Engineered stone offers a durable, non-porous surface composed of crushed quartz and resin, making it resistant to stains and scratches, ideal for countertops. Cultured stone, made from natural aggregates and cement, provides a lightweight, versatile option for architectural accents and veneers with a natural stone appearance. Both materials combine aesthetic appeal with functional benefits, but engineered stone typically excels in durability and low maintenance.
Table of Comparison
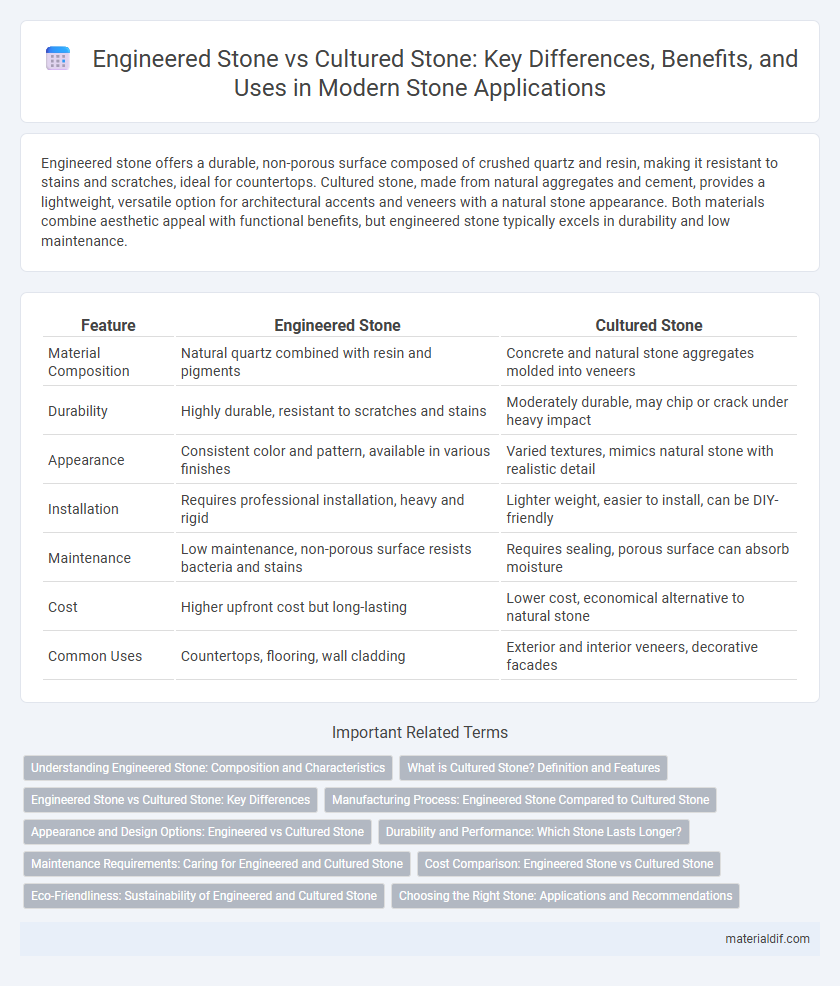
| Feature | Engineered Stone | Cultured Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural quartz combined with resin and pigments | Concrete and natural stone aggregates molded into veneers |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches and stains | Moderately durable, may chip or crack under heavy impact |
| Appearance | Consistent color and pattern, available in various finishes | Varied textures, mimics natural stone with realistic detail |
| Installation | Requires professional installation, heavy and rigid | Lighter weight, easier to install, can be DIY-friendly |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, non-porous surface resists bacteria and stains | Requires sealing, porous surface can absorb moisture |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost but long-lasting | Lower cost, economical alternative to natural stone |
| Common Uses | Countertops, flooring, wall cladding | Exterior and interior veneers, decorative facades |
Understanding Engineered Stone: Composition and Characteristics
Engineered stone is composed of crushed natural quartz combined with resin and pigments, creating a non-porous and highly durable surface resistant to stains and scratches. Its uniform appearance and consistent coloration make it ideal for modern countertops and flooring applications, offering superior strength compared to natural stone. Unlike cultured stone, which is typically a cement-based veneer replicating natural stone, engineered stone integrates resin as a binding agent, enhancing its structural integrity and ease of maintenance.
What is Cultured Stone? Definition and Features
Cultured stone, also known as manufactured stone veneer, is a lightweight building material made from a blend of natural aggregates, cement, and iron oxides, designed to replicate the appearance of natural stone. Its features include easy installation, durability, and a wide range of colors and textures, making it popular for exterior and interior cladding. Unlike engineered stone, cultured stone is primarily used for decorative facades rather than structural applications.
Engineered Stone vs Cultured Stone: Key Differences
Engineered stone is composed primarily of natural quartz mixed with resins and pigments, offering high durability, non-porous surface, and consistent coloration, ideal for countertops and flooring. Cultured stone, crafted from a blend of crushed natural stone, cement, and pigments, mimics the appearance of natural stone but is more porous and less durable than engineered stone. Key differences include the manufacturing process, material composition, and performance characteristics such as resistance to stains, scratches, and maintenance requirements.
Manufacturing Process: Engineered Stone Compared to Cultured Stone
Engineered stone is manufactured by combining crushed natural stone with resin and pigments, then cured under high pressure and temperature to create a dense, durable surface. Cultured stone is produced using a mix of cement, aggregates, and iron oxides molded into shapes that imitate natural stone, then cured to harden the material. The engineered process results in a more consistent and non-porous material, while cultured stone offers lighter weight and versatility for decorative applications.
Appearance and Design Options: Engineered vs Cultured Stone
Engineered stone offers a consistent appearance with a wide range of colors and patterns, achieved through advanced manufacturing techniques that allow for uniformity and customization. Cultured stone provides natural-looking textures and irregularities, mimicking real stone with variations in color and shape that enhance rustic or traditional designs. While engineered stone suits modern, sleek aesthetics with precise finishes, cultured stone excels in creating organic, authentic looks for exterior facades and landscaping.
Durability and Performance: Which Stone Lasts Longer?
Engineered stone, composed of natural quartz and resin, offers superior durability with high resistance to scratches, stains, and impact, making it ideal for heavily used surfaces. Cultured stone, a composite of natural stone fragments and cement or resin, generally has lower durability and may be more susceptible to chipping and weathering over time. In terms of longevity and performance, engineered stone typically outperforms cultured stone due to its dense, non-porous structure and enhanced strength.
Maintenance Requirements: Caring for Engineered and Cultured Stone
Engineered stone requires low maintenance with non-porous surfaces that resist stains and do not need sealing, making cleaning simple with mild soap and water. Cultured stone, being porous, demands regular sealing to prevent moisture penetration and staining, along with gentle cleaning to avoid surface damage. Proper care for both materials ensures durability and preserves their aesthetic appearance over time.
Cost Comparison: Engineered Stone vs Cultured Stone
Engineered stone typically costs between $50 and $100 per square foot, offering durability and low maintenance at a higher price point than cultured stone, which ranges from $30 to $60 per square foot. Cultured stone, made from lightweight concrete and resins, provides a more affordable decorative option but often requires more upkeep and has less durability compared to engineered stone's quartz composition. Budget-conscious projects favor cultured stone for cost savings, while engineered stone suits long-term investments demanding strength and resistance.
Eco-Friendliness: Sustainability of Engineered and Cultured Stone
Engineered stone typically boasts higher eco-friendliness by utilizing recycled materials and reducing quarrying impacts, aligning with sustainable construction goals. Cultured stone, often made from concrete and natural aggregates, may involve higher energy consumption during production and less recycling potential. Choosing engineered stone supports sustainability through resource efficiency and lower environmental footprints in building projects.
Choosing the Right Stone: Applications and Recommendations
Engineered stone, composed primarily of quartz and resin, offers superior durability and stain resistance, making it ideal for kitchen countertops and high-traffic areas requiring minimal maintenance. Cultured stone, a blend of natural stone and concrete, provides a versatile and cost-effective option suitable for decorative facades, fireplaces, and landscaping features due to its lightweight and customizable appearance. Selecting the right stone depends on the specific application, desired aesthetics, and performance requirements, with engineered stone favored for surfaces exposed to heavy use and cultured stone preferred for architectural accents and exterior enhancements.
Engineered Stone vs Cultured Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com