Jute blending combines jute fibers with other natural or synthetic materials to enhance durability, texture, and versatility in fabric production, making it ideal for diverse pet accessories. Jute spinning, on the other hand, involves twisting jute fibers into yarns, providing strength and a rustic aesthetic primarily suited for sturdy pet products like leashes and toys. Understanding the distinction between jute blending and jute spinning helps in selecting the right material for pet goods that balance comfort, strength, and eco-friendliness.
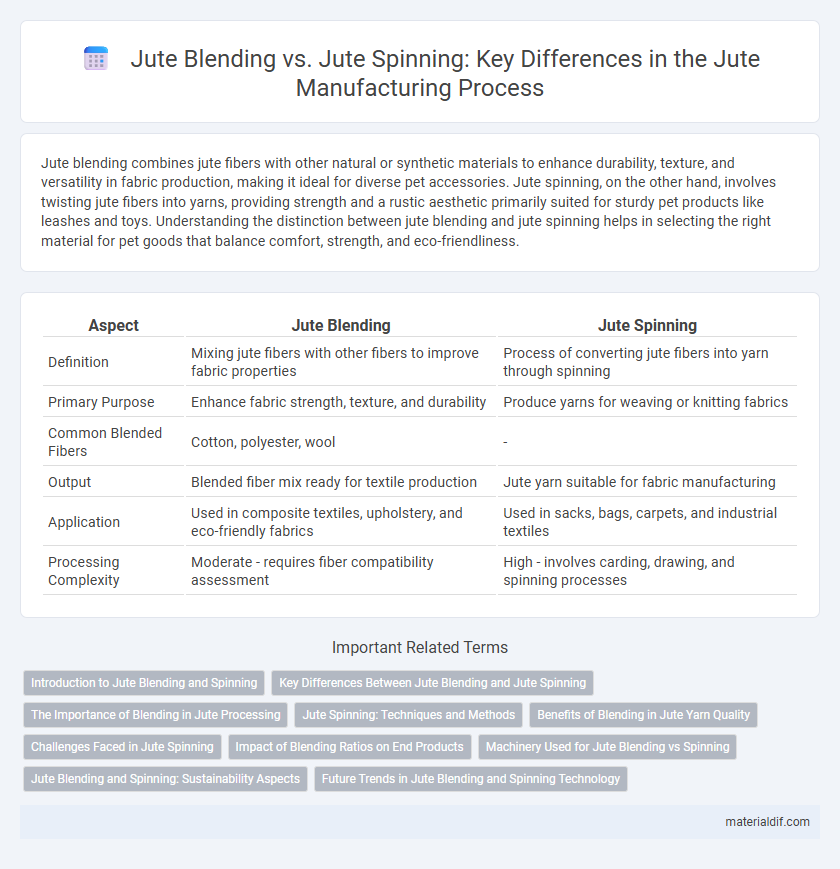
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Jute Blending | Jute Spinning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mixing jute fibers with other fibers to improve fabric properties | Process of converting jute fibers into yarn through spinning |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance fabric strength, texture, and durability | Produce yarns for weaving or knitting fabrics |
| Common Blended Fibers | Cotton, polyester, wool | - |
| Output | Blended fiber mix ready for textile production | Jute yarn suitable for fabric manufacturing |
| Application | Used in composite textiles, upholstery, and eco-friendly fabrics | Used in sacks, bags, carpets, and industrial textiles |
| Processing Complexity | Moderate - requires fiber compatibility assessment | High - involves carding, drawing, and spinning processes |
Introduction to Jute Blending and Spinning
Jute blending involves combining jute fibers with other natural or synthetic fibers to enhance the strength, texture, and dye absorption of the final fabric. Jute spinning is the process of twisting raw jute fibers into yarn, providing the foundation for weaving and knitting in textile production. Both techniques are essential in the jute industry for producing versatile materials used in bags, carpets, and upholstery.
Key Differences Between Jute Blending and Jute Spinning
Jute blending involves mixing jute fibers with other natural or synthetic fibers to enhance the fabric's strength, texture, and versatility, typically used in producing composite textiles. Jute spinning refers to the process of converting raw jute fibers into yarn by carding, drawing, and twisting, which directly influences yarn quality and fabric durability. The key difference lies in jute blending combining multiple fiber types for improved characteristics, while jute spinning transforms single fiber types into continuous yarn.
The Importance of Blending in Jute Processing
Jute blending plays a crucial role in enhancing the fiber's durability, texture, and color consistency by combining jute with other fibers such as cotton, polyester, or wool. This process improves the overall quality and versatility of the final textile product, making it suitable for a wider range of applications compared to pure jute yarn produced through traditional jute spinning. Blending optimizes the mechanical properties and aesthetic appeal of jute fabrics, driving innovation and expanding market potential in the jute industry.
Jute Spinning: Techniques and Methods
Jute spinning involves transforming raw jute fibers into yarn through techniques like ring spinning, rotor spinning, and air-jet spinning, which enhance yarn strength and uniformity. Advanced methods such as blending jute with cotton or polyester fibers improve fabric durability and texture, catering to diverse textile applications. Modern spindle machinery and tension control systems optimize the spinning process, increasing production efficiency and yarn quality.
Benefits of Blending in Jute Yarn Quality
Jute blending enhances yarn quality by combining natural fiber strengths, resulting in improved softness, durability, and color retention compared to pure jute spinning. Blending jute with cotton or synthetic fibers reduces fiber brittleness and increases tensile strength, making the yarn more versatile for diverse textile applications. The process also lowers cost and environmental impact by optimizing raw material use while maintaining high-quality output.
Challenges Faced in Jute Spinning
Jute spinning encounters significant challenges due to the fiber's coarse texture and short staple length, which complicate consistent yarn production and weaken tensile strength. Variability in fiber quality leads to uneven yarn thickness, increasing breakage rates and reducing machine efficiency. Controlling fiber moisture content is critical, as improper moisture affects spinnability and final product durability in jute yarn manufacturing.
Impact of Blending Ratios on End Products
Blending ratios in jute yarn production significantly influence the strength, texture, and durability of the end products, with higher synthetic fiber inclusion enhancing tensile strength and moisture resistance. Variations in jute spinning parameters affect fiber alignment and yarn uniformity, impacting the fabric's overall performance and aesthetic appeal. Optimal blending of jute with cotton, polyester, or other fibers creates versatile textiles suited for packaging, upholstery, and eco-friendly fashion.
Machinery Used for Jute Blending vs Spinning
Jute blending machinery typically includes carding machines, blending mixers, and opener machines designed to mix jute fibers with other natural or synthetic fibers for enhanced fabric properties. Jute spinning machinery involves jute spinning frames, roving machines, and ring spinning machines that convert carded jute fibers into yarn or thread for weaving and textile production. The key difference lies in blending equipment focusing on fiber preparation and mixing, while spinning machinery emphasizes yarn formation and tension control.
Jute Blending and Spinning: Sustainability Aspects
Jute blending enhances fabric durability and texture by combining natural fibers while maintaining biodegradability and reducing reliance on synthetic materials, thus promoting eco-friendly textile production. Jute spinning transforms raw fibers into yarn with minimal chemical usage, conserving water and energy resources compared to synthetic fiber processing. Both processes prioritize sustainability by supporting renewable fiber utilization and minimizing environmental impact throughout the textile manufacturing lifecycle.
Future Trends in Jute Blending and Spinning Technology
Future trends in jute blending emphasize the integration of synthetic fibers to enhance durability and moisture resistance, promoting versatility in textile applications. Advances in jute spinning technology focus on automation and precision machinery to improve fiber alignment and yarn strength, reducing production costs and boosting output quality. Innovations such as bio-based fiber blends and eco-friendly spinning processes are driving sustainable growth in the jute industry.
Jute Blending vs Jute Spinning Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com