Porcelain stoneware offers high durability and water resistance, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications with a smooth, polished finish. Sintered stone surpasses porcelain by providing enhanced resistance to heat, scratches, and stains due to its manufacturing process involving extreme pressure and temperature. Both materials excel in longevity and aesthetic appeal, but sintered stone is preferred for environments requiring superior performance and minimal maintenance.
Table of Comparison
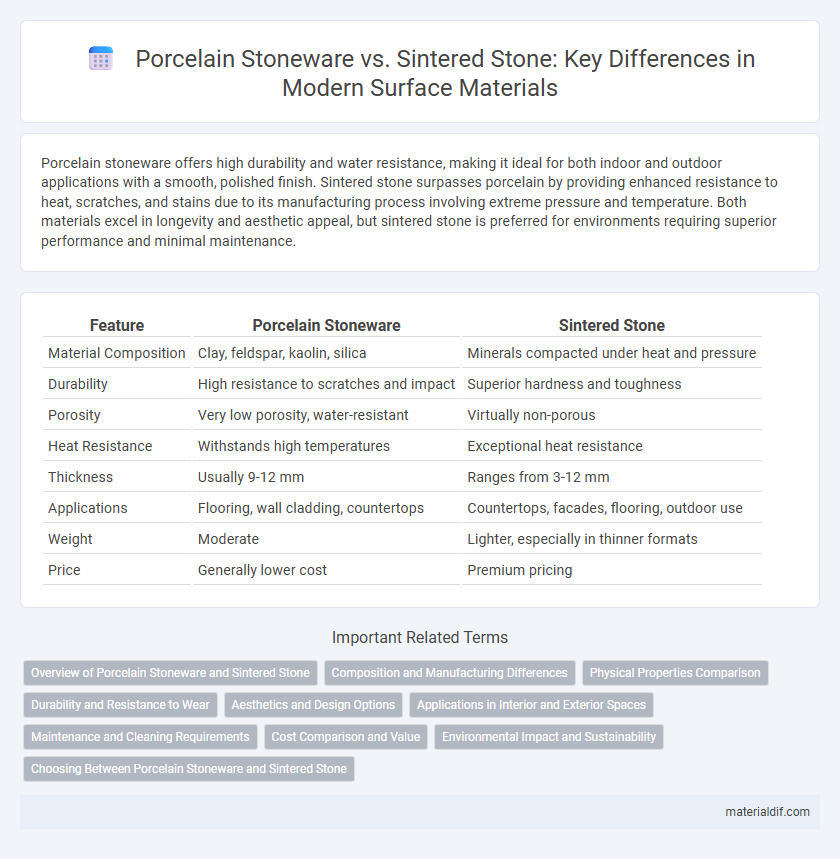
| Feature | Porcelain Stoneware | Sintered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay, feldspar, kaolin, silica | Minerals compacted under heat and pressure |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and impact | Superior hardness and toughness |
| Porosity | Very low porosity, water-resistant | Virtually non-porous |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures | Exceptional heat resistance |
| Thickness | Usually 9-12 mm | Ranges from 3-12 mm |
| Applications | Flooring, wall cladding, countertops | Countertops, facades, flooring, outdoor use |
| Weight | Moderate | Lighter, especially in thinner formats |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Premium pricing |
Overview of Porcelain Stoneware and Sintered Stone
Porcelain stoneware is a dense, durable ceramic material fired at high temperatures, known for its low porosity and resistance to stains, scratches, and thermal shock, making it ideal for flooring and wall cladding. Sintered stone, produced through a high-pressure and high-temperature process, combines natural minerals and raw materials to create a non-porous, highly resistant surface with exceptional tensile strength and minimal maintenance requirements. Both materials offer superior durability and aesthetic versatility, with porcelain stoneware excelling in ceramic applications and sintered stone favored for its engineered stone-like performance in outdoor and heavy-use environments.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Porcelain stoneware is composed primarily of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, fired at high temperatures around 1200-1400degC, creating a dense, vitrified, and water-resistant surface. In contrast, sintered stone combines natural minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and various oxides, sintered under extreme heat and pressure, resulting in superior mechanical strength and minimal porosity. Manufacturing porcelain stoneware relies on traditional ceramic firing techniques, while sintered stone uses an advanced dry pressing and sintering process, enhancing its durability and resistance to chemicals and thermal shock.
Physical Properties Comparison
Porcelain stoneware exhibits high density and low porosity, resulting in excellent water absorption rates below 0.5%, which enhances its resistance to frost and stains. Sintered stone, engineered through advanced sintering processes, features superior hardness and mechanical strength with a Mohs hardness exceeding 7, surpassing traditional porcelain stoneware. Both materials offer impressive thermal resistance, but sintered stone demonstrates enhanced scratch and impact resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Durability and Resistance to Wear
Porcelain stoneware exhibits high durability with a dense, non-porous surface resistant to scratches, stains, and moisture, making it ideal for heavy foot traffic areas. Sintered stone offers superior resistance to wear due to its advanced manufacturing process, resulting in enhanced hardness and resistance to chemicals and UV rays. Both materials provide excellent long-term performance, but sintered stone typically outperforms porcelain stoneware in extreme conditions requiring exceptional toughness.
Aesthetics and Design Options
Porcelain stoneware offers a wide variety of colors, patterns, and finishes that mimic natural stone, providing versatile aesthetic options for both contemporary and traditional designs. Sintered stone features a more uniform, consistent surface with enhanced color stability and richer textures, ideal for large-format applications requiring seamless visual continuity. Both materials deliver excellent design flexibility, but sintered stone excels in customization and durability for high-end architectural projects.
Applications in Interior and Exterior Spaces
Porcelain stoneware excels in interior applications such as kitchen countertops, bathroom floors, and wall cladding due to its low porosity, high durability, and resistance to stains and scratches. Sintered stone, with its superior resistance to UV rays, thermal shock, and chemical exposure, is ideal for exterior spaces including facades, outdoor flooring, and landscaping elements. Both materials offer versatile design options, but sintered stone's enhanced weather resistance makes it preferable for demanding outdoor conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Porcelain stoneware offers low maintenance with high resistance to stains, scratches, and moisture, requiring only regular cleaning with mild detergents and water. Sintered stone features a non-porous, highly durable surface that resists chemical agents and UV rays, making it easy to clean with neutral pH cleaners without the need for sealing or special treatments. Both materials provide excellent hygiene and longevity, but sintered stone generally demands less frequent upkeep due to its superior resistance to surface damage and staining.
Cost Comparison and Value
Porcelain stoneware typically offers a lower initial cost compared to sintered stone, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale projects. Sintered stone, while more expensive upfront due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior durability, provides better long-term value by resisting stains, scratches, and heat with minimal maintenance. The choice between the two depends on balancing initial investment against longevity and performance in specific applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Porcelain stoneware is often favored for its lower environmental impact due to the use of natural clay and minerals, and energy-efficient firing processes that reduce CO2 emissions. Sintered stone, while durable and resistant, typically requires higher energy inputs and synthetic additives, leading to a larger carbon footprint and resource consumption. Sustainable architecture increasingly prioritizes porcelain stoneware for eco-friendly flooring and cladding solutions due to its recyclability and minimal environmental degradation.
Choosing Between Porcelain Stoneware and Sintered Stone
Porcelain stoneware offers high durability, water resistance, and a wide range of design options, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Sintered stone excels in extreme resistance to heat, scratches, and UV rays, providing superior performance in high-traffic commercial spaces or harsh environments. Selecting between porcelain stoneware and sintered stone depends on specific project requirements, balancing aesthetic preferences with durability and functional demands.
Porcelain Stoneware vs Sintered Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com