Linen, made from flax fibers, offers exceptional breathability and durability, making it ideal for warm climates, while Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood, is renowned for its softness and moisture-wicking properties. Linen's natural texture and wrinkles provide a casual, organic aesthetic, whereas Tencel boasts a smooth, silky finish that feels gentle against the skin. Both fabrics are eco-friendly options, but Tencel requires less water and energy during production, enhancing its sustainable appeal.
Table of Comparison
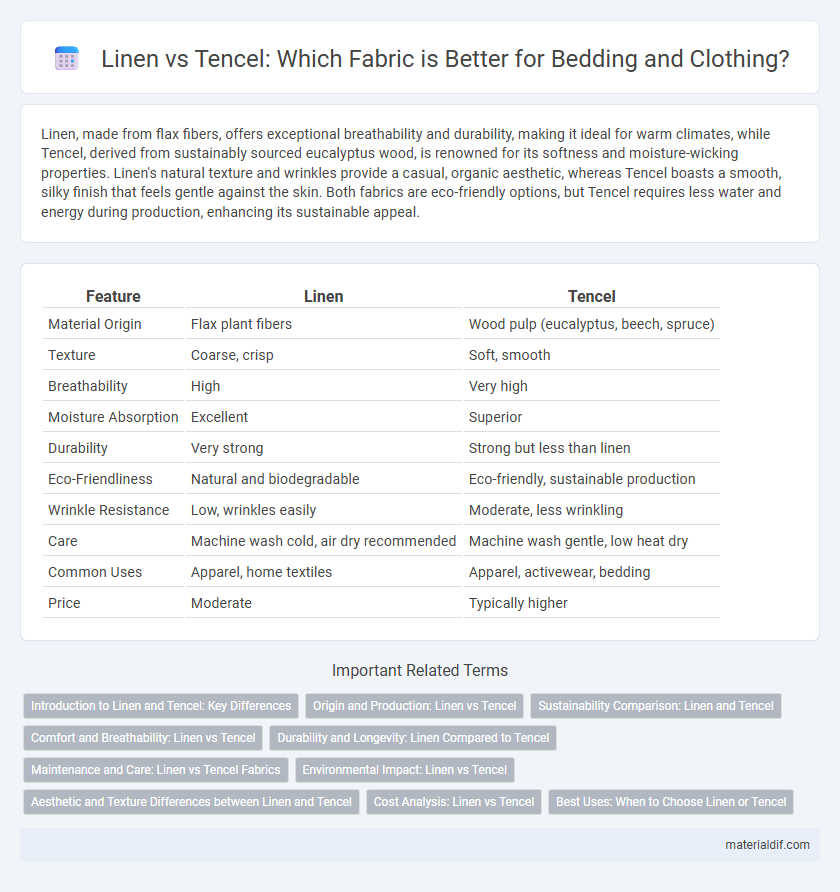
| Feature | Linen | Tencel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Flax plant fibers | Wood pulp (eucalyptus, beech, spruce) |
| Texture | Coarse, crisp | Soft, smooth |
| Breathability | High | Very high |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent | Superior |
| Durability | Very strong | Strong but less than linen |
| Eco-Friendliness | Natural and biodegradable | Eco-friendly, sustainable production |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Low, wrinkles easily | Moderate, less wrinkling |
| Care | Machine wash cold, air dry recommended | Machine wash gentle, low heat dry |
| Common Uses | Apparel, home textiles | Apparel, activewear, bedding |
| Price | Moderate | Typically higher |
Introduction to Linen and Tencel: Key Differences
Linen, made from flax fibers, is renowned for its breathability, durability, and natural texture, making it ideal for warm climates and sustainable fashion. Tencel, a branded fabric derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp through a closed-loop process, offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking abilities, and wrinkle resistance. Key differences include linen's coarser, textured feel versus Tencel's smooth, silky touch, as well as linen's higher breathability compared to Tencel's superior moisture absorption and drape.
Origin and Production: Linen vs Tencel
Linen is derived from flax fibers, harvested from the flax plant cultivated primarily in Europe, using a labor-intensive retting process to separate fibers. Tencel, branded lyocell, is produced from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood pulp through an eco-friendly solvent spinning method utilizing closed-loop technology. The natural origins of linen and Tencel highlight their renewable sources, while production methods distinguish linen's traditional, manual processing from Tencel's modern, chemically advanced manufacturing.
Sustainability Comparison: Linen and Tencel
Linen, derived from flax plants, boasts a low environmental impact due to its minimal water and pesticide requirements, making it highly sustainable. Tencel, produced from sustainably sourced eucalyptus trees through a closed-loop process, emphasizes water efficiency and biodegradability. Both textiles promote eco-friendly practices, with linen excelling in natural cultivation and Tencel advancing innovative, resource-conscious production.
Comfort and Breathability: Linen vs Tencel
Linen offers exceptional breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for hot and humid climates by keeping the skin cool and dry. Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, provides a soft, smooth texture with excellent moisture absorption, enhancing comfort for sensitive skin. Both materials excel in comfort, but linen's porous weave promotes superior airflow, while Tencel's fiber structure offers a silky feel and temperature regulation.
Durability and Longevity: Linen Compared to Tencel
Linen is renowned for its exceptional durability, with fibers that become stronger and softer over time, often lasting for decades without significant wear. Tencel, made from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood pulp, offers a smooth texture and resistance to wrinkles but generally has a shorter lifespan compared to linen. The natural fiber composition of linen provides superior longevity, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting textiles and everyday wear.
Maintenance and Care: Linen vs Tencel Fabrics
Linen offers exceptional durability and improves with each wash but requires careful ironing to maintain its crisp texture and prevent wrinkles. Tencel, made from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is wrinkle-resistant and softer, requiring less frequent ironing and gentle washing to preserve its smooth feel and color vibrancy. Both fabrics benefit from air drying and avoiding harsh detergents to extend lifespan and maintain fabric integrity.
Environmental Impact: Linen vs Tencel
Linen, derived from flax plants, has a lower environmental impact due to minimal water usage and reduced need for pesticides compared to Tencel, which, although produced from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood, requires a chemically intensive closed-loop process. The biodegradability of linen fibers further enhances its eco-friendly profile, while Tencel's manufacturing process emphasizes water and chemical recycling to reduce its ecological footprint. Both fibers represent sustainable textile options, but linen's natural cultivation methods generally result in a smaller overall environmental burden.
Aesthetic and Texture Differences between Linen and Tencel
Linen offers a natural, textured appearance with visible fibers and a slightly rough feel that softens over time, creating a breathable and rustic aesthetic. Tencel, made from sustainably sourced wood pulp, provides a smooth, silky texture with a subtle sheen and drapes more fluidly compared to linen's stiffer structure. The distinct tactile qualities and visual finishes make linen favored for a casual, earthy look, while Tencel suits a polished, modern style with enhanced softness.
Cost Analysis: Linen vs Tencel
Linen typically costs more than Tencel due to its labor-intensive production process and durability. Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers a more affordable price point while maintaining softness and moisture-wicking properties. Cost analysis reveals that while Linen carries a premium for longevity and breathability, Tencel provides budget-friendly performance suitable for eco-conscious consumers.
Best Uses: When to Choose Linen or Tencel
Linen excels in breathability and durability, making it ideal for warm weather clothing, upholstery, and home textiles requiring natural moisture-wicking properties. Tencel, known for its softness and eco-friendly production, suits sensitive skin apparel, activewear, and sustainable fashion seeking a silky texture with excellent moisture management. Choose Linen for robust, breathable fabrics in casual or rustic settings and Tencel for smooth, drapey garments prioritizing comfort and environmental impact.
Linen vs Tencel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com