Silk is a natural protein fiber known for its luxurious softness, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin. Satin refers to a weaving technique that creates a glossy and smooth surface, which can be made from various fibers including silk, polyester, or nylon. While silk satin combines the elegance of silk with the sheen of satin, synthetic satin offers a more affordable alternative with less breathability and moisture-wicking capabilities.
Table of Comparison
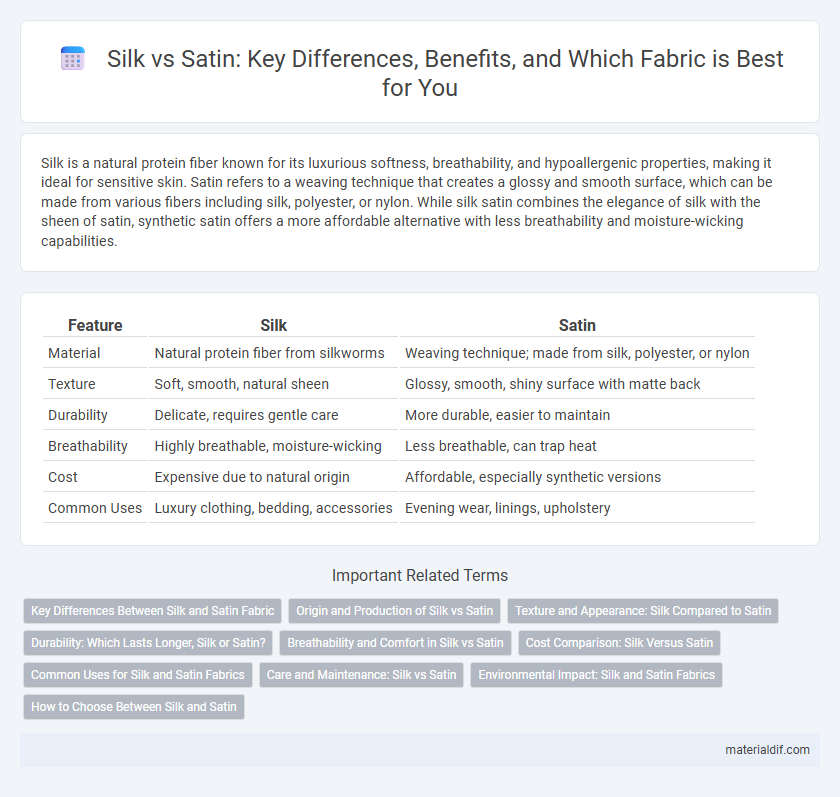
| Feature | Silk | Satin |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural protein fiber from silkworms | Weaving technique; made from silk, polyester, or nylon |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, natural sheen | Glossy, smooth, shiny surface with matte back |
| Durability | Delicate, requires gentle care | More durable, easier to maintain |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Less breathable, can trap heat |
| Cost | Expensive due to natural origin | Affordable, especially synthetic versions |
| Common Uses | Luxury clothing, bedding, accessories | Evening wear, linings, upholstery |
Key Differences Between Silk and Satin Fabric
Silk is a natural protein fiber derived from silkworm cocoons, renowned for its softness, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties, while satin is a weave pattern that can be made from various fibers including polyester, nylon, and silk itself. Silk fabrics exhibit a natural sheen and excellent moisture-wicking capabilities, making them ideal for luxury garments and delicate bedding, whereas satin's glossy surface results from the weave structure, offering a smooth, lustrous finish often used in evening wear and linings. Durability and care also differ; silk requires gentle handling and is prone to damage from sunlight and perspiration, whereas synthetic satin tends to be more resilient and easier to maintain.
Origin and Production of Silk vs Satin
Silk is a natural fiber produced by silkworms during cocoon formation, primarily cultivated in countries like China, India, and Thailand using sericulture techniques. Satin, in contrast, is a weave pattern rather than a fiber, traditionally made from silk but now often produced with synthetic fibers such as polyester or nylon, using a weaving process that creates a glossy surface and dull back. The origin of silk fabric is rooted in ancient Chinese textile history, whereas satin fabric's origin lies in the weaving method developed in the West, enabling versatility across multiple fiber types.
Texture and Appearance: Silk Compared to Satin
Silk features a naturally smooth, lustrous texture with a subtle sheen that changes under different lighting, creating an elegant and rich appearance. Satin, made from various fibers such as polyester or nylon, displays a glossy surface with a more reflective and uniform shine but lacks silk's natural softness. The tactile experience of silk is cooler and softer against the skin, while satin feels slicker and can sometimes trap heat.
Durability: Which Lasts Longer, Silk or Satin?
Silk, a natural protein fiber produced by silkworms, offers superior durability due to its strong, long fibers and resistance to stretching. Satin, a weave that can be made from silk, polyester, or nylon, varies in durability depending on the fiber type, with synthetic satins generally outperforming pure silk in wear resistance. For longevity, silk requires more delicate care, while polyester satin provides a sturdier, more resilient option for everyday use.
Breathability and Comfort in Silk vs Satin
Silk is a natural protein fiber known for its exceptional breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly comfortable for wear in warm climates. Satin, often made from synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon, lacks the same level of breathability, which can trap heat and moisture against the skin. As a result, silk provides superior comfort by allowing better air circulation and temperature regulation compared to satin.
Cost Comparison: Silk Versus Satin
Silk is a natural protein fiber derived from silkworms, typically commanding higher prices due to its labor-intensive production and luxurious texture. Satin, often made from synthetic fibers like polyester or nylon, is more affordable, providing a glossy finish that mimics silk's sheen but with less durability and breathability. Buyers prioritize silk for premium garments and bedding, while satin suits budget-conscious choices without sacrificing aesthetic appeal.
Common Uses for Silk and Satin Fabrics
Silk is commonly used in luxury garments such as evening gowns, ties, and lingerie due to its natural sheen and breathability. Satin, often made from polyester or nylon, is favored for affordable evening wear, linings, and bedding because of its smooth, glossy surface and durability. Both fabrics are popular in wedding dresses, but silk offers a more breathable and natural option while satin provides a cost-effective alternative with a similar elegant appearance.
Care and Maintenance: Silk vs Satin
Silk requires gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to preserve its natural protein fibers, avoiding harsh detergents and excessive heat that can damage its delicate structure. Satin, often made from synthetic fibers like polyester, is more durable and can usually be machine washed on a gentle cycle with mild detergent, but ironing should be done cautiously on a low setting to prevent melting. Proper storage for both fabrics involves keeping them away from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain their luster and prevent deterioration.
Environmental Impact: Silk and Satin Fabrics
Silk production involves harvesting silk from silkworms, which requires significant water and mulberry leaf resources, but it is biodegradable and renewable. Satin, a weave rather than a fiber, is often made from synthetic fibers like polyester that have high energy consumption and non-biodegradable waste concerns. Choosing silk over satin can reduce plastic pollution, though both fabrics have environmental impacts based on sourcing and manufacturing practices.
How to Choose Between Silk and Satin
When choosing between silk and satin, consider the fabric's origin and feel: silk is a natural fiber renowned for its breathability, softness, and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin and luxury apparel. Satin refers to the weave, not the fiber, and can be made from silk, polyester, or nylon, offering a glossy finish with varying durability and affordability. Prioritize silk for natural elegance and comfort, while satin suits budget-friendly options with a similar lustrous appearance.
Silk vs Satin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com