Natural fibers, such as cotton, wool, and silk, offer breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and biodegradability, making them an eco-friendly choice for textiles. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon provide enhanced durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness, often outperforming natural fibers in strength and elasticity. Choosing between natural and synthetic fibers depends on the desired balance of comfort, performance, and environmental impact in fabric applications.
Table of Comparison
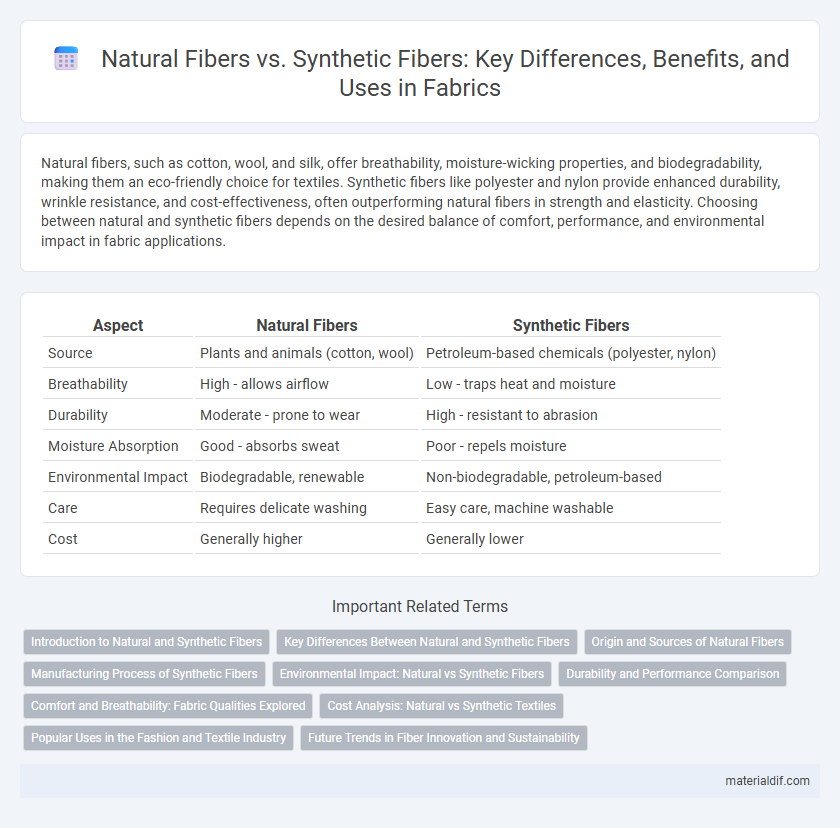
| Aspect | Natural Fibers | Synthetic Fibers |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plants and animals (cotton, wool) | Petroleum-based chemicals (polyester, nylon) |
| Breathability | High - allows airflow | Low - traps heat and moisture |
| Durability | Moderate - prone to wear | High - resistant to abrasion |
| Moisture Absorption | Good - absorbs sweat | Poor - repels moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Care | Requires delicate washing | Easy care, machine washable |
| Cost | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Introduction to Natural and Synthetic Fibers
Natural fibers, derived from plants, animals, or minerals, include cotton, wool, silk, and flax, known for their breathability, biodegradability, and comfort. Synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic, created through chemical processes, offer durability, elasticity, and resistance to moisture and wrinkles. Understanding the distinct properties of natural and synthetic fibers is essential for selecting fabrics suited to specific applications and performance requirements.
Key Differences Between Natural and Synthetic Fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk are derived from plants and animals, offering breathability, biodegradability, and comfort. Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic are chemically engineered for durability, resistance to wrinkles, and moisture-wicking properties. The key differences hinge on origin, environmental impact, moisture absorption, and longevity in textile applications.
Origin and Sources of Natural Fibers
Natural fibers originate from plants, animals, and minerals, with common sources including cotton, flax, wool, silk, and hemp. Plant-based fibers like cotton and flax are derived from cellulose, while animal fibers such as wool and silk come from protein-based sources like sheep fleece and silkworm cocoons. These fibers are renewable, biodegradable, and often preferred for their breathability and comfort compared to synthetic fibers produced from petrochemicals.
Manufacturing Process of Synthetic Fibers
Synthetic fibers are produced through chemical processes that involve polymerization, where raw materials like petroleum derivatives are transformed into long-chain polymers. These polymers are then extruded through spinnerets to form fibers, which are solidified by cooling or chemical treatment. The manufacturing process allows precise control over fiber properties such as strength, elasticity, and resistance to moisture.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Synthetic Fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and linen are biodegradable and generally have a lower environmental footprint due to their renewable cultivation, but they may require significant water and land resources. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, derived from petrochemicals, contribute to microplastic pollution and are non-biodegradable, persisting in ecosystems for decades. The environmental impact of natural fibers is often mitigated by sustainable farming practices, while synthetic fibers demand advanced recycling technologies to reduce their ecological damage.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and linen offer breathability and comfort but generally have lower durability and less resistance to abrasion compared to synthetic fibers. Synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic provide superior strength, moisture-wicking properties, and resistance to stretching, shrinking, and fading. In performance-heavy applications, synthetics outperform natural fibers by maintaining structural integrity and color retention under frequent wear and harsh conditions.
Comfort and Breathability: Fabric Qualities Explored
Natural fibers such as cotton, linen, and wool excel in comfort and breathability due to their ability to absorb moisture and allow air circulation, making them ideal for warm climates. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon often trap heat and moisture, resulting in reduced breathability and less comfort during prolonged wear. The moisture-wicking properties and softness of natural fibers significantly enhance fabric comfort compared to the typically less breathable synthetic alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Natural vs Synthetic Textiles
Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and linen generally have higher production costs due to labor-intensive cultivation and harvesting processes compared to synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, which are produced from petrochemicals through large-scale industrial manufacturing. Synthetic textiles often offer lower prices and greater cost efficiency because of their faster production rates and ability to be mass-produced with consistent quality. However, natural fibers tend to demand higher market prices driven by their biodegradable properties, comfort, and breathability, which influence consumer preference despite elevated costs.
Popular Uses in the Fashion and Textile Industry
Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk dominate fashion for breathable, biodegradable clothing and luxury textiles, favored in eco-conscious and high-end markets. Synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic offer durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effective production, making them prevalent in activewear, fast fashion, and technical textiles. Blended fabrics combining natural and synthetic fibers enhance performance and comfort, expanding their application across diverse garment styles and textile products.
Future Trends in Fiber Innovation and Sustainability
Future trends in fiber innovation emphasize biodegradable natural fibers like organic cotton, hemp, and bamboo, which reduce environmental impact by decomposing rapidly. Advances in bioengineering are producing synthetic fibers derived from renewable resources, combining durability with eco-friendly attributes to address sustainability challenges. The textile industry increasingly invests in circular economy models, promoting fiber recycling and reducing waste to achieve a carbon-neutral future.
Natural Fibers vs Synthetic Fibers Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com