Cast stone offers a versatile and cost-effective alternative to cut stone, replicating the appearance of natural stone with greater uniformity and ease of installation. Cut stone provides unmatched durability and authentic texture, making it ideal for projects requiring long-lasting structural integrity and a genuine stone aesthetic. Choosing between cast stone and cut stone depends on budget constraints, design preferences, and project requirements for strength and authenticity.
Table of Comparison
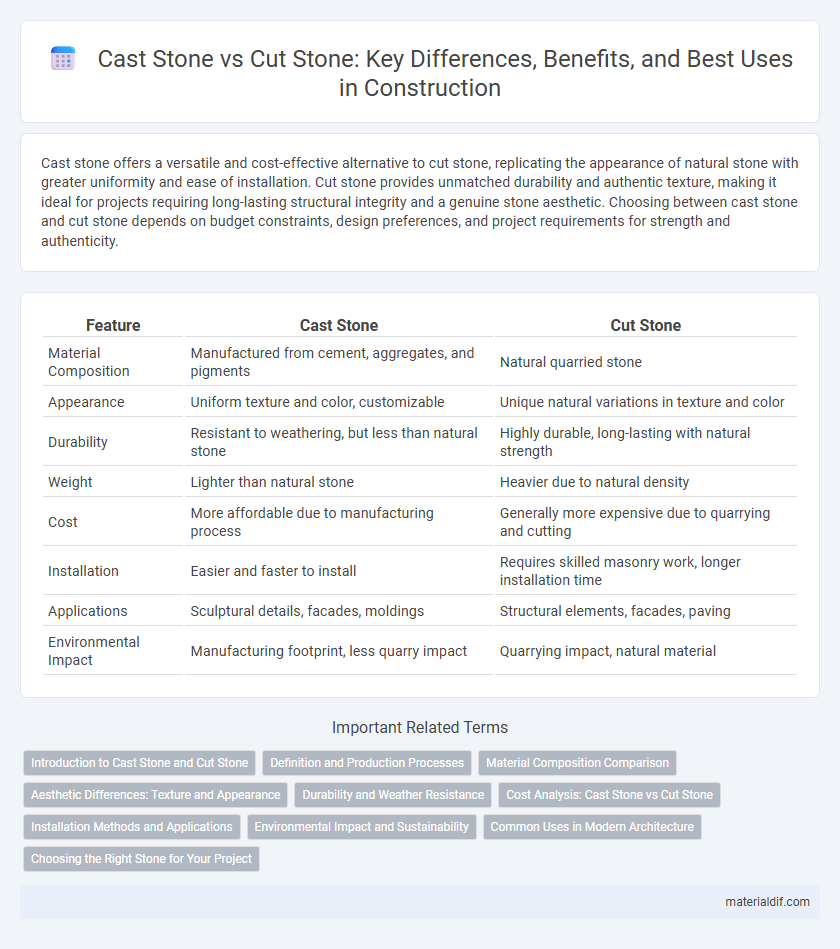
| Feature | Cast Stone | Cut Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Manufactured from cement, aggregates, and pigments | Natural quarried stone |
| Appearance | Uniform texture and color, customizable | Unique natural variations in texture and color |
| Durability | Resistant to weathering, but less than natural stone | Highly durable, long-lasting with natural strength |
| Weight | Lighter than natural stone | Heavier due to natural density |
| Cost | More affordable due to manufacturing process | Generally more expensive due to quarrying and cutting |
| Installation | Easier and faster to install | Requires skilled masonry work, longer installation time |
| Applications | Sculptural details, facades, moldings | Structural elements, facades, paving |
| Environmental Impact | Manufacturing footprint, less quarry impact | Quarrying impact, natural material |
Introduction to Cast Stone and Cut Stone
Cast stone is a manufactured architectural precast concrete product designed to simulate natural cut stone, offering uniformity in color and texture while allowing for intricate shapes and details. Cut stone, quarried and shaped from natural rock, provides unique, authentic patterns with high durability and a traditional aesthetic favored for heritage and restoration projects. Both materials serve distinct structural and decorative purposes in construction, with cast stone offering cost-effective versatility and cut stone delivering timeless natural beauty.
Definition and Production Processes
Cast stone is a manufactured masonry product made from cement, aggregates, and pigments, designed to simulate natural cut stone's appearance and texture. Its production involves casting a slurry mixture into molds and allowing it to cure, enabling consistent shapes and intricate details. Cut stone, by contrast, is quarried natural stone that is mechanically cut or chiseled into specific sizes and shapes, preserving the stone's inherent properties and natural variance.
Material Composition Comparison
Cast stone is a composite material made primarily from cement, aggregates, and mineral pigments, engineered to replicate natural stone's appearance and texture. Cut stone, on the other hand, consists of solid natural stone blocks quarried directly from geological formations, such as granite, limestone, or sandstone, retaining inherent mineralogical properties and structural integrity. The synthetic composition of cast stone allows for greater uniformity and versatility, whereas cut stone maintains authentic natural variations and durability linked to its geological origin.
Aesthetic Differences: Texture and Appearance
Cast stone offers a uniform texture with consistent color tones due to its manufacturing process, creating smooth and refined surfaces ideal for modern architectural designs. In contrast, cut stone reveals natural variations in grain, color, and texture that provide a unique, organic appearance valued in traditional and rustic aesthetics. These distinct aesthetic qualities influence the choice between cast stone's controlled finish and cut stone's authentic, rugged character in construction projects.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Cast stone, made from refined aggregates and cement, offers superior durability and consistent weather resistance due to its engineered composition, making it less prone to chipping and erosion over time. Cut stone, naturally quarried and shaped, provides excellent strength but can vary in weather resistance depending on the stone type and porosity, often requiring additional sealing to prevent water damage and freeze-thaw deterioration. Both materials withstand environmental challenges well, but cast stone's controlled manufacturing process ensures more uniform performance in harsh climates.
Cost Analysis: Cast Stone vs Cut Stone
Cast stone typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to cut stone due to lower material and labor expenses, as it is manufactured using concrete molds rather than quarried and hand-carved natural stone. The production of cast stone allows for consistent shapes and quicker installation, reducing overall project timelines and labor costs. Cut stone, while providing unparalleled natural aesthetics and durability, often incurs higher costs related to extraction, precision cutting, and skilled masonry work.
Installation Methods and Applications
Cast stone offers versatile installation options due to its lightweight composition and uniformity, enabling easier handling and faster assembly compared to cut stone. Cut stone, known for its natural durability and unique texture, requires skilled labor and precise fitting, making it ideal for high-end architectural projects and structural applications. Cast stone suits decorative facades and ornamental elements, while cut stone excels in load-bearing walls and historical restorations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cast stone offers a more sustainable alternative to cut stone by utilizing industrial byproducts and reducing quarrying activities, which minimizes habitat disruption and resource depletion. Its manufacturing process generally consumes less energy and produces lower carbon emissions compared to the extensive extraction and shaping required for natural cut stone. Recycled materials and controlled fabrication in cast stone contribute to waste reduction, supporting environmentally friendly construction practices.
Common Uses in Modern Architecture
Cast stone is widely used in modern architecture for decorative elements such as facades, window trims, and garden features due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Cut stone finds common applications in load-bearing structures, flooring, and cladding, providing natural durability and an authentic appearance. Both materials complement contemporary architectural designs by balancing aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Choosing the Right Stone for Your Project
Cast stone offers versatility and consistent quality, making it ideal for intricate designs and cost-effective construction projects. Cut stone provides natural durability and authentic texture, preferred for historic restorations and high-end architectural features. Evaluate project requirements, budget, and aesthetic goals to select the most appropriate option for lasting results.
Cast Stone vs Cut Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com