Polyester nonwoven fabrics are produced by bonding fibers together using mechanical, chemical, or thermal methods, resulting in a versatile material with diverse applications in filtration, insulation, and hygiene products. Polyester spunbond fabric is a specific type of nonwoven made by extruding continuous filaments that are laid randomly and then thermally bonded, offering higher strength, uniformity, and durability compared to other nonwoven types. The main difference between polyester nonwoven and polyester spunbond lies in their manufacturing process and fiber structure, influencing their performance in various industrial and consumer uses.
Table of Comparison
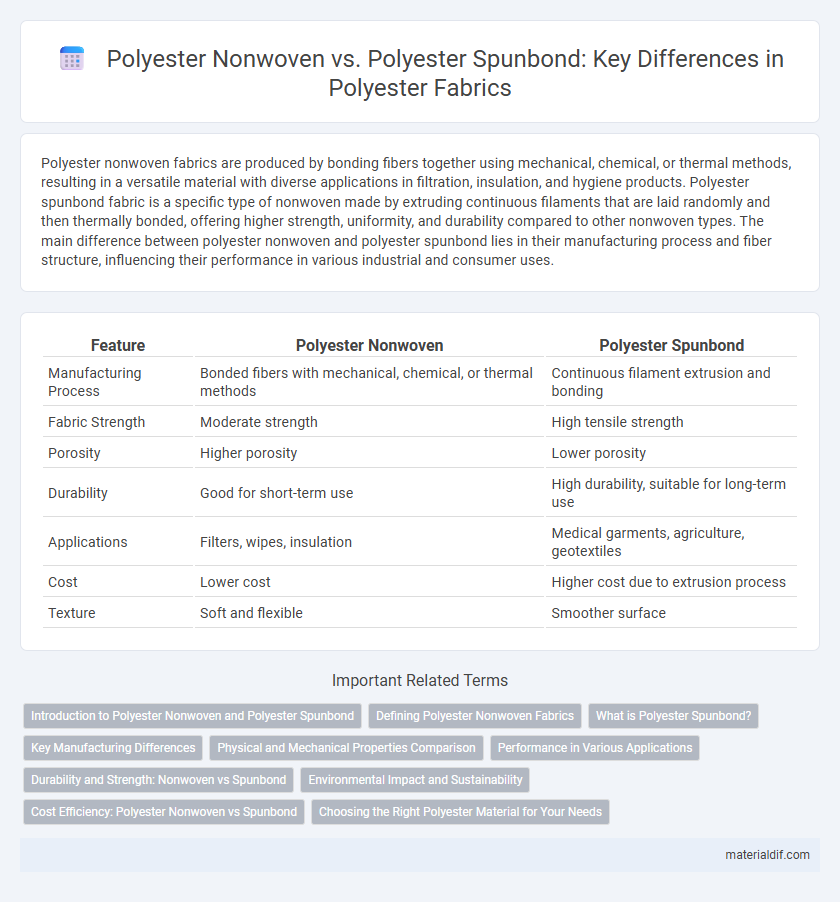
| Feature | Polyester Nonwoven | Polyester Spunbond |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Bonded fibers with mechanical, chemical, or thermal methods | Continuous filament extrusion and bonding |
| Fabric Strength | Moderate strength | High tensile strength |
| Porosity | Higher porosity | Lower porosity |
| Durability | Good for short-term use | High durability, suitable for long-term use |
| Applications | Filters, wipes, insulation | Medical garments, agriculture, geotextiles |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to extrusion process |
| Texture | Soft and flexible | Smoother surface |
Introduction to Polyester Nonwoven and Polyester Spunbond
Polyester nonwoven fabrics consist of fibers bonded together through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes without weaving, offering versatility in applications such as filtration, medical products, and geotextiles. Polyester spunbond is a type of nonwoven fabric made by directly extruding continuous polyester filaments onto a conveyor belt, producing a strong, lightweight material widely used in hygiene products, agriculture, and industrial applications. Both materials provide durability, breathability, and cost-effectiveness, but spunbond excels in strength and uniformity due to its filament-based production method.
Defining Polyester Nonwoven Fabrics
Polyester nonwoven fabrics are engineered materials made by bonding polyester fibers through mechanical, thermal, or chemical processes without weaving or knitting. These fabrics offer enhanced durability, breathability, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for applications like filtration, medical masks, and geotextiles. Polyester spunbond, a subset of nonwoven fabrics, is produced using continuous filament extrusion, providing superior strength and uniformity for industrial and consumer uses.
What is Polyester Spunbond?
Polyester spunbond is a type of nonwoven fabric made by directly extruding continuous filaments of polyester fibers, which are then laid down and bonded to form a strong, durable, and lightweight material. Unlike general polyester nonwoven fabrics produced by bonding staple fibers, spunbond fabrics offer enhanced tensile strength, uniformity, and resistance to tearing, making them ideal for medical, agricultural, and industrial applications. This manufacturing process results in a fabric with high breathability and moisture resistance, distinguishing spunbond as a premium choice in the nonwoven polyester category.
Key Manufacturing Differences
Polyester nonwoven fabric is created through various methods such as meltblown, needle-punching, or hydroentangling, allowing diverse textures and properties depending on the process. Polyester spunbond, a specific type of nonwoven, is manufactured by extruding continuous polyester filaments which are then laid randomly and bonded thermally, resulting in a strong, uniform web. Key manufacturing differences lie in the fiber formation and bonding techniques, with spunbond focusing on continuous filament extrusion and thermal bonding, while nonwoven includes a broader range of fiber sources and bonding methods.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyester nonwoven fabric, produced through bonding fibers using needle-punching or heat, offers higher porosity and flexibility compared to polyester spunbond, which is manufactured by extruding continuous filaments for enhanced tensile strength and uniformity. Physically, spunbond polyester exhibits superior abrasion resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for long-lasting applications, whereas nonwovens provide better cushioning and breathability due to their open structure. Mechanically, spunbond materials withstand greater stress and elongation before failure, while polyester nonwoven fabrics excel in impact absorption and tear resistance under low strain conditions.
Performance in Various Applications
Polyester nonwoven fabrics and polyester spunbond materials both offer robust durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for filtration, medical, and geotextile applications. Polyester spunbond excels in strength and uniformity due to its continuous filament production, providing superior tensile properties for industrial uses like automotive and construction. In contrast, polyester nonwoven, often made via bonding loose fibers, delivers enhanced softness and absorbency, favoring hygiene products and disposable items where comfort is essential.
Durability and Strength: Nonwoven vs Spunbond
Polyester spunbond fabrics exhibit superior durability and tensile strength compared to polyester nonwoven materials due to their continuous filament structure and thermal bonding process. Polyester nonwoven fabrics, typically made from short fibers bonded mechanically or chemically, offer less resistance to tearing and abrasion but provide better flexibility and softness. Industrial applications favor spunbond polyester for load-bearing uses, while nonwoven variants suit disposable or lightweight products.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyester nonwoven fabrics and polyester spunbond materials differ in environmental impact, with spunbond generally offering better sustainability due to its energy-efficient manufacturing process and recyclability. Nonwoven polyester often involves bonding techniques that consume more energy and may incorporate adhesives or binders, potentially complicating recycling efforts. Sustainable practices in polyester spunbond production include reduced resource use and enhanced potential for closed-loop recycling, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly textile applications.
Cost Efficiency: Polyester Nonwoven vs Spunbond
Polyester nonwoven fabrics typically offer greater cost efficiency compared to polyester spunbond due to lower production costs and simpler manufacturing processes. Nonwoven polyester uses less energy-intensive bonding methods, reducing overall material expenses while maintaining adequate durability for many applications. Spunbond polyester, though more expensive, provides enhanced strength and longevity, justifying its higher cost in performance-critical uses.
Choosing the Right Polyester Material for Your Needs
Polyester nonwoven fabrics offer versatility with their lightweight, breathable, and cost-effective properties, ideal for applications requiring disposable or short-term use, such as medical masks and hygiene products. Polyester spunbond, characterized by its strong, durable, and tear-resistant structure, suits long-term uses in automotive, filtration, and geotextiles. Selecting the right polyester material depends on specific requirements like strength, durability, and intended application lifespan to maximize performance and cost efficiency.
Polyester Nonwoven vs Polyester Spunbond Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com