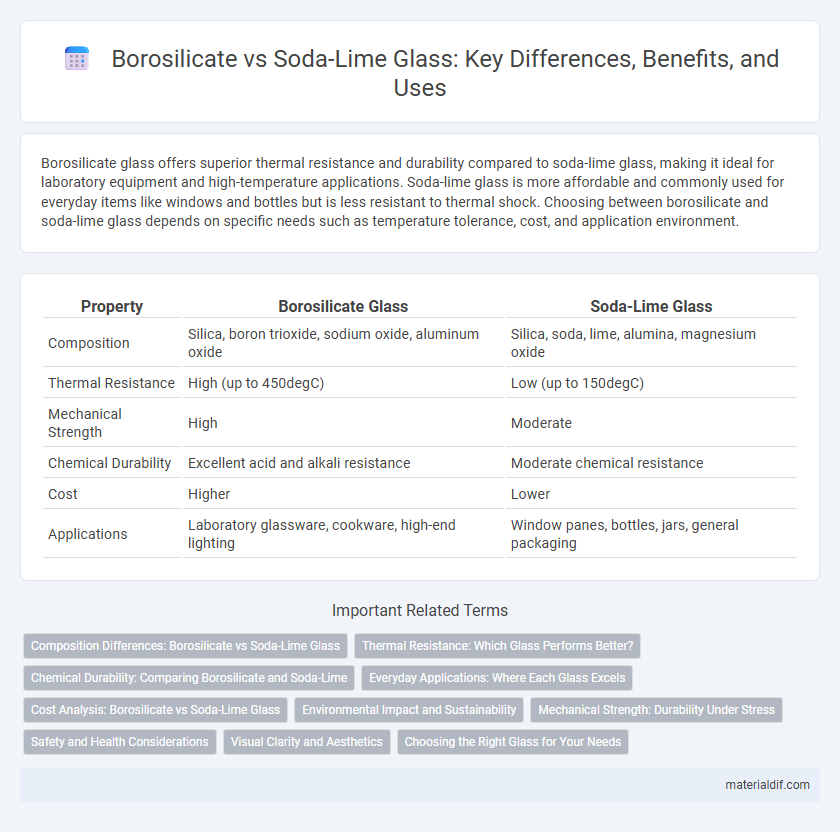
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability compared to soda-lime glass, making it ideal for laboratory equipment and high-temperature applications. Soda-lime glass is more affordable and commonly used for everyday items like windows and bottles but is less resistant to thermal shock. Choosing between borosilicate and soda-lime glass depends on specific needs such as temperature tolerance, cost, and application environment.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | Soda-Lime Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, boron trioxide, sodium oxide, aluminum oxide | Silica, soda, lime, alumina, magnesium oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Low (up to 150degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Durability | Excellent acid and alkali resistance | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Laboratory glassware, cookware, high-end lighting | Window panes, bottles, jars, general packaging |
Composition Differences: Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass contains approximately 80% silica, 12-13% boron trioxide, and small amounts of sodium oxide and aluminum oxide, which enhance its chemical resistance and thermal stability. Soda-lime glass primarily consists of about 70-75% silica, 12-15% sodium oxide, and 5-10% calcium oxide, making it more affordable but less resistant to temperature changes and chemicals. The boron trioxide in borosilicate significantly reduces thermal expansion compared to the higher alkali content in soda-lime glass.
Thermal Resistance: Which Glass Performs Better?
Borosilicate glass outperforms soda-lime glass in thermal resistance due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, typically around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC compared to soda-lime's 9 x 10^-6 /degC. This property enables borosilicate to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking, making it ideal for labware and cookware exposed to thermal shock. In contrast, soda-lime glass, commonly used in windows and bottles, is more prone to breakage under thermal stress due to its higher expansion rate.
Chemical Durability: Comparing Borosilicate and Soda-Lime
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical durability compared to soda-lime glass, making it resistant to thermal shock, acids, and alkaline substances. This enhanced chemical resistance is due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion and a higher silica content with boron oxide, which stabilizes the glass network. Soda-lime glass, commonly used in everyday applications, is more susceptible to chemical corrosion and degradation when exposed to harsh environments.
Everyday Applications: Where Each Glass Excels
Borosilicate glass excels in everyday applications requiring high thermal resistance and chemical durability, such as laboratory glassware, cookware like measuring cups, and high-quality drinkware. Soda-lime glass dominates in common household items including windows, beverage bottles, and jars due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. The distinct properties make borosilicate ideal for heat-exposed environments, while soda-lime is best suited for standard, low-stress uses.
Cost Analysis: Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime Glass
Borosilicate glass typically incurs higher production costs due to its superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory and industrial applications, whereas soda-lime glass is more cost-effective and widely used in everyday items like windows and bottles. The raw materials for soda-lime glass are more abundant and less expensive, contributing to its lower market price compared to borosilicate. Despite the upfront higher cost, borosilicate glass offers long-term value in specialized uses where durability and heat resistance reduce replacement frequency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Borosilicate glass has a lower environmental impact due to its durability and resistance to thermal shock, which extends product lifespan and reduces waste compared to soda-lime glass. Soda-lime glass, while more energy-intensive to produce, is widely recycled, supporting sustainability efforts through established curbside recycling programs. The choice between borosilicate and soda-lime glass affects carbon footprint and waste management, with borosilicate favored for long-term use and soda-lime for its recyclability.
Mechanical Strength: Durability Under Stress
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability under stress compared to soda-lime glass, making it more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical impact. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion (approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC) reduces the risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes, whereas soda-lime glass, with a higher expansion coefficient (about 9 x 10^-6 /degC), is more prone to breakage under similar conditions. This enhanced durability makes borosilicate glass ideal for laboratory glassware, cookware, and applications requiring high precision and thermal resilience.
Safety and Health Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it safer for use in laboratory and cooking applications where exposure to high temperatures and reactive substances is common. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable and widely used in everyday containers, contains higher levels of sodium and calcium oxides, which can leach harmful substances under stress or prolonged use. Borosilicate's enhanced durability reduces the risk of breakage and chemical exposure, contributing to improved health safety in environments requiring stringent glass performance standards.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetics
Borosilicate glass offers superior visual clarity due to its low iron content, resulting in a clearer, more transparent appearance compared to soda-lime glass. Its resistance to thermal stress and chemical durability ensures the glass maintains its pristine aesthetic over time without yellowing or clouding. Soda-lime glass, while more affordable, often exhibits slight greenish tints and lower transparency, which can diminish the overall visual quality and appeal in high-end applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory and high-temperature applications. Soda-lime glass, known for its affordability and ease of manufacture, suits everyday use such as windows and bottles. Selecting the right glass depends on factors like heat tolerance, durability, and budget considerations.
Borosilicate vs Soda-Lime Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com