Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles, offering durability and a structured texture ideal for tailored garments and upholstery. Knitted fabrics consist of interlooped yarns, providing superior stretch, flexibility, and comfort, making them perfect for activewear and casual clothing. Understanding the differences in construction affects fabric performance, appearance, and suitability for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
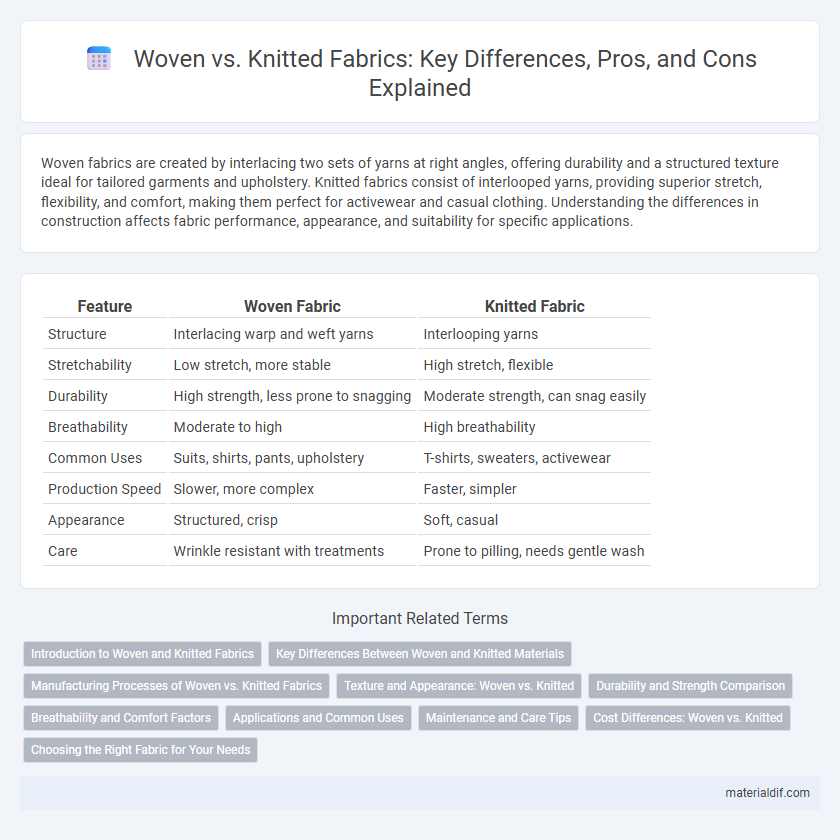
| Feature | Woven Fabric | Knitted Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Interlacing warp and weft yarns | Interlooping yarns |
| Stretchability | Low stretch, more stable | High stretch, flexible |
| Durability | High strength, less prone to snagging | Moderate strength, can snag easily |
| Breathability | Moderate to high | High breathability |
| Common Uses | Suits, shirts, pants, upholstery | T-shirts, sweaters, activewear |
| Production Speed | Slower, more complex | Faster, simpler |
| Appearance | Structured, crisp | Soft, casual |
| Care | Wrinkle resistant with treatments | Prone to pilling, needs gentle wash |
Introduction to Woven and Knitted Fabrics
Woven fabrics consist of two sets of yarns interlaced at right angles, creating a durable and structured textile commonly used in apparel, upholstery, and industrial applications. Knitted fabrics are produced by interlooping one or more yarns, resulting in a stretchy and flexible material favored for activewear, casual clothing, and seamless garments. The distinct construction methods influence fabric characteristics such as breathability, stretch, and strength.
Key Differences Between Woven and Knitted Materials
Woven fabrics consist of interlaced yarns at right angles, providing high durability and structure ideal for tailoring and upholstery. Knitted materials feature interlooped yarns, resulting in stretchability, softness, and breathability, making them perfect for activewear and casual clothing. The key differences lie in their construction methods, texture, elasticity, and typical applications across fashion and textile industries.
Manufacturing Processes of Woven vs. Knitted Fabrics
Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles using loom machines, resulting in a structured, stable textile ideal for tailored garments and upholstery. Knitted fabrics form by interlooping yarns with knitting machines or hand techniques, offering stretchability and flexibility suited for activewear and casual clothing. Manufacturing woven textiles involves intricate setups of warp and weft yarns, while knitted fabric production emphasizes loop formation and tension control for diverse fabric textures.
Texture and Appearance: Woven vs. Knitted
Woven fabrics have a crisp texture and a structured appearance due to their interlaced yarns running perpendicular, creating patterns like twill or satin. Knitted fabrics exhibit a softer, more elastic texture with a looped construction that results in a stretchy and flexible surface. The distinct differences in texture and appearance influence fabric choice for applications requiring durability or comfort.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Woven fabrics exhibit higher durability and strength due to their interlaced yarn structure, providing resistance to abrasion and tearing. Knitted fabrics, made from interlooped yarns, offer greater elasticity but tend to be less robust under heavy stress and prone to snagging. Industrial applications demanding long-lasting, strong fabrics typically favor woven materials for their superior tensile strength and dimensional stability.
Breathability and Comfort Factors
Woven fabrics typically offer less stretch but provide greater durability and breathability due to their tight interlacing of yarns, making them ideal for structured garments. Knitted fabrics, characterized by interlooped yarns, excel in comfort and elasticity, allowing better airflow and moisture-wicking properties that enhance breathability. The choice between woven and knitted fabric directly impacts garment comfort, temperature regulation, and suitability for various activities or weather conditions.
Applications and Common Uses
Woven fabrics, characterized by interlacing warp and weft threads, are widely used in applications requiring durability and structure, such as dress shirts, upholstery, and denim jeans. Knitted fabrics, made from interlooping yarns, offer superior stretch and comfort, making them ideal for activewear, casual clothing, and undergarments. Common uses for woven fabric emphasize formality and resilience, while knitted fabric dominates in sportswear and knitwear due to its flexibility and breathability.
Maintenance and Care Tips
Woven fabrics, characterized by their interlaced threads, typically require gentle washing and ironing at moderate temperatures to maintain structure and prevent shrinkage. Knitted fabrics, known for their elasticity and looped construction, benefit from hand washing or machine washing on a gentle cycle with cold water to avoid stretching and pilling. Proper drying methods, such as air-drying flat for knits and tumble drying low for wovens, help extend the lifespan and preserve the texture of both fabric types.
Cost Differences: Woven vs. Knitted
Woven fabrics generally cost more than knitted fabrics due to the complexity of the weaving process and higher production time. Knitted fabrics use fewer yarns and involve less labor-intensive machinery, making them more affordable for mass production. However, woven fabrics often offer greater durability and structure, which can justify their higher price in applications requiring long-term use.
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Needs
Woven fabrics offer durability and structure, making them ideal for formal wear and upholstery due to their tight, interlaced yarns. Knitted fabrics provide excellent stretch and flexibility, perfect for activewear and casual clothing where comfort and movement are priorities. Selecting between woven and knitted depends on the desired fabric performance, with woven suited for stability and knitted favored for elasticity and softness.
Woven vs Knitted Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com