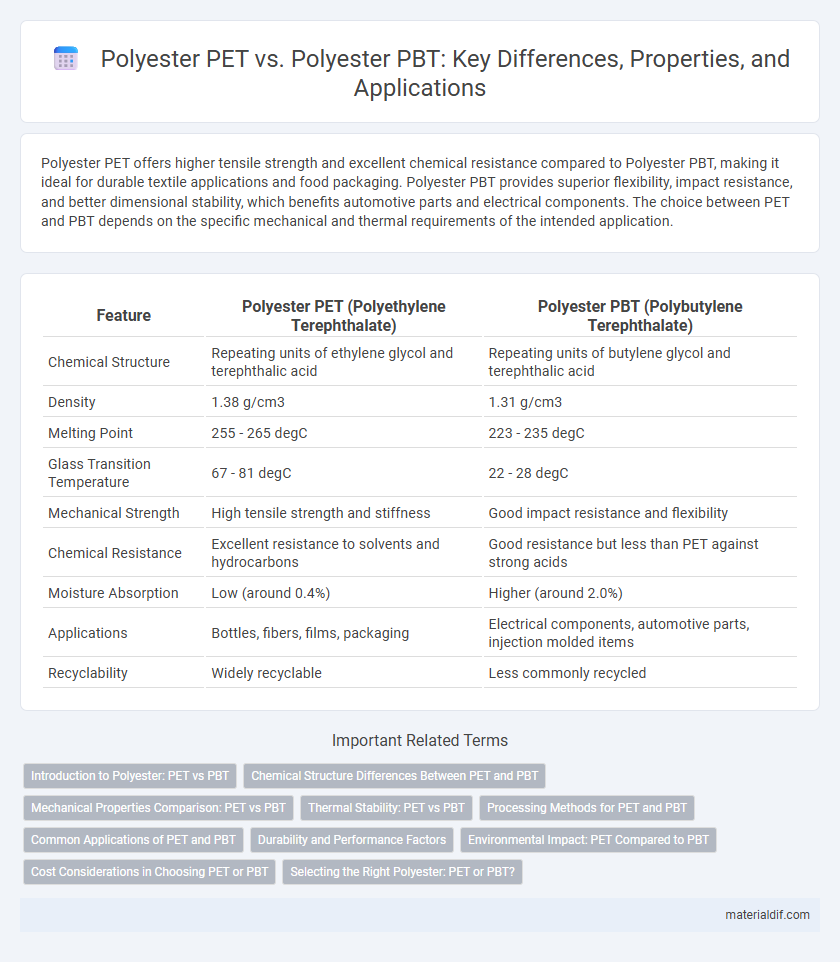
| Feature | Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Repeating units of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid | Repeating units of butylene glycol and terephthalic acid |
| Density | 1.38 g/cm3 | 1.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 255 - 265 degC | 223 - 235 degC |
| Glass Transition Temperature | 67 - 81 degC | 22 - 28 degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Good impact resistance and flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and hydrocarbons | Good resistance but less than PET against strong acids |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (around 0.4%) | Higher (around 2.0%) |
| Applications | Bottles, fibers, films, packaging | Electrical components, automotive parts, injection molded items |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable | Less commonly recycled |
Introduction to Polyester: PET vs PBT
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) are two common types of thermoplastic polyesters used in fiber and plastic manufacturing. PET offers high strength, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for fibers, packaging, and engineering plastics. PBT provides superior impact resistance, faster crystallization, and better electrical properties, often preferred in automotive and electrical applications where durability under stress is critical.
Chemical Structure Differences Between PET and PBT
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) differ primarily in their chemical backbone structure; PET is derived from ethylene glycol, while PBT is derived from butylene glycol, resulting in variations in polymer chain flexibility and crystallinity. The additional methylene groups in PBT's butylene glycol segment contribute to lower glass transition temperature and faster crystallization compared to PET. These structural differences influence thermal stability, mechanical properties, and processing conditions of the two polyesters.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: PET vs PBT
Polyester PET exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to Polyester PBT, making it suitable for applications requiring rigidity and dimensional stability. In contrast, Polyester PBT offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, with better elongation at break and fatigue resistance. Both polymers display excellent chemical resistance, but PBT's enhanced toughness and thermal stability provide advantages in automotive and electrical components.
Thermal Stability: PET vs PBT
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) exhibits higher thermal stability with a melting point around 255degC, making it suitable for applications requiring endurance to elevated temperatures. Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) has a lower melting point near 223degC but offers improved crystallization rates and dimensional stability under thermal stress. The choice between PET and PBT depends on the specific thermal requirements, with PET preferred for high-temperature resistance and PBT favored for superior thermal deformation resistance in moderate heat conditions.
Processing Methods for PET and PBT
Polyester PET is primarily processed through melt spinning and injection molding, benefiting from its high melting point and crystallinity for producing strong fibers and films. Polyester PBT, with a lower melting temperature, is favorably processed using injection molding and extrusion techniques, offering faster cycle times and enhanced dimensional stability. Both materials require precise temperature control during processing to optimize mechanical properties and surface finish.
Common Applications of PET and PBT
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is widely used in textile fibers, beverage bottles, and food packaging due to its high strength, clarity, and chemical resistance. Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) finds common applications in automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial machinery because of its excellent dimensional stability and resistance to heat and chemicals. Both materials play critical roles in manufacturing, with PET favored for packaging and fibers, while PBT is primarily utilized in engineering plastics.
Durability and Performance Factors
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for applications requiring robustness and resistance to environmental stress. Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) excels in impact resistance and dimensional stability at high temperatures, providing enhanced performance in automotive and electrical components exposed to heat. Both materials exhibit excellent mechanical properties, but PET is preferred where rigidity and chemical endurance are critical, while PBT is favored for flexible, high-temperature environments.
Environmental Impact: PET Compared to PBT
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) exhibits a lower environmental impact than Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) due to its widespread recyclability and established global recycling infrastructure. PET's production relies more heavily on terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol derived from petroleum, but its recycling reduces dependency on virgin raw materials, lowering carbon emissions. PBT, while offering excellent mechanical properties, has limited recycling options and higher energy consumption during manufacturing, contributing to a larger environmental footprint.
Cost Considerations in Choosing PET or PBT
Polyester PET typically offers lower raw material and production costs compared to Polyester PBT, making it a cost-effective choice for high-volume applications. PBT entails higher expenses due to its enhanced chemical resistance and superior mechanical properties, which justify the investment in specialized uses. Evaluating budget constraints alongside performance requirements is crucial to selecting between PET and PBT for optimized cost-efficiency.
Selecting the Right Polyester: PET or PBT?
Polyester PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and high-temperature stability. Polyester PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) provides better impact resistance and flexibility, suitable for electrical components and automotive parts. Selecting the right polyester depends on specific performance requirements such as mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical exposure in the intended application.
Polyester PET vs Polyester PBT Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com