Linen fiber, derived from the flax plant, is known for its strength, breathability, and natural antibacterial properties, making it an excellent choice for pet bedding and accessories. Bamboo fiber offers a softer texture with natural moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic qualities, ideal for sensitive pets. Both fibers are eco-friendly, but linen provides superior durability, while bamboo excels in softness and moisture management.
Table of Comparison
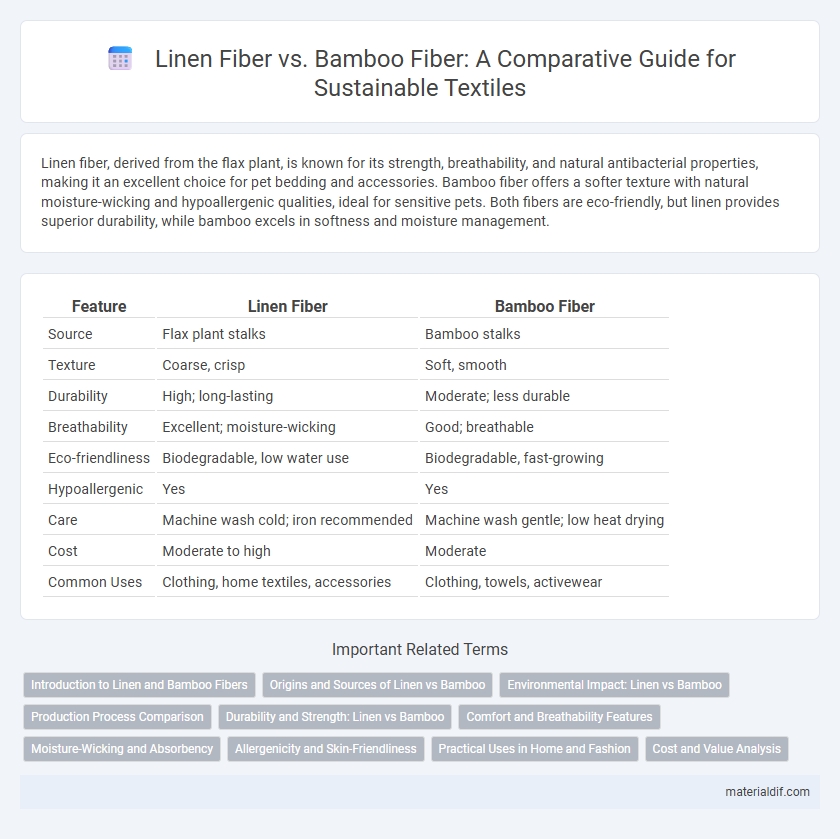
| Feature | Linen Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Flax plant stalks | Bamboo stalks |
| Texture | Coarse, crisp | Soft, smooth |
| Durability | High; long-lasting | Moderate; less durable |
| Breathability | Excellent; moisture-wicking | Good; breathable |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, low water use | Biodegradable, fast-growing |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes | Yes |
| Care | Machine wash cold; iron recommended | Machine wash gentle; low heat drying |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Common Uses | Clothing, home textiles, accessories | Clothing, towels, activewear |
Introduction to Linen and Bamboo Fibers
Linen fiber, derived from the flax plant, is renowned for its natural strength, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for warm climates and durable textiles. Bamboo fiber, extracted from the bamboo plant, offers exceptional softness, antibacterial qualities, and eco-friendly benefits due to its rapid growth and minimal pesticide requirements. Both fibers serve sustainable fashion, but linen excels in texture and longevity while bamboo provides superior comfort and antimicrobial features.
Origins and Sources of Linen vs Bamboo
Linen fiber is derived from the flax plant (Linum usitatissimum), primarily cultivated in regions such as Western Europe, Russia, and China, known for its long, strong fibers ideal for textile production. Bamboo fiber originates from the bamboo plant, predominantly grown in East Asia, especially China, where the fast-growing grass is processed into a soft, breathable textile. The agricultural practices for flax emphasize sustainable, low-water cultivation, while bamboo benefits from rapid renewability and natural pest resistance.
Environmental Impact: Linen vs Bamboo
Linen fiber, derived from flax plants, has a lower environmental impact compared to bamboo fiber due to its minimal water usage and reduced need for pesticides during cultivation. Bamboo fibers often require chemical processing to turn the raw plant into soft fabric, increasing pollution and energy consumption, while linen production typically involves fewer chemicals. The biodegradability of linen also contributes to a smaller ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable choice than bamboo in textile manufacturing.
Production Process Comparison
Linen fiber, derived from the flax plant, undergoes a natural retting process where the stalks are soaked or dew-retted to separate fibers, followed by mechanical extraction and combing for softness. Bamboo fiber production often involves chemically intensive processes like viscose or lyocell methods, which dissolve bamboo pulp before regenerating it into fibers, impacting environmental sustainability. The flax-based linen process is more eco-friendly due to minimal chemical use and lower water consumption compared to chemically processed bamboo fibers.
Durability and Strength: Linen vs Bamboo
Linen fiber, derived from flax plants, exhibits exceptional durability and strength, often surpassing bamboo fiber in tensile resilience and resistance to wear over time. Bamboo fiber, while softer and more pliable, tends to be less robust and may degrade faster under heavy use or frequent washing. The superior strength of linen makes it ideal for long-lasting textiles requiring high durability, whereas bamboo fiber suits applications where softness and flexibility are prioritized.
Comfort and Breathability Features
Linen fiber is highly valued for its natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it exceptionally comfortable in hot and humid conditions by promoting airflow and quick drying. Bamboo fiber also offers excellent breathability and is naturally antimicrobial, which enhances comfort by reducing odor and maintaining freshness. While both fibers are soft, linen tends to have a slightly rougher texture initially but becomes softer over time, whereas bamboo fiber is typically smoother and silkier right from the start.
Moisture-Wicking and Absorbency
Linen fiber excels in moisture-wicking due to its natural hollow fibers that allow rapid evaporation and breathability, making it ideal for hot, humid climates. Bamboo fiber offers superior absorbency, capable of retaining up to 3-4 times its weight in water, which enhances comfort by effectively managing perspiration. Both fibers provide excellent moisture management, but linen is preferred for quick drying while bamboo is favored for superior moisture retention.
Allergenicity and Skin-Friendliness
Linen fiber, derived from flax plants, is naturally hypoallergenic and highly breathable, reducing the risk of skin irritation and allergic reactions. Bamboo fiber also offers skin-friendly properties, including antimicrobial qualities that help prevent the growth of bacteria and allergens on fabric surfaces. Both fibers excel in promoting comfort for sensitive skin, but linen's durability and natural breathability make it particularly effective for minimizing allergen exposure.
Practical Uses in Home and Fashion
Linen fiber, derived from the flax plant, excels in home textiles like bedding and curtains due to its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and natural breathability, making it ideal for warm climates. Bamboo fiber, known for its softness, antibacterial qualities, and eco-friendliness, is increasingly popular in fashion apparel, especially activewear and casual clothing. Both fibers offer sustainable options, but linen's strength suits heavy-duty home uses while bamboo's smooth texture enhances comfort in everyday wear.
Cost and Value Analysis
Linen fiber typically incurs higher production costs compared to bamboo fiber due to labor-intensive flax cultivation and processing, which impacts its market price. Bamboo fiber offers a more cost-effective alternative, benefiting from faster growth cycles and lower water usage, enhancing its value for eco-conscious consumers. Despite the higher price, linen's durability and natural texture often justify the investment, positioning it as a premium choice in sustainable textiles.
Linen Fiber vs Bamboo Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com