Virgin pulp offers superior fiber strength and brightness compared to recycled pulp, making it ideal for high-quality paper products. Recycled pulp contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and conserving natural resources, though it may contain shorter fibers that affect durability. Balancing virgin and recycled pulp in paper manufacturing enhances both performance and eco-friendliness.
Table of Comparison
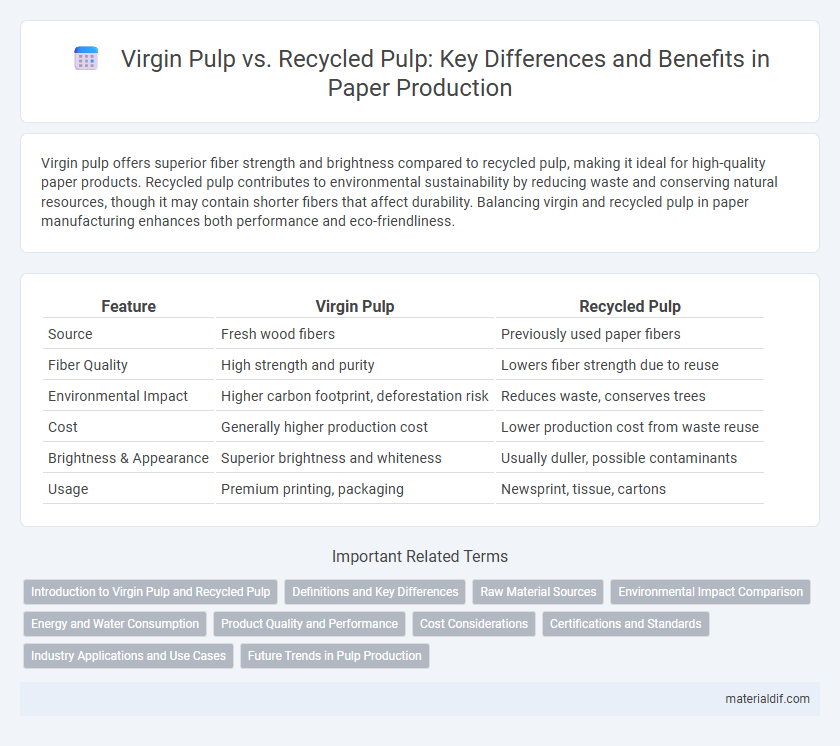
| Feature | Virgin Pulp | Recycled Pulp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fresh wood fibers | Previously used paper fibers |
| Fiber Quality | High strength and purity | Lowers fiber strength due to reuse |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint, deforestation risk | Reduces waste, conserves trees |
| Cost | Generally higher production cost | Lower production cost from waste reuse |
| Brightness & Appearance | Superior brightness and whiteness | Usually duller, possible contaminants |
| Usage | Premium printing, packaging | Newsprint, tissue, cartons |
Introduction to Virgin Pulp and Recycled Pulp
Virgin pulp is derived directly from fresh wood fibers, offering higher purity and strength ideal for producing high-quality paper products. Recycled pulp, sourced from used paper materials, reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation and energy consumption during production. Understanding the differences in fiber integrity and processing is essential for selecting appropriate pulp types in paper manufacturing.
Definitions and Key Differences
Virgin pulp consists of fibers extracted directly from wood or other raw plant materials, offering superior strength and brightness ideal for high-quality paper production. Recycled pulp is derived from reused paper products, promoting environmental sustainability by reducing waste and conserving natural resources, though it may result in weaker fiber quality. Key differences include fiber length, environmental impact, and production cost, with virgin pulp typically providing higher durability and recycled pulp emphasizing eco-friendliness and cost efficiency.
Raw Material Sources
Virgin pulp is derived directly from primary wood sources, such as softwood and hardwood trees, offering high fiber quality and strength essential for premium paper production. Recycled pulp originates from post-consumer and post-industrial paper waste, reducing the need for deforestation but often containing shorter fibers that may impact the paper's durability. The choice between virgin and recycled pulp significantly affects raw material sustainability, production costs, and paper quality characteristics.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Virgin pulp production consumes significantly more water and energy compared to recycled pulp, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation rates. Recycled pulp reduces waste sent to landfills, lowers water usage by up to 60%, and decreases energy consumption by approximately 40%. Choosing recycled pulp minimizes environmental footprint by conserving natural resources and reducing pollution associated with virgin fiber processing.
Energy and Water Consumption
Virgin pulp production consumes significantly more energy and water compared to recycled pulp, with energy usage often exceeding 30% higher due to intensive chemical processing and mechanical treatment of raw wood fibers. Water consumption in virgin pulp mills is substantially greater, primarily because of processes like wood chip washing and bleaching, which require large volumes of clean water. Recycled pulp production reduces energy demand and water usage by reusing fibers, minimizing the need for harsh chemical treatments and extensive washing procedures.
Product Quality and Performance
Virgin pulp offers superior fiber strength and brightness, resulting in higher-quality paper with enhanced durability and smoother texture compared to recycled pulp. Recycled pulp often contains shorter fibers and contaminants, which can reduce paper strength and brightness, affecting performance in printing and usage. Choosing virgin pulp ensures consistent product quality, while recycled pulp supports sustainability with some compromises in paper performance.
Cost Considerations
Virgin pulp generally incurs higher production costs due to raw material acquisition and intensive processing compared to recycled pulp, which leverages post-consumer fibers and reduces expenses related to fiber sourcing. Recycled pulp often demands additional energy and chemical inputs for de-inking and contaminant removal, impacting overall cost efficiency. Evaluating total cost requires balancing the premium of virgin fibers' quality and consistency against the variable but typically lower costs associated with recycled pulp supply chains.
Certifications and Standards
Virgin pulp often meets rigorous certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification), ensuring sustainable forest management practices. Recycled pulp is frequently certified under standards like the Blue Angel and the EU Ecolabel, highlighting its environmental benefits by reducing waste and conserving resources. Both pulp types must comply with ISO 14001 for environmental management, reinforcing their commitment to sustainable production processes.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
Virgin pulp offers superior fiber strength and brightness, making it ideal for high-quality paper products such as premium printing paper, packaging, and hygiene items. Recycled pulp is cost-effective and environmentally friendly, widely used in newsprint, corrugated containers, and lower-grade paperboard applications. Industries prioritize virgin pulp when durability and appearance are critical, while recycled pulp supports sustainability goals in mass-market paper goods.
Future Trends in Pulp Production
Future trends in pulp production emphasize sustainable sourcing, with a growing shift toward virgin pulp derived from responsibly managed forests to meet high-quality paper demands. Innovations in recycling technologies enhance recycled pulp's fiber strength and purity, expanding its use in premium paper products. Market forecasts predict increasing investment in hybrid pulp processes combining virgin and recycled fibers to optimize environmental benefits and production efficiency.
Virgin Pulp vs Recycled Pulp Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com