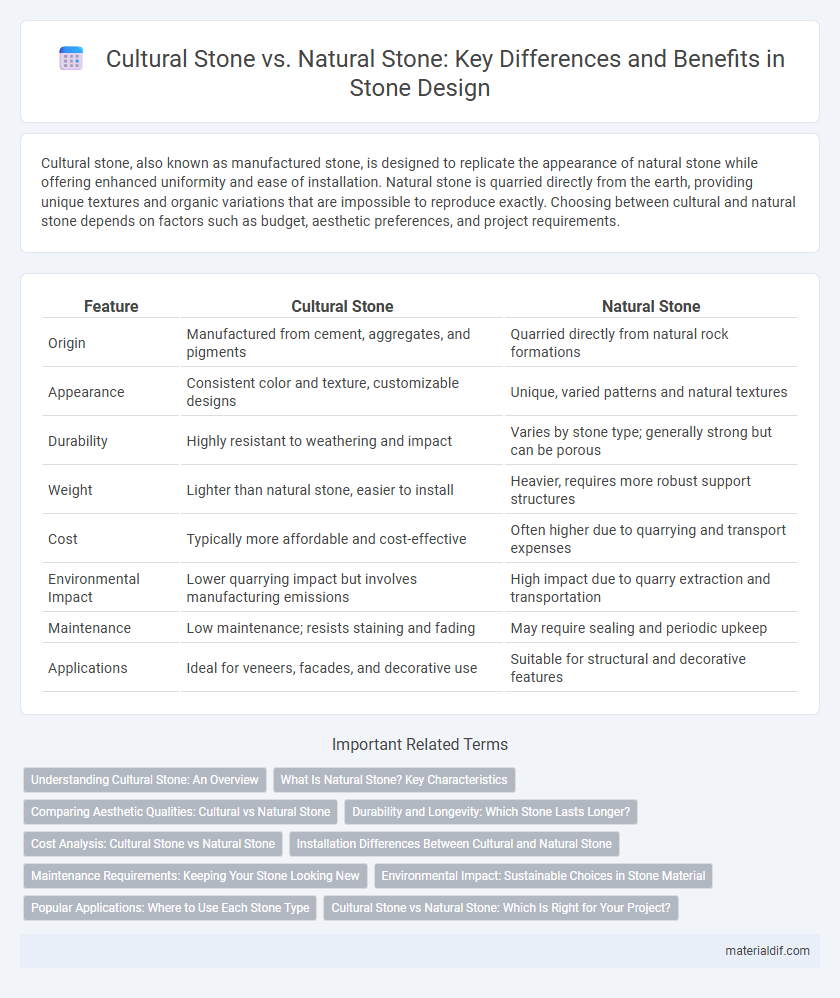
Cultural stone, also known as manufactured stone, is designed to replicate the appearance of natural stone while offering enhanced uniformity and ease of installation. Natural stone is quarried directly from the earth, providing unique textures and organic variations that are impossible to reproduce exactly. Choosing between cultural and natural stone depends on factors such as budget, aesthetic preferences, and project requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cultural Stone | Natural Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Manufactured from cement, aggregates, and pigments | Quarried directly from natural rock formations |
| Appearance | Consistent color and texture, customizable designs | Unique, varied patterns and natural textures |
| Durability | Highly resistant to weathering and impact | Varies by stone type; generally strong but can be porous |
| Weight | Lighter than natural stone, easier to install | Heavier, requires more robust support structures |
| Cost | Typically more affordable and cost-effective | Often higher due to quarrying and transport expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Lower quarrying impact but involves manufacturing emissions | High impact due to quarry extraction and transportation |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resists staining and fading | May require sealing and periodic upkeep |
| Applications | Ideal for veneers, facades, and decorative use | Suitable for structural and decorative features |
Understanding Cultural Stone: An Overview
Cultural stone, often known as manufactured or synthetic stone, is engineered from concrete and natural aggregates to replicate the appearance and texture of natural stone while offering greater uniformity and customization. It provides advantages in cost, installation ease, and consistent quality compared to natural stone, which is quarried directly from the earth and varies in composition, color, and durability. Understanding cultural stone involves recognizing its versatility in architectural and landscaping applications, where it serves as an affordable, lightweight, and sustainable alternative to traditional natural stone materials.
What Is Natural Stone? Key Characteristics
Natural stone refers to materials extracted directly from the earth, including granite, marble, limestone, and slate, valued for their unique textures, colors, and durability. Key characteristics include its geological origin, organic formation processes, and inherent variations in pattern and composition that cannot be replicated artificially. Its use in construction and design emphasizes authenticity, environmental sustainability, and long-lasting structural integrity.
Comparing Aesthetic Qualities: Cultural vs Natural Stone
Cultural stone offers highly customizable aesthetic qualities, including uniform colors, shapes, and textures that can be tailored to specific design needs, while natural stone displays unique, organic patterns and variations that enhance its authentic appearance. Natural stone's rich textures and color variations create a distinct visual appeal rooted in geological history, providing an unmatched natural beauty that cannot be replicated. The choice between cultural and natural stone hinges on whether consistency and controlled design or organic uniqueness and natural imperfections are preferred for the project.
Durability and Longevity: Which Stone Lasts Longer?
Natural stone, formed through geological processes over millions of years, typically exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to cultural stone, which is manufactured from a mixture of cement, aggregates, and pigments. The high-density composition of natural stone, such as granite or marble, provides enhanced resistance to weathering, wear, and erosion, making it ideal for long-term applications in construction and landscaping. Cultural stone may offer aesthetic flexibility but generally lacks the same lifespan and structural integrity as natural stone, often requiring more frequent maintenance or replacement.
Cost Analysis: Cultural Stone vs Natural Stone
Cultural stone generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to natural stone due to lower extraction and transportation expenses. Natural stone involves higher costs linked to quarrying, cutting, and irregular supply, which can increase overall project budgets. Budget planners often prefer cultural stone for its affordability and consistent availability without compromising aesthetic appeal.
Installation Differences Between Cultural and Natural Stone
Cultural stone, often manufactured from concrete and pigments, offers uniform shape and size, simplifying installation with interlocking designs and requiring less skilled labor compared to natural stone. Natural stone installation demands meticulous selection, cutting, and fitting due to its irregular shapes and varying thickness, making the process labor-intensive and time-consuming. Adhesives and mortar choices differ as cultural stone frequently uses lightweight substrates, whereas natural stone requires robust support to handle its heavier weight and natural texture.
Maintenance Requirements: Keeping Your Stone Looking New
Cultural stone, often manufactured from concrete or other composites, requires regular sealing to prevent moisture absorption and staining, making maintenance essential for preserving its appearance. Natural stone, such as granite or marble, demands routine cleaning with pH-neutral products and periodic sealing to protect against weathering and surface damage, ensuring longevity. Both types benefit from prompt stain removal and gentle care to maintain their original look and durability over time.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Choices in Stone Material
Cultural stone often involves synthetic production processes, which can result in higher carbon emissions and energy consumption compared to natural stone, quarried directly from the earth. Natural stone, sourced sustainably through responsible quarrying and minimal processing, generally offers a lower environmental impact, supporting biodiversity and reducing waste. Choosing sustainable natural stone enhances eco-friendly construction practices by conserving resources and minimizing ecological disruption.
Popular Applications: Where to Use Each Stone Type
Cultural stone, crafted for aesthetic consistency and ease of installation, is popular for interior wall cladding, fireplaces, and landscaping features where uniform appearance and precise shapes are desired. Natural stone, valued for its durability and unique textures, is typically used in exterior facades, paving, monuments, and retaining walls that benefit from its strength and weather resistance. Both materials complement garden pathways, pool surrounds, and decorative elements, with cultural stone favored for design flexibility and natural stone for rugged, long-lasting appeal.
Cultural Stone vs Natural Stone: Which Is Right for Your Project?
Cultural stone, often known as manufactured or cultured stone, replicates the appearance of natural stone using concrete mixtures and pigments, offering greater uniformity and design flexibility. Natural stone, including granite, marble, and limestone, provides unique textures and authenticity derived from geological processes, ensuring durability and a timeless aesthetic. Choosing between cultural stone and natural stone depends on factors such as budget, project scale, installation ease, and the desired visual appeal.
Cultural Stone vs Natural Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com