Genuine leather is crafted from natural animal hide, offering durability, breathability, and a unique texture that improves with age, making it a premium choice for long-lasting products. Bonded leather, on the other hand, is made by combining leather scraps with polyurethane or latex, resulting in a product that mimics the appearance of genuine leather but lacks its strength and longevity. Understanding the difference helps consumers make informed decisions based on quality, price, and intended use.
Table of Comparison
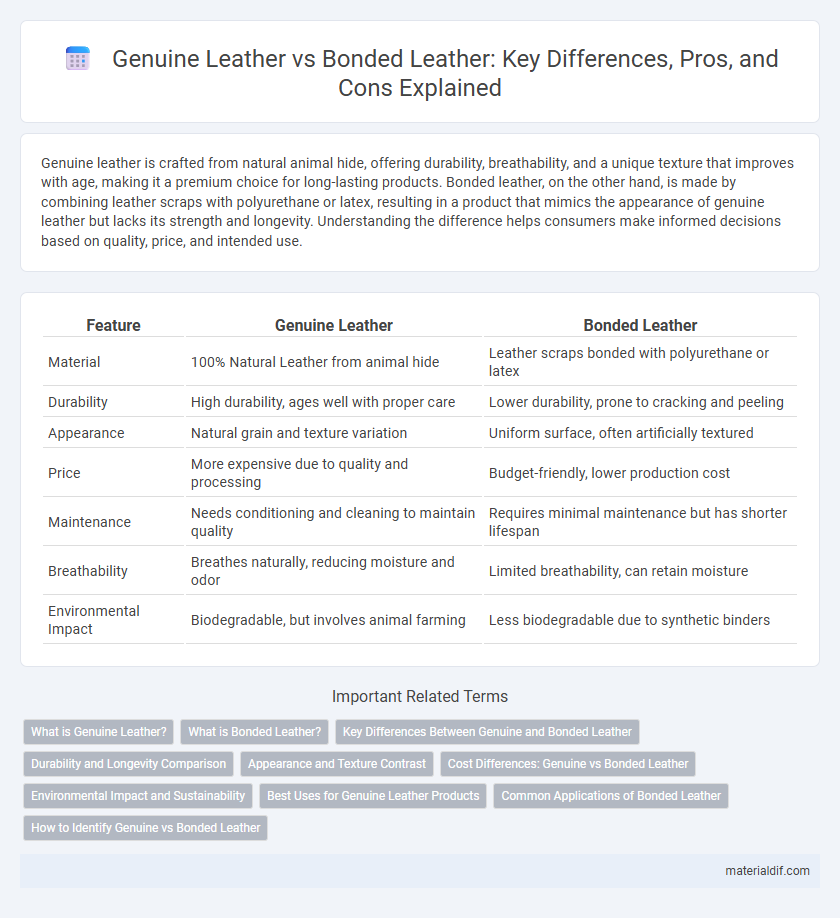
| Feature | Genuine Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | 100% Natural Leather from animal hide | Leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex |
| Durability | High durability, ages well with proper care | Lower durability, prone to cracking and peeling |
| Appearance | Natural grain and texture variation | Uniform surface, often artificially textured |
| Price | More expensive due to quality and processing | Budget-friendly, lower production cost |
| Maintenance | Needs conditioning and cleaning to maintain quality | Requires minimal maintenance but has shorter lifespan |
| Breathability | Breathes naturally, reducing moisture and odor | Limited breathability, can retain moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, but involves animal farming | Less biodegradable due to synthetic binders |
What is Genuine Leather?
Genuine leather is made from the top layer of animal hides, offering natural durability, breathability, and a unique grain pattern that develops character over time. Unlike bonded leather, which consists of shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane or latex, genuine leather retains its original animal hide structure, ensuring superior strength and longevity. High-quality genuine leather is often used in premium furniture, accessories, and apparel for its authentic texture and lasting performance.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made by combining shredded leather fibers with a polyurethane or latex backing, creating a composite that mimics the look and feel of genuine leather. It contains a lower percentage of actual leather content, often around 10-20%, compared to genuine leather, which is crafted from solid animal hides. Bonded leather offers a more affordable alternative but usually lacks the durability, breathability, and natural aging characteristics of genuine leather.
Key Differences Between Genuine and Bonded Leather
Genuine leather is made from whole animal hides, offering durability, breathability, and natural aging characteristics, whereas bonded leather is created by bonding shredded leather fibers with polyurethane or latex, resulting in a less durable and lower-quality material. Genuine leather features a consistent texture and develops a unique patina over time, while bonded leather often has an artificial, uniform appearance and tends to peel or crack. The price point of genuine leather is significantly higher due to its authentic composition, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting furniture and fashion products.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Genuine leather offers superior durability and longevity compared to bonded leather, containing full-grain or top-grain hides that withstand wear and develop a natural patina over time. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with adhesives, tends to deteriorate faster, peeling and cracking within a few years due to weaker fiber bonds. Investing in genuine leather ensures extended usability and retains aesthetic appeal, making it the preferred choice for long-lasting leather goods.
Appearance and Texture Contrast
Genuine leather exhibits a natural grain pattern with unique imperfections, offering a rich texture that deepens and softens over time. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, tends to have a uniform appearance with an artificial, smoother surface lacking natural grain complexity. The tactile experience of genuine leather is supple and warm, while bonded leather feels stiffer and less breathable.
Cost Differences: Genuine vs Bonded Leather
Genuine leather typically costs significantly more than bonded leather due to its durability, natural grain, and longer lifespan, making it a higher-quality investment. Bonded leather is made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, resulting in a lower price but reduced strength and wear resistance. Consumers seeking affordable options often choose bonded leather, while those prioritizing longevity and premium texture prefer genuine leather despite the higher expense.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Genuine leather, derived from animal hides through a complex tanning process, has a significant environmental footprint due to livestock farming's resource-intensive nature and chemical usage in tanning. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps combined with synthetic materials and adhesives, often involves lower raw material consumption but relies on non-biodegradable components, complicating recycling and biodegradability. Sustainable leather alternatives prioritize reducing waste and chemical processes, while genuine leather durability can extend product life, partially offsetting its environmental impact.
Best Uses for Genuine Leather Products
Genuine leather, known for its durability and natural breathability, is best suited for high-quality furniture, premium footwear, and luxury accessories that require long-lasting performance and aesthetic appeal. It offers superior resistance to wear and tear compared to bonded leather, making it ideal for products exposed to frequent use and stress. Additionally, genuine leather develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its beauty and value in items such as wallets, jackets, and upholstery.
Common Applications of Bonded Leather
Bonded leather is commonly used in furniture upholstery, bookbinding, and automotive interiors due to its cost-effectiveness and similar appearance to genuine leather. It is often found in budget-friendly sofas, office chairs, and car seats where durability and aesthetics are important but full-grain leather is not necessary. The material combines leather scraps and fibers with polyurethane or latex, making it less expensive and more uniform in texture than genuine leather.
How to Identify Genuine vs Bonded Leather
Genuine leather can be identified by its natural grain pattern, distinctive smell, and durability, whereas bonded leather consists of leather scraps bonded together and often feels smoother, with a synthetic backing visible on the underside. Look for irregularities in the texture and pores on genuine leather, which contrast with the uniform surface of bonded leather created through manufacturing. Pressing a fingernail into genuine leather will leave a slight indentation due to its flexibility, while bonded leather tends to be stiffer and less responsive to pressure.
Genuine Leather vs Bonded Leather Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com