Shearing involves removing wool directly from the sheep, preserving the fleece's natural texture and length. Carding is a process that follows shearing, where wool fibers are disentangled and aligned to prepare for spinning. While shearing harvests raw wool, carding refines and cleans it, enhancing its quality for textile production.
Table of Comparison
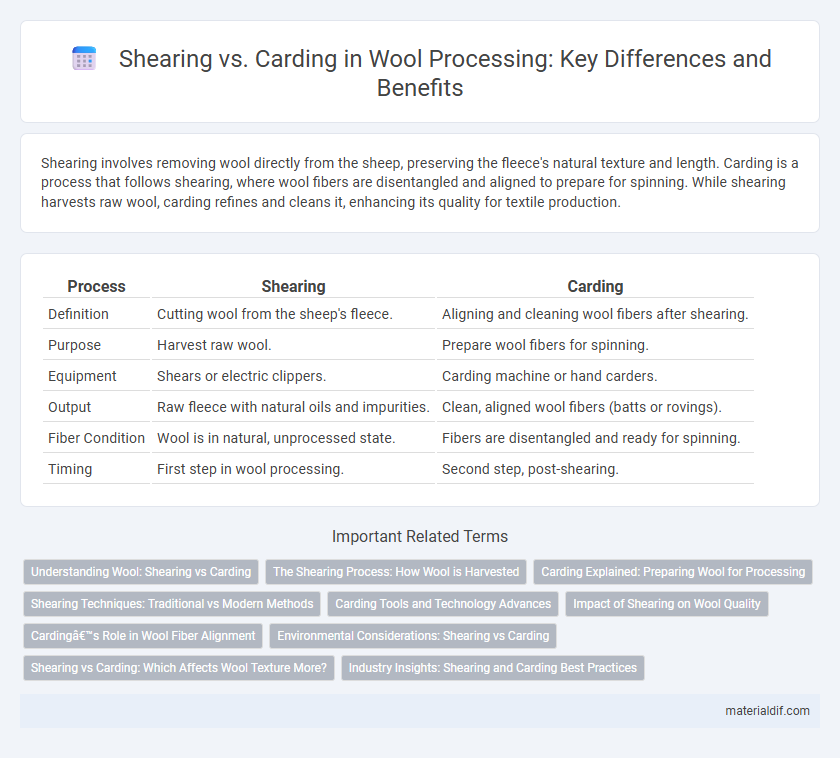
| Process | Shearing | Carding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cutting wool from the sheep's fleece. | Aligning and cleaning wool fibers after shearing. |
| Purpose | Harvest raw wool. | Prepare wool fibers for spinning. |
| Equipment | Shears or electric clippers. | Carding machine or hand carders. |
| Output | Raw fleece with natural oils and impurities. | Clean, aligned wool fibers (batts or rovings). |
| Fiber Condition | Wool is in natural, unprocessed state. | Fibers are disentangled and ready for spinning. |
| Timing | First step in wool processing. | Second step, post-shearing. |
Understanding Wool: Shearing vs Carding
Shearing is the process of cutting raw fleece from sheep, providing the primary source of wool fiber in its natural state, while carding involves disentangling and aligning these fibers to prepare them for spinning into yarn. Shearing impacts wool quality by determining fiber length and cleanliness, whereas carding enhances fiber uniformity and texture, which are crucial for producing consistent and high-quality textiles. Understanding the distinction between shearing and carding is essential for optimizing wool processing and achieving desired fabric characteristics.
The Shearing Process: How Wool is Harvested
The shearing process involves carefully removing fleece from sheep using electric clippers or manual shears, typically performed once a year to harvest raw wool. Skilled shearers ensure the wool is taken off in one piece, preserving fiber length and quality essential for textile production. This fresh fleece then undergoes cleaning and sorting before being processed further through carding to align and prepare fibers for spinning.
Carding Explained: Preparing Wool for Processing
Carding is a crucial step in wool processing that aligns and cleans the fibers, transforming raw wool into a continuous web or sliver suitable for spinning. This mechanical action removes impurities such as dirt, grease, and vegetable matter, enhancing fiber uniformity and improving the texture of the final yarn. By disentangling and organizing fibers, carding ensures consistent quality and prepares wool for subsequent stages like spinning and felting.
Shearing Techniques: Traditional vs Modern Methods
Shearing techniques in wool harvesting range from traditional blade shearing to modern machine shearing, each impacting fiber quality and animal welfare differently. Traditional shearing, often manual and slower, provides careful control but can cause stress to sheep and inconsistent fleece length. Modern methods utilize electric shears with ergonomic designs, enhancing efficiency, reducing shearing time, and improving fleece uniformity while prioritizing animal safety.
Carding Tools and Technology Advances
Carding tools have evolved from traditional hand carders to advanced mechanical carding machines that efficiently align wool fibers for improved texture and quality. Modern carding technology employs precision rollers and fine wire teeth to separate and clean fibers, enhancing the uniformity and softness of the wool. Innovations such as automated feed systems and adjustable tension controls optimize fiber processing, increasing productivity while reducing waste in wool preparation.
Impact of Shearing on Wool Quality
Shearing directly affects wool quality by determining fiber length and cleanliness at the source, as proper shearing prevents fiber damage and contamination. In contrast to carding, which aligns and cleans fibers post-shearing, the initial shearing process sets the foundation for wool strength, uniformity, and overall value. Careful shearing minimizes vegetable matter and reduces broken fibers, enhancing the final wool's performance and dye uptake.
Carding’s Role in Wool Fiber Alignment
Carding plays a crucial role in wool fiber alignment by disentangling, cleaning, and arranging fibers into a continuous web or sliver, essential for uniform yarn production. Unlike shearing, which is the process of removing wool from sheep, carding enhances fiber cohesion and consistency, directly impacting the quality and strength of the final textile. This alignment optimizes the wool's texture and prepares it for subsequent spinning stages, ensuring durability and comfort in woolen products.
Environmental Considerations: Shearing vs Carding
Shearing wool directly from sheep minimizes waste and reduces energy consumption compared to carding, which processes loose or recycled fibers and often requires additional chemicals and water. Shearing supports sustainable farming practices by maintaining animal health and promoting fiber quality without intensive processing steps. Carding, while essential for fiber preparation, can increase carbon footprint through mechanical energy use and potential water pollution from fiber treatment chemicals.
Shearing vs Carding: Which Affects Wool Texture More?
Shearing directly impacts wool texture by determining fiber length and cleanliness, removing the fleece in one piece and preserving its natural state. Carding, on the other hand, aligns and separates wool fibers, influencing softness and smoothness but not the inherent fiber quality. Shearing affects the fundamental texture more significantly, while carding refines the wool for further processing.
Industry Insights: Shearing and Carding Best Practices
Shearing removes fleece from sheep efficiently, yielding high-quality wool essential for industry standards, while carding aligns and cleans fibers to enhance spinnability and fabric strength. Optimizing shearing techniques minimizes contamination and fiber damage, directly impacting wool grade and market value. Implementing precise carding protocols boosts fiber uniformity, promoting superior yarn production and reducing waste in textile manufacturing.
Shearing vs Carding Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com