PET Polyester offers high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it ideal for everyday apparel and industrial applications. PCDT Polyester, or polycyclohexylene dimethylene terephthalate, provides enhanced stretch recovery and superior wrinkle resistance, suited for activewear and performance fabrics. Comparing PET and PCDT polyester reveals differences in chemical structure that influence flexibility, moisture management, and overall fabric resilience.
Table of Comparison
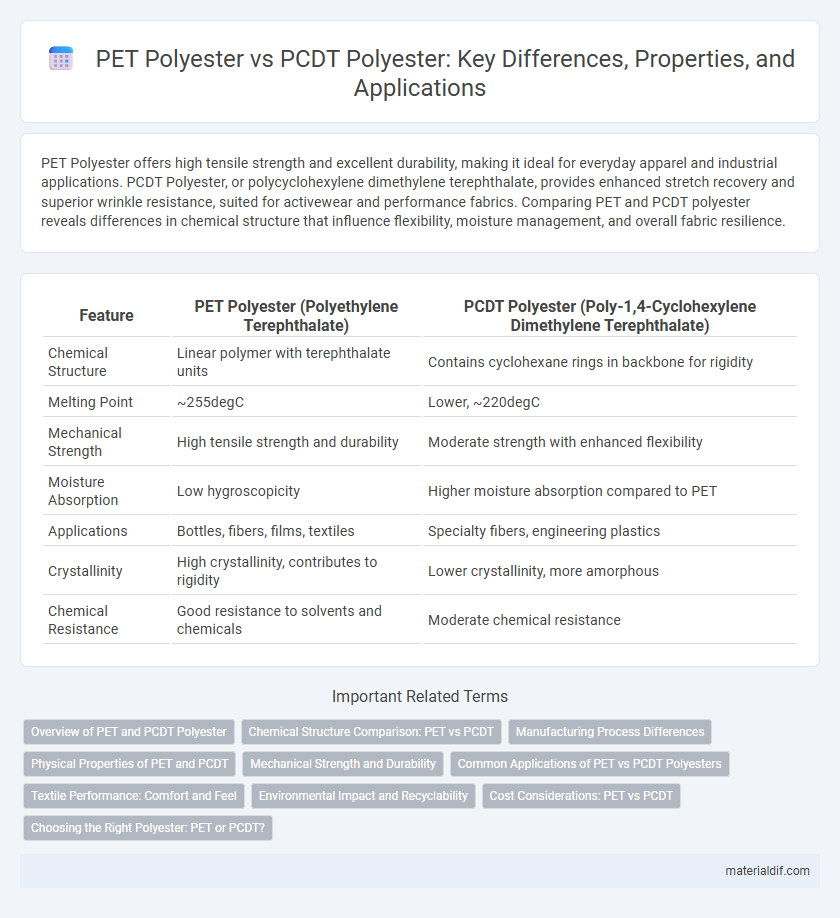
| Feature | PET Polyester (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | PCDT Polyester (Poly-1,4-Cyclohexylene Dimethylene Terephthalate) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Linear polymer with terephthalate units | Contains cyclohexane rings in backbone for rigidity |
| Melting Point | ~255degC | Lower, ~220degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and durability | Moderate strength with enhanced flexibility |
| Moisture Absorption | Low hygroscopicity | Higher moisture absorption compared to PET |
| Applications | Bottles, fibers, films, textiles | Specialty fibers, engineering plastics |
| Crystallinity | High crystallinity, contributes to rigidity | Lower crystallinity, more amorphous |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Moderate chemical resistance |
Overview of PET and PCDT Polyester
PET polyester, or polyethylene terephthalate, is a widely used synthetic fiber known for its strength, durability, and resistance to shrinking and stretching, commonly found in textiles and packaging. PCDT polyester, or polyethylene 2,5-cyclohexanedicarboxylate, offers enhanced properties such as higher crystallinity and improved thermal stability, making it suitable for specialized applications like high-performance fibers and films. Both PET and PCDT polyesters belong to the polyester family but differ significantly in molecular structure and application performance, with PCDT emerging as a promising alternative in advanced material industries.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PET vs PCDT
PET polyester features a repeating unit of polyethylene terephthalate characterized by an aromatic terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, resulting in a linear polymer chain with strong ester linkages. PCDT polyester, or poly(1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene terephthalate), differs by incorporating a cyclohexane ring within its diol component, replacing the ethylene glycol segment, which introduces increased rigidity and alters crystallinity. These structural differences impact thermal resistance, mechanical properties, and chemical stability, distinguishing PET and PCDT polyesters in various industrial applications.
Manufacturing Process Differences
PET polyester is produced through the polymerization of terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol using a melt polycondensation method, resulting in a linear polymer structure. PCDT polyester is synthesized by incorporating 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM) with terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, which requires a modified polymerization process to accommodate the cyclic diol, leading to a copolymer with altered molecular chain flexibility. The manufacturing process of PCDT involves higher temperature control and precise catalyst selection to ensure proper integration of CHDM units, differentiating it from the conventional PET production method.
Physical Properties of PET and PCDT
PET polyester exhibits high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and good thermal stability, making it ideal for durable textile and packaging applications. PCDT polyester, modified with cyclohexanedimethanol, offers enhanced flexibility, lower glass transition temperature, and improved impact resistance compared to PET. The physical properties of PCDT enable superior wrinkle resistance and better dimensional stability under stress, which are critical for high-performance fibers and films.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
PET polyester exhibits high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it suitable for applications demanding strong mechanical performance. PCDT polyester, characterized by its enhanced flexibility and superior impact resistance, offers improved durability in dynamic environments where mechanical stress varies. Comparative studies reveal PET's rigidity suits static load-bearing uses, while PCDT provides better performance under cyclic mechanical stress due to its molecular structure.
Common Applications of PET vs PCDT Polyesters
PET polyester is widely used in packaging materials such as beverage bottles, food containers, and synthetic fibers for textiles due to its excellent strength and thermal stability. PCDT polyester, known for its superior durability and resistance to heat and chemicals, is commonly applied in automotive parts, industrial components, and high-performance fibers. Both polyesters serve distinct markets, with PET dominating consumer packaging and textiles, while PCDT is preferred in specialized engineering and industrial applications.
Textile Performance: Comfort and Feel
PET polyester offers high tensile strength and excellent wrinkle resistance, making it suitable for durable textiles, yet it tends to trap heat, reducing breathability and comfort in wear. PCDT polyester, featuring a more flexible molecular structure, enhances moisture-wicking properties and provides a softer, silkier hand feel, improving overall comfort in clothing applications. The improved elongation and lower crystallinity of PCDT fibers contribute to better stretch and drape, making garments more comfortable and aesthetically appealing compared to conventional PET fibers.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
PET polyester, derived from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol, is widely recyclable through established post-consumer recycling streams, reducing plastic waste and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin production. PCDT polyester, made from 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol and terephthalic acid, offers enhanced durability and thermal resistance but faces limited recycling availability due to less developed recovery processes. The environmental impact of PCDT polyester is higher at present because its recycling infrastructure is not as mature, resulting in lower circularity compared to the well-established PET polyester recycling systems.
Cost Considerations: PET vs PCDT
PET polyester generally offers lower production costs due to its widely available raw materials and established manufacturing processes, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications. PCDT polyester incurs higher expenses because of more complex synthesis routes and specialty applications that demand superior thermal and mechanical properties. Balancing initial investment with long-term performance benefits is essential when comparing the cost considerations between PET and PCDT polyester.
Choosing the Right Polyester: PET or PCDT?
PET polyester offers high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and widespread availability, making it ideal for packaging and textile applications. PCDT polyester provides superior elasticity, improved UV stability, and enhanced dyeability, which suits high-performance fabrics and automotive components. Selecting between PET and PCDT depends on specific requirements like durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure.
PET Polyester vs PCDT Polyester Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com