Fieldstone offers a natural, rustic appeal with its irregular shapes and rough texture, making it ideal for landscaping and rustic construction. Cut stone is precisely shaped and smoothed, providing a refined, uniform look suitable for formal architecture and detailed masonry work. Choosing between fieldstone and cut stone depends on the desired aesthetic, structural requirements, and budget considerations.
Table of Comparison
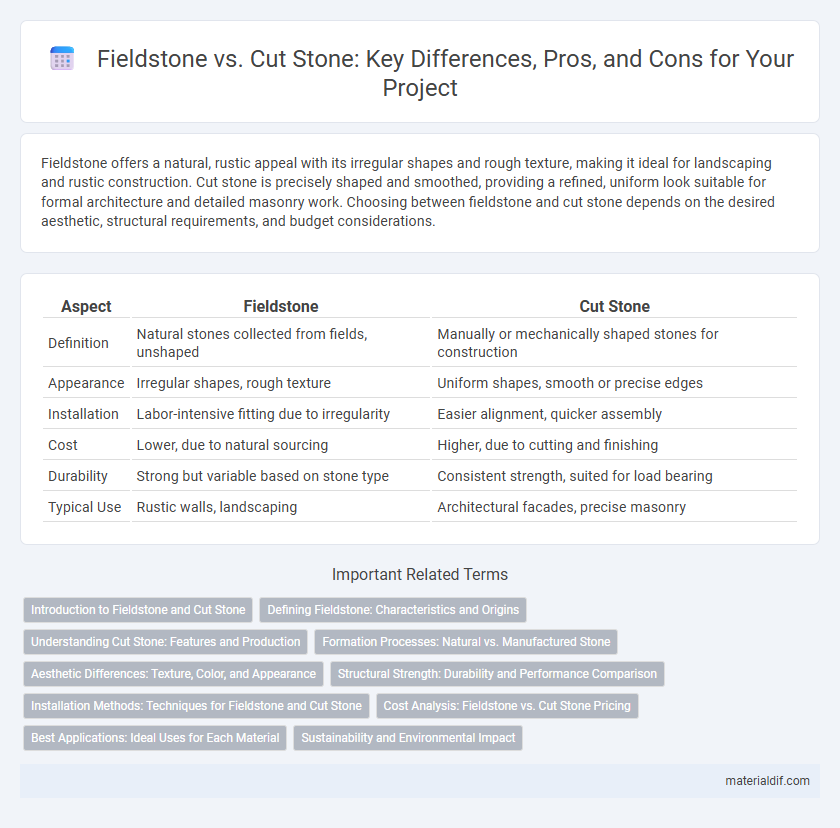
| Aspect | Fieldstone | Cut Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural stones collected from fields, unshaped | Manually or mechanically shaped stones for construction |
| Appearance | Irregular shapes, rough texture | Uniform shapes, smooth or precise edges |
| Installation | Labor-intensive fitting due to irregularity | Easier alignment, quicker assembly |
| Cost | Lower, due to natural sourcing | Higher, due to cutting and finishing |
| Durability | Strong but variable based on stone type | Consistent strength, suited for load bearing |
| Typical Use | Rustic walls, landscaping | Architectural facades, precise masonry |
Introduction to Fieldstone and Cut Stone
Fieldstone consists of naturally occurring, irregularly shaped stones collected from fields, often used in rustic or traditional construction for its organic appearance and texture. Cut stone is quarried and precisely shaped into uniform blocks or slabs, favored for its clean lines and structural consistency in formal architecture. Both materials offer unique aesthetic and functional benefits, with fieldstone emphasizing natural ruggedness and cut stone providing refined craftsmanship.
Defining Fieldstone: Characteristics and Origins
Fieldstone refers to naturally occurring stones collected from the surface of fields, characterized by their irregular shapes, rough textures, and diverse colors influenced by local geological formations. Unlike cut stone, which is quarried and shaped for uniformity, fieldstone retains a rustic, organic appearance that reflects its historical use in traditional construction and landscaping. Originating from glacial deposits or weathered bedrock, fieldstone provides a durable and aesthetically unique material for walls, pathways, and garden features.
Understanding Cut Stone: Features and Production
Cut stone is characterized by its precisely shaped and smooth surfaces, achieved through systematic cutting and dressing processes that enhance structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Produced by skilled masons using advanced tools such as diamond-tipped saws and chisels, cut stone often features uniform dimensions, making it ideal for architectural elements like facades, columns, and flooring. Unlike irregular fieldstone, cut stone allows for tighter joints and more refined construction, contributing to both durability and visual elegance in masonry projects.
Formation Processes: Natural vs. Manufactured Stone
Fieldstone forms naturally through geological processes like weathering and erosion, resulting in irregular shapes and textures commonly found on the surface of fields. Cut stone, however, is manufactured by quarrying raw stone and precisely shaping it with machinery for consistent size and smooth finishes. The distinction in formation impacts durability, appearance, and suitability for construction applications, with fieldstone offering rustic aesthetics and cut stone providing uniformity and structural reliability.
Aesthetic Differences: Texture, Color, and Appearance
Fieldstone presents a natural, rustic appearance with irregular shapes and varied textures, often showcasing earthy tones like browns, grays, and rusts. Cut stone offers a more refined and uniform look due to precise shaping and smoothing, with consistent colors that can range from stark whites to deep blacks depending on the type of stone. These aesthetic differences influence architectural styles, with fieldstone lending a rugged, organic feel while cut stone suits formal, polished designs.
Structural Strength: Durability and Performance Comparison
Fieldstone typically offers a rugged, natural aesthetic but varies in density and shape, which can affect its structural strength and durability in load-bearing applications. Cut stone is precisely shaped and uniformly dense, providing superior performance in stability and long-term resistance to weathering and mechanical stress. Engineers often prefer cut stone for construction projects requiring consistent strength and enhanced durability.
Installation Methods: Techniques for Fieldstone and Cut Stone
Fieldstone installation involves stacking irregularly shaped stones with mortar or dry-laid techniques, emphasizing natural contours and requiring skill to fit varied shapes securely. Cut stone installation uses precisely shaped blocks, often installed in uniform courses with mortar or mechanical fasteners, resulting in a polished, consistent appearance. Proper foundation preparation and precise alignment are essential in both methods to ensure structural stability and aesthetic durability.
Cost Analysis: Fieldstone vs. Cut Stone Pricing
Fieldstone generally costs less than cut stone due to its irregular shapes and minimal processing requirements, making it a budget-friendly option for natural stone projects. Cut stone involves precise shaping and finishing, resulting in higher labor and production costs that increase the overall price. Project budgets considering stone selection should weigh the cost-benefit of fieldstone's rustic aesthetic against cut stone's uniformity and durability.
Best Applications: Ideal Uses for Each Material
Fieldstone, naturally sourced and irregular in shape, excels in rustic landscaping projects, garden walls, and outdoor fireplaces where a natural, rugged aesthetic is desired. Cut stone, precisely shaped and finished, offers superior structural integrity and uniformity, making it ideal for architectural facades, formal building facades, and high-end interior designs. Choosing between fieldstone and cut stone depends largely on desired visual appeal, structural requirements, and budget constraints.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Fieldstone, naturally sourced and minimally processed, offers superior sustainability due to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions compared to cut stone, which requires intensive quarrying and shaping. The use of fieldstone supports local ecosystems by minimizing landscape disruption and preserving natural stone formations, whereas cut stone manufacturing generates significant waste and environmental strain. Choosing fieldstone aligns with eco-friendly building practices, promoting long-term environmental stewardship and resource efficiency.
Fieldstone vs Cut Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com