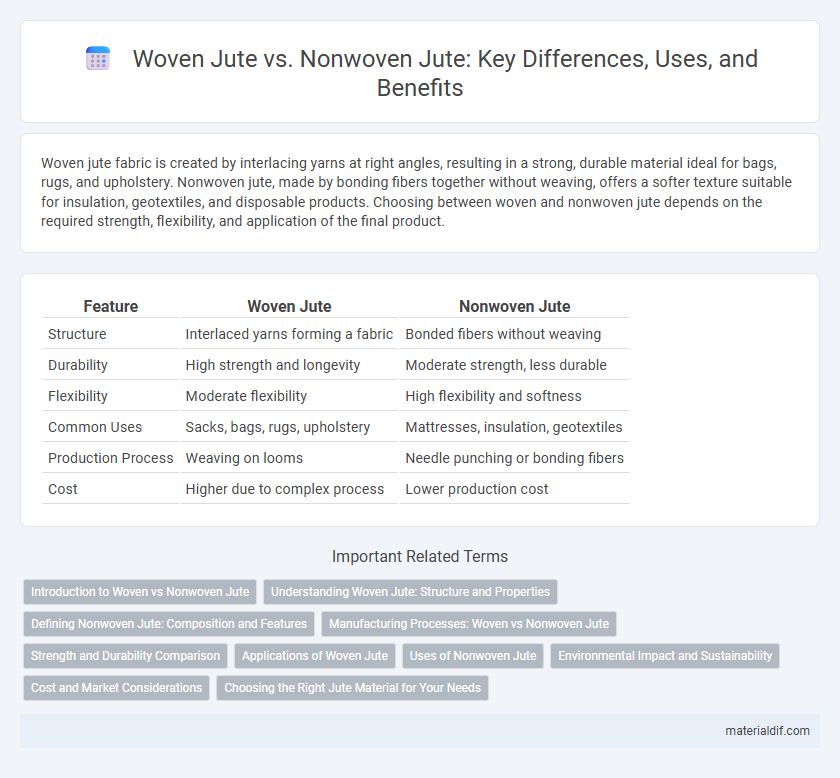
Woven jute fabric is created by interlacing yarns at right angles, resulting in a strong, durable material ideal for bags, rugs, and upholstery. Nonwoven jute, made by bonding fibers together without weaving, offers a softer texture suitable for insulation, geotextiles, and disposable products. Choosing between woven and nonwoven jute depends on the required strength, flexibility, and application of the final product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Woven Jute | Nonwoven Jute |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Interlaced yarns forming a fabric | Bonded fibers without weaving |
| Durability | High strength and longevity | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and softness |
| Common Uses | Sacks, bags, rugs, upholstery | Mattresses, insulation, geotextiles |
| Production Process | Weaving on looms | Needle punching or bonding fibers |
| Cost | Higher due to complex process | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Woven vs Nonwoven Jute
Woven jute consists of interlaced yarns forming a durable, breathable fabric commonly used in sacks, rugs, and upholstery, providing strength and flexibility. Nonwoven jute, created by bonding fibers directly without weaving, offers a lightweight, uniform texture ideal for geotextiles, insulation, and packaging applications. Understanding the structural differences between woven and nonwoven jute aids in selecting the appropriate material based on durability, texture, and end-use requirements.
Understanding Woven Jute: Structure and Properties
Woven jute features an interlaced structure created by weaving longitudinal warp and horizontal weft yarns, providing enhanced tensile strength and durability compared to nonwoven jute. This structured pattern allows for greater flexibility, abrasion resistance, and dimensional stability, making woven jute ideal for heavy-duty applications such as sacks, rugs, and upholstery. The natural fiber's breathability and biodegradability further contribute to its sustainability in various industrial and eco-friendly uses.
Defining Nonwoven Jute: Composition and Features
Nonwoven jute consists of fibers bonded together through mechanical, chemical, or thermal processes rather than traditional weaving, resulting in a fabric with enhanced flexibility and durability. Its composition typically includes short jute fibers combined with synthetic or natural binders to improve strength and resistance to tearing. This structure provides superior insulation, water resistance, and versatility compared to woven jute, making it suitable for upholstery, geotextiles, and eco-friendly packaging applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Woven vs Nonwoven Jute
Woven jute involves interlacing warp and weft yarns on a loom, creating a strong, durable fabric ideal for bags and upholstery. Nonwoven jute is produced by bonding fibers together through mechanical, chemical, or thermal methods without weaving, resulting in a versatile, lightweight material used in geotextiles and insulation. The manufacturing process differences significantly influence the fabric's texture, strength, and applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Woven jute fabrics exhibit superior strength and durability compared to nonwoven jute due to their interlaced fiber structure, which enhances tensile resistance and longevity. Nonwoven jute, produced by bonding fibers together without weaving, tends to be less robust, making it more suitable for applications with lower mechanical stress. The inherent durability and tensile strength of woven jute make it ideal for heavy-duty uses like upholstery, sacks, and industrial packaging.
Applications of Woven Jute
Woven jute is widely used in applications requiring durability and breathability, such as in the production of bags, rugs, and upholstery fabrics. Its interlaced fibers provide enhanced strength and resistance to tearing, making it ideal for packaging materials and geo-textiles in agriculture and construction. Compared to nonwoven jute, woven jute excels in products where flexibility and prolonged wear are essential.
Uses of Nonwoven Jute
Nonwoven jute fabric is primarily used in geotextiles, agriculture, and erosion control due to its excellent water permeability and biodegradability. It provides strong soil reinforcement, weed control, and moisture retention, making it ideal for landscaping and horticulture applications. The versatility of nonwoven jute extends to packaging and upholstery, where its cushioning and protective properties are highly valued.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Woven jute exhibits superior durability and reusability, significantly reducing waste and promoting sustainable consumption patterns compared to nonwoven jute, which often relies on chemical binders that may hinder biodegradability. The environmental footprint of woven jute is lower due to its natural fiber interlacing, minimizing the need for synthetic additives and facilitating easier recycling and composting processes. Sustainable practices in woven jute manufacturing contribute to carbon sequestration benefits and soil conservation, enhancing its role as an eco-friendly material in textile and packaging industries.
Cost and Market Considerations
Woven jute fabric, characterized by interlacing yarns, typically incurs higher production costs due to its complex manufacturing process, which directly impacts pricing in the packaging and textile markets. Nonwoven jute, produced through bonding fibers without weaving, offers a cost-effective alternative favored for disposable products and geotextiles, resulting in broader adoption in cost-sensitive market segments. Market demand for woven jute remains strong in premium and durable goods, while nonwoven jute captures budget-oriented niches, influencing strategic decisions in sourcing and product development.
Choosing the Right Jute Material for Your Needs
Woven jute features interlaced fibers that offer enhanced strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like sacks and rugs. Nonwoven jute, bonded through chemical or mechanical means, provides flexibility and softness suitable for insulation and carpet backing. Selecting the right jute material depends on prioritizing tensile strength for load-bearing uses or pliability for cushioning and insulation purposes.
Woven Jute vs Nonwoven Jute Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com