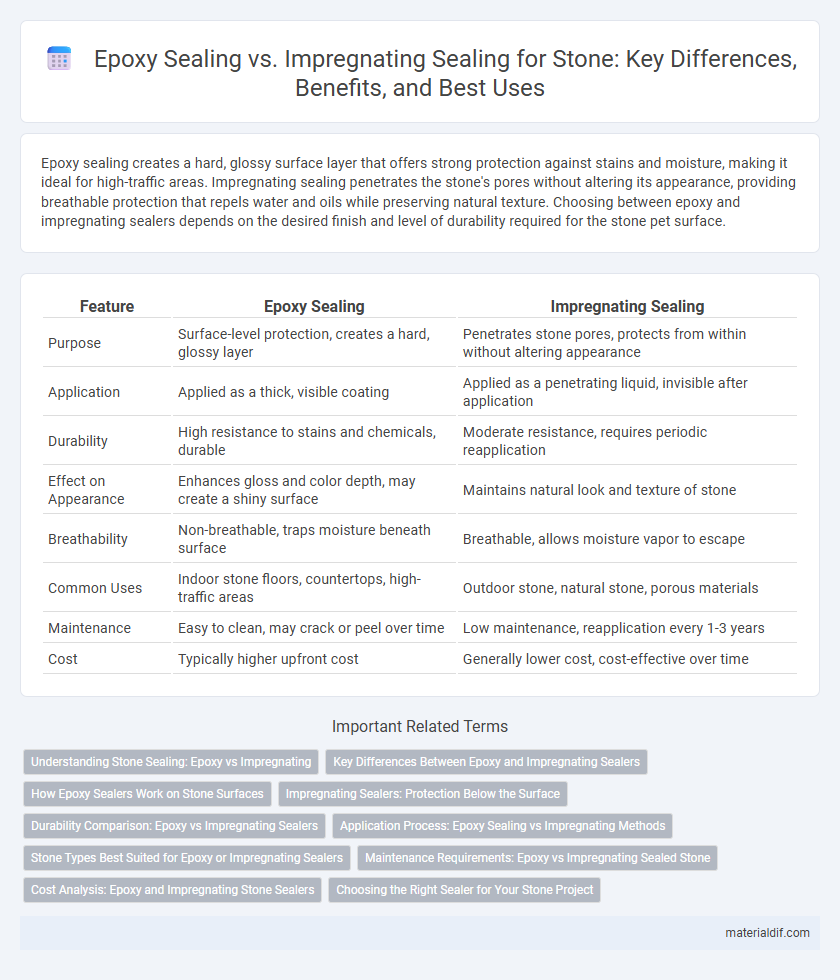
Epoxy sealing creates a hard, glossy surface layer that offers strong protection against stains and moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic areas. Impregnating sealing penetrates the stone's pores without altering its appearance, providing breathable protection that repels water and oils while preserving natural texture. Choosing between epoxy and impregnating sealers depends on the desired finish and level of durability required for the stone pet surface.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Epoxy Sealing | Impregnating Sealing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface-level protection, creates a hard, glossy layer | Penetrates stone pores, protects from within without altering appearance |
| Application | Applied as a thick, visible coating | Applied as a penetrating liquid, invisible after application |
| Durability | High resistance to stains and chemicals, durable | Moderate resistance, requires periodic reapplication |
| Effect on Appearance | Enhances gloss and color depth, may create a shiny surface | Maintains natural look and texture of stone |
| Breathability | Non-breathable, traps moisture beneath surface | Breathable, allows moisture vapor to escape |
| Common Uses | Indoor stone floors, countertops, high-traffic areas | Outdoor stone, natural stone, porous materials |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, may crack or peel over time | Low maintenance, reapplication every 1-3 years |
| Cost | Typically higher upfront cost | Generally lower cost, cost-effective over time |
Understanding Stone Sealing: Epoxy vs Impregnating
Epoxy sealing forms a durable, glossy surface layer that protects stone from stains and moisture, ideal for high-traffic areas and decorative finishes. Impregnating sealers penetrate the stone's pores without altering its natural texture or appearance, providing invisible protection against water and oil-based stains. Choosing between epoxy and impregnating sealers depends on stone type, desired finish, and exposure conditions, ensuring optimal stone preservation and longevity.
Key Differences Between Epoxy and Impregnating Sealers
Epoxy sealers create a thick, durable coating that sits on the surface of stone, providing strong resistance to stains and abrasions, whereas impregnating sealers penetrate deeply into the stone pores to offer protection from within without changing the surface appearance. Epoxy sealers are ideal for high-traffic areas requiring heavy-duty protection, while impregnating sealers are better suited for natural stone types where maintaining breathability and natural texture is essential. The longevity and moisture resistance of epoxy sealers generally exceed those of impregnating sealers, but impregnating sealers offer superior vapor permeability, preventing trapped moisture and potential damage.
How Epoxy Sealers Work on Stone Surfaces
Epoxy sealers create a durable, non-porous layer on stone surfaces by chemically bonding with the substrate, effectively preventing water, stains, and contaminants from penetrating the material. This sealing method enhances stone's gloss and color depth while providing strong resistance against abrasion and chemical damage. Unlike impregnating sealers that penetrate the stone, epoxy sealers form a protective film on top, making them ideal for high-traffic areas requiring robust surface protection.
Impregnating Sealers: Protection Below the Surface
Impregnating sealers penetrate porous stone surfaces, forming a barrier beneath the exterior to protect against water, oil, and stains without altering the stone's natural appearance. Unlike epoxy sealing, which creates a surface layer susceptible to chipping and discoloration, impregnating sealers preserve breathability and durability by sealing the stone internally. This deep protection ensures long-lasting resistance against moisture infiltration and enhances the stone's structural integrity.
Durability Comparison: Epoxy vs Impregnating Sealers
Epoxy sealers create a durable, thick protective layer on stone surfaces that resists stains, chemicals, and wear, making them ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy use. Impregnating sealers penetrate the stone to protect from within, maintaining breathability and natural appearance but offer less surface resistance compared to epoxy. For long-term durability, epoxy sealers outperform by providing stronger surface protection, whereas impregnating sealers require more frequent reapplication to maintain effectiveness.
Application Process: Epoxy Sealing vs Impregnating Methods
Epoxy sealing involves applying a two-part resin that chemically bonds to stone surfaces, creating a durable, glossy finish ideal for high-traffic areas and heavy-duty protection. Impregnating sealing penetrates deep into the stone's pores without altering its appearance, providing water and stain resistance while preserving natural textures. The application process for epoxy requires careful mixing and curing times, whereas impregnating sealers are typically applied with a brush or spray and absorb quickly without needing extensive drying periods.
Stone Types Best Suited for Epoxy or Impregnating Sealers
Epoxy sealers are ideal for non-porous stones such as granite and quartz, providing a durable, glossy finish that enhances stain resistance. Impregnating sealers best suit porous stones like marble, limestone, and sandstone by penetrating the surface to protect against moisture and oil without altering the stone's natural appearance. Choosing the appropriate sealer based on stone porosity ensures optimal protection and longevity.
Maintenance Requirements: Epoxy vs Impregnating Sealed Stone
Epoxy sealing creates a thick, durable barrier on stone surfaces that requires minimal maintenance, typically involving only occasional cleaning with non-abrasive detergents to preserve its protective layer. In contrast, impregnating sealers penetrate the stone to protect from within, necessitating more frequent reapplication--usually every 1 to 3 years--due to gradual wear and environmental exposure. Choosing between epoxy and impregnating sealing depends on balancing long-term durability with maintenance intervals specific to stone type and usage conditions.
Cost Analysis: Epoxy and Impregnating Stone Sealers
Epoxy stone sealers generally incur higher upfront costs due to the specialized materials and application process but provide superior durability and chemical resistance, making them cost-effective for long-term protection. Impregnating sealers tend to have lower initial expenses and easier application, though they may require more frequent reapplication, leading to increased maintenance costs over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that epoxy sealers are better suited for high-traffic or industrial stone surfaces, while impregnating sealers offer economical protection for residential or low-traffic areas.
Choosing the Right Sealer for Your Stone Project
Epoxy sealing creates a durable, waterproof barrier ideal for high-traffic stone surfaces, while impregnating sealing penetrates the stone to protect against stains and moisture without altering its appearance. Selecting the appropriate sealer depends on the stone type, project location, and desired finish, with epoxy suited for heavy-use areas and impregnating sealers preferred for preserving natural aesthetics. Proper application enhances stone durability, prevents damage, and maintains long-term beauty.
Epoxy Sealing vs Impregnating Sealing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com