Jute matting is primarily used for surface erosion control and landscaping, providing a natural barrier that protects soil while allowing plant growth. Jute geotextile, on the other hand, offers enhanced soil stabilization and drainage capabilities, making it ideal for civil engineering projects like road construction and slope reinforcement. Both materials are biodegradable and eco-friendly, but jute geotextile delivers greater durability and strength for long-term soil management solutions.
Table of Comparison
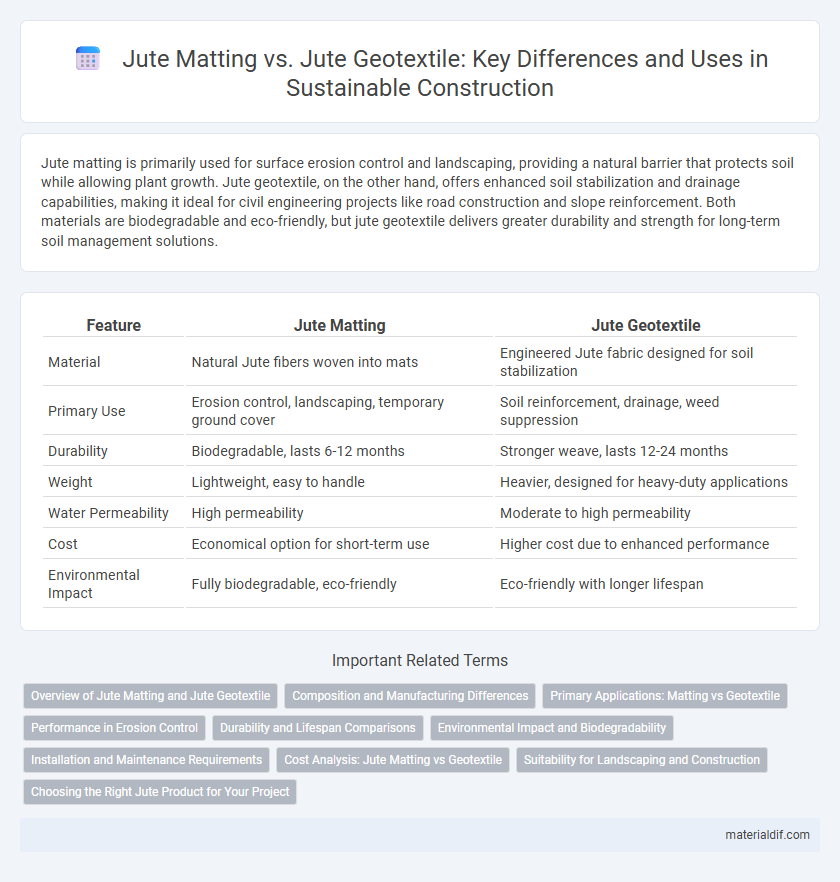
| Feature | Jute Matting | Jute Geotextile |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural Jute fibers woven into mats | Engineered Jute fabric designed for soil stabilization |
| Primary Use | Erosion control, landscaping, temporary ground cover | Soil reinforcement, drainage, weed suppression |
| Durability | Biodegradable, lasts 6-12 months | Stronger weave, lasts 12-24 months |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier, designed for heavy-duty applications |
| Water Permeability | High permeability | Moderate to high permeability |
| Cost | Economical option for short-term use | Higher cost due to enhanced performance |
| Environmental Impact | Fully biodegradable, eco-friendly | Eco-friendly with longer lifespan |
Overview of Jute Matting and Jute Geotextile
Jute matting, made from woven natural jute fibers, is primarily used for erosion control and landscaping due to its biodegradable properties and soil stabilization capabilities. Jute geotextile, on the other hand, is a more engineered product designed for ground reinforcement, filtration, and drainage in civil engineering applications, combining strength with environmental sustainability. Both materials offer effective soil protection, but jute geotextiles provide enhanced durability and performance for long-term infrastructure projects.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Jute matting is typically woven from raw jute fibers, creating a thick, coarse fabric primarily used for erosion control and landscaping applications. In contrast, jute geotextiles consist of processed jute fibers that are either nonwoven or stitched, offering enhanced tensile strength and uniformity for soil stabilization and drainage. The manufacturing process of jute geotextiles involves advanced techniques like needle punching or heat bonding, whereas jute matting relies on traditional weaving methods, affecting durability and performance characteristics.
Primary Applications: Matting vs Geotextile
Jute matting is primarily used for soil erosion control on slopes, landscaping, and temporary ground cover due to its ability to stabilize soil and promote vegetation growth. Jute geotextiles serve more technical applications such as soil reinforcement, drainage, and filtration in civil engineering projects, offering enhanced durability and permeability. Both materials leverage jute's natural biodegradability but differ significantly in mechanical strength and application scope.
Performance in Erosion Control
Jute geotextiles exhibit superior performance in erosion control compared to jute matting due to their higher tensile strength and permeability, which facilitates effective water flow while stabilizing soil. Jute geotextiles provide long-term durability and enhanced root reinforcement, promoting vegetation growth and reducing soil displacement on slopes and embankments. In contrast, jute matting mainly offers temporary surface protection and degrades faster, limiting its effectiveness in sustained erosion control applications.
Durability and Lifespan Comparisons
Jute geotextiles typically exhibit higher durability and a longer lifespan compared to jute matting due to their tighter weave and enhanced resistance to environmental stressors. Jute matting, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, tends to degrade faster under moisture and UV exposure, limiting its effective use period. The lifespan of jute geotextiles can range from 2 to 5 years, whereas jute matting generally lasts around 1 to 2 years, making geotextiles more suitable for long-term erosion control and soil stabilization.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Jute matting and jute geotextile both offer eco-friendly solutions with high biodegradability, decomposing naturally within 6 to 12 months, which minimizes environmental pollution. Jute geotextiles, designed for soil erosion control and moisture retention, provide enhanced soil stabilization with zero synthetic waste, making them superior in sustainable land management. In contrast, jute matting, mainly used for decorative or protective purposes, has slightly less environmental utility but maintains strong eco-credentials due to its 100% natural fiber composition.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Jute matting requires straightforward installation, typically laid directly over soil to provide immediate erosion control with minimal preparation. Jute geotextiles involve more precise placement and anchoring techniques to ensure effective soil stabilization and drainage, often necessitating professional installation. Maintenance for jute matting is minimal, primarily involving periodic inspection for wear, while jute geotextiles demand monitoring to manage sediment build-up and preserve permeability.
Cost Analysis: Jute Matting vs Geotextile
Jute matting generally incurs lower initial costs compared to jute geotextiles due to simpler manufacturing processes and less intensive treatment requirements. Jute geotextiles, designed for enhanced durability and erosion control, involve higher production expenses but provide longer service life and better performance in soil stabilization applications. Cost analysis must factor in installation savings and lifespan benefits when choosing between budget-friendly matting and more expensive geotextile solutions.
Suitability for Landscaping and Construction
Jute matting excels in landscaping applications due to its natural degradation, providing excellent erosion control and seed protection for short-term projects. Jute geotextiles offer superior durability and soil stabilization, making them more suitable for long-term construction and civil engineering uses. The choice depends on project sustainability needs, with jute mats preferred for biodegradable ground cover and jute geotextiles for reinforcement and drainage functions.
Choosing the Right Jute Product for Your Project
Jute matting offers excellent erosion control and soil protection for landscaping and gardening projects, providing a natural, biodegradable cover that encourages plant growth. Jute geotextile, designed with a denser weave and higher tensile strength, is suitable for civil engineering applications such as road construction and slope stabilization, where durability and soil reinforcement are critical. Selecting the right jute product depends on project requirements, balancing factors like strength, biodegradability, and environmental impact to achieve optimal performance.
Jute matting vs Jute geotextile Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com