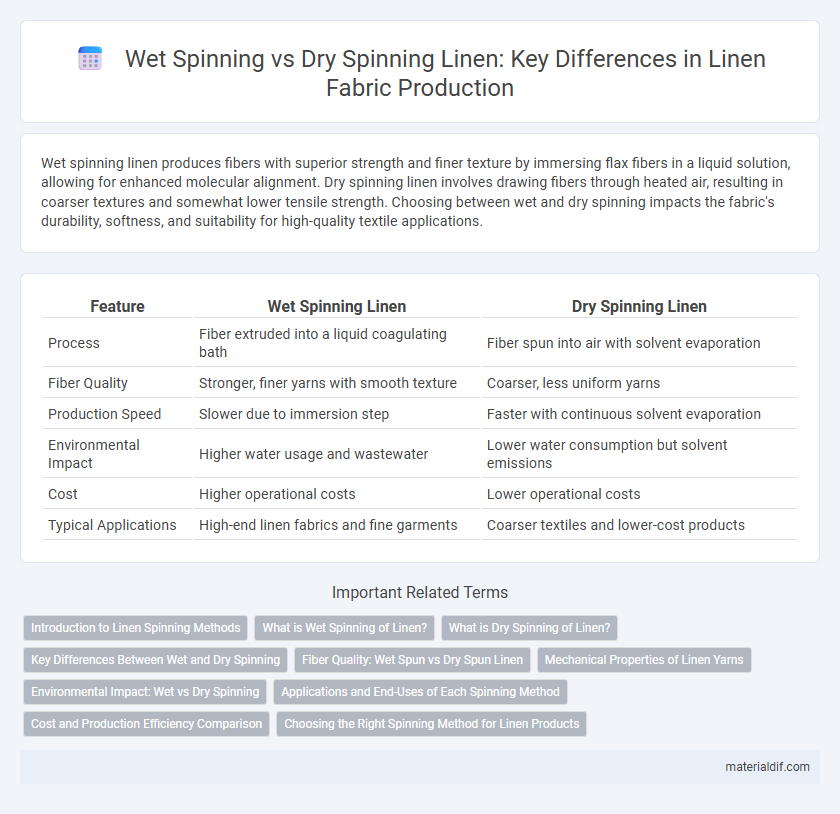
Wet spinning linen produces fibers with superior strength and finer texture by immersing flax fibers in a liquid solution, allowing for enhanced molecular alignment. Dry spinning linen involves drawing fibers through heated air, resulting in coarser textures and somewhat lower tensile strength. Choosing between wet and dry spinning impacts the fabric's durability, softness, and suitability for high-quality textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wet Spinning Linen | Dry Spinning Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Fiber extruded into a liquid coagulating bath | Fiber spun into air with solvent evaporation |
| Fiber Quality | Stronger, finer yarns with smooth texture | Coarser, less uniform yarns |
| Production Speed | Slower due to immersion step | Faster with continuous solvent evaporation |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water usage and wastewater | Lower water consumption but solvent emissions |
| Cost | Higher operational costs | Lower operational costs |
| Typical Applications | High-end linen fabrics and fine garments | Coarser textiles and lower-cost products |
Introduction to Linen Spinning Methods
Wet spinning linen involves immersing flax fibers in water to improve flexibility and alignment, producing finer, smoother yarn ideal for high-quality textiles. Dry spinning, by contrast, processes fibers without water, resulting in coarser, stronger yarns suited for durable fabrics and industrial uses. Each method leverages the unique properties of flax fibers to optimize yarn characteristics for specific applications in the linen industry.
What is Wet Spinning of Linen?
Wet spinning of linen involves dissolving flax fibers in a chemical bath to create a viscous solution, which is then extruded through fine spinnerets into a coagulating liquid, solidifying the fibers. This process results in smoother, finer, and stronger linen yarns compared to dry spinning, enhancing fabric durability and softness. Wet spinning is preferred for producing high-quality linen textiles with improved moisture absorption and breathability.
What is Dry Spinning of Linen?
Dry spinning of linen involves dissolving flax fibers in a solvent to create a viscous solution, which is then extruded through spinnerets into warm air, where the solvent evaporates, leaving solid fibers. This process produces fine, continuous filaments with smooth texture and high tensile strength, suitable for lightweight linen fabrics. Dry spinning allows better control over fiber uniformity compared to wet spinning, making it ideal for producing high-quality linen textiles.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Spinning
Wet spinning linen involves dissolving flax fibers in a chemical bath before extrusion, resulting in more uniform and fine yarn with enhanced strength. Dry spinning linen extrudes the fiber solution into warm air without a liquid bath, producing yarn with higher porosity and a rougher texture. Key differences include fiber structure, yarn uniformity, and overall fabric texture, with wet spinning offering smoother, stronger linen compared to the more breathable but coarser dry-spun counterpart.
Fiber Quality: Wet Spun vs Dry Spun Linen
Wet spinning linen produces fibers with superior tensile strength and finer fineness, resulting in a smoother and more lustrous fabric compared to dry spinning. The wet spinning process allows for better fiber alignment and fewer impurities, enhancing overall fiber quality and durability. Dry spun linen fibers tend to be coarser and less uniform, which can affect the softness and longevity of the final textile product.
Mechanical Properties of Linen Yarns
Wet spinning linen produces fibers with superior tensile strength and enhanced elongation compared to dry spinning, resulting in yarns that exhibit greater durability and flexibility. The wet spinning process allows for better molecular alignment and reduced fiber defects, which improves the mechanical properties such as abrasion resistance and elasticity. In contrast, dry spinning yields yarns with a coarser texture and lower mechanical performance, making wet spinning the preferred method for high-quality linen textile production.
Environmental Impact: Wet vs Dry Spinning
Wet spinning linen consumes significantly more water and energy compared to dry spinning, contributing to higher environmental strain. Dry spinning processes reduce water usage and chemical runoff, resulting in a smaller ecological footprint and lower emissions. Choosing dry spinning methods supports sustainable textile production by minimizing resource depletion and pollution.
Applications and End-Uses of Each Spinning Method
Wet spinning linen produces fibers with higher tenacity and uniformity, making it ideal for high-quality textiles such as fine apparel, luxury furnishings, and industrial fabrics requiring strength and durability. Dry spinning linen, offering a softer hand and greater elasticity, is better suited for breathable summer clothing, casual wear, and home textiles like curtains and lightweight upholstery. Each spinning method tailors linen's characteristics to specific applications, optimizing performance and comfort based on end-use demands.
Cost and Production Efficiency Comparison
Wet spinning linen involves dissolving flax fibers in a chemical bath, resulting in higher production costs due to the use of specialized solvents and extensive drying processes. Dry spinning linen bypasses the chemical bath, lowering energy consumption and reducing overall expenses, making it more cost-effective and faster for large-scale textile manufacturing. Production efficiency is enhanced in dry spinning by minimizing fiber damage and shortening cycle times, whereas wet spinning, though producing finer fibers, demands more time and resources.
Choosing the Right Spinning Method for Linen Products
Choosing between wet spinning and dry spinning for linen production hinges on the desired fiber quality and end-use application. Wet spinning produces finer, stronger fibers ideal for high-quality, soft fabrics, while dry spinning yields coarser fibers suited for more durable, textured textiles. Understanding these differences ensures selecting the optimal spinning method that aligns with fabric performance and aesthetic requirements.
Wet Spinning Linen vs Dry Spinning Linen Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com