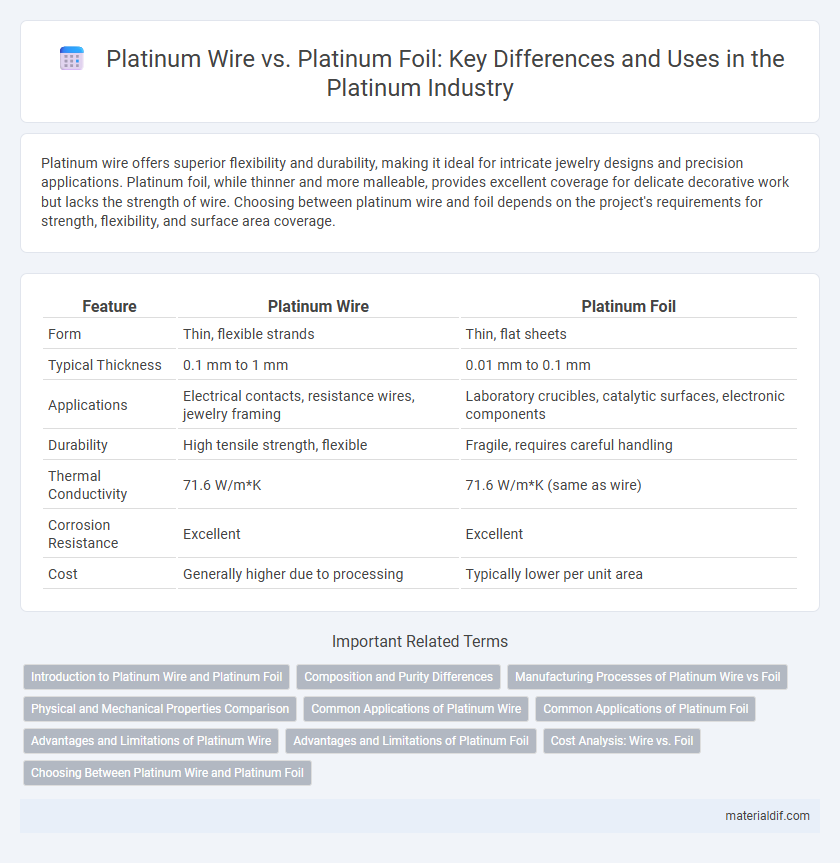
Platinum wire offers superior flexibility and durability, making it ideal for intricate jewelry designs and precision applications. Platinum foil, while thinner and more malleable, provides excellent coverage for delicate decorative work but lacks the strength of wire. Choosing between platinum wire and foil depends on the project's requirements for strength, flexibility, and surface area coverage.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Platinum Wire | Platinum Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, flexible strands | Thin, flat sheets |
| Typical Thickness | 0.1 mm to 1 mm | 0.01 mm to 0.1 mm |
| Applications | Electrical contacts, resistance wires, jewelry framing | Laboratory crucibles, catalytic surfaces, electronic components |
| Durability | High tensile strength, flexible | Fragile, requires careful handling |
| Thermal Conductivity | 71.6 W/m*K | 71.6 W/m*K (same as wire) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | Generally higher due to processing | Typically lower per unit area |
Introduction to Platinum Wire and Platinum Foil
Platinum wire, known for its high melting point and exceptional corrosion resistance, is widely used in electrical contacts, thermocouples, and laboratory equipment due to its flexibility and durability. Platinum foil, characterized by its thin, malleable nature, serves crucial roles in catalytic converters, chemical reactions, and fine art applications where its purity and surface area optimize performance. Both materials leverage platinum's unique chemical stability and conductivity but differ primarily in form and specific industrial uses.
Composition and Purity Differences
Platinum wire typically consists of nearly pure platinum, often 99.95% or higher, ensuring excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for precision applications like electrodes and thermocouples. Platinum foil, while also composed primarily of platinum, may vary slightly in purity and often contains added alloys to enhance flexibility and durability for uses such as catalytic supports and laboratory equipment. The difference in composition and purity between platinum wire and foil directly impacts their mechanical properties and suitability for specific industrial and scientific purposes.
Manufacturing Processes of Platinum Wire vs Foil
Platinum wire is manufactured through a process called drawing, where platinum rods are pulled through progressively smaller dies to achieve thin, flexible strands with high tensile strength. Platinum foil is produced by rolling platinum ingots into thin sheets using heavy rollers, which imparts a uniform thickness and smooth surface ideal for applications requiring flat, flexible material. The manufacturing process of wire emphasizes elongation and strength, while foil production focuses on flatness and malleability for precise dimensional control.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Platinum wire exhibits higher tensile strength and flexibility compared to platinum foil, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and intricate shaping. Platinum foil, characterized by its thinness and malleability, offers superior surface area and ease of layering, suitable for chemical catalysts and electrode coatings. Both forms maintain excellent corrosion resistance and high melting points, but wire typically excels in mechanical resilience while foil prioritizes adaptability and surface uniformity.
Common Applications of Platinum Wire
Platinum wire is widely utilized in high-temperature industrial applications such as thermocouples, electrical contacts, and laboratory equipment due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to oxidation. In contrast, platinum foil is favored for catalytic converters, electrode fabrication, and thin-film applications because of its malleability and surface area. The unique properties of platinum wire make it indispensable in precision instruments and environments requiring sustained durability under extreme conditions.
Common Applications of Platinum Foil
Platinum foil is commonly used in high-temperature applications such as laboratory crucibles, catalysts in chemical reactions, and electrical contacts due to its excellent thermal stability and resistance to corrosion. Unlike platinum wire, which is often employed in jewelry and electrodes, platinum foil provides a larger surface area ideal for catalytic converters and thin-film coatings. Its flexibility and malleability make it suitable for precise industrial and scientific uses where uniform thickness and high conductivity are essential.
Advantages and Limitations of Platinum Wire
Platinum wire offers superior flexibility and durability compared to platinum foil, making it ideal for precise applications such as electrical contacts and high-temperature resistance environments. Its advantages include excellent tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, enhancing longevity in industrial and laboratory settings. Limitations of platinum wire include higher cost and difficulty in achieving large surface areas compared to foil, which can restrict its use in applications requiring extensive coverage.
Advantages and Limitations of Platinum Foil
Platinum foil offers superior flexibility and ease of shaping compared to platinum wire, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate designs such as fine jewelry and electronic contacts. Its thin, flat structure allows for better surface area coverage and heat distribution, enhancing performance in catalytic converters and laboratory equipment. However, platinum foil is more prone to tearing and deformation under mechanical stress, limiting its use in high-tensile strength applications where the durability of platinum wire is preferred.
Cost Analysis: Wire vs. Foil
Platinum wire typically costs more per gram than platinum foil due to its higher manufacturing complexity and tensile strength requirements. Foil, being thinner and easier to produce, offers a more cost-effective option for applications requiring less mechanical durability. When evaluating overall expenses, consider that platinum wire provides greater longevity and resistance to deformation, potentially reducing replacement frequency despite a higher initial investment.
Choosing Between Platinum Wire and Platinum Foil
Choosing between platinum wire and platinum foil depends on the specific application and desired properties. Platinum wire offers excellent tensile strength and flexibility, ideal for fine jewelry and delicate electronic components, while platinum foil provides superior surface area and malleability, making it suitable for catalytic converters and laboratory use. Consider the mechanical strength requirements and surface exposure when selecting the appropriate platinum form.
Platinum Wire vs Platinum Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com