Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, offers superior softness and a finer texture ideal for lightweight, breathable linen fabrics. Hemp fiber is stronger and more durable, providing enhanced resistance to wear and environmental factors, making it suitable for heavy-duty textiles. Both fibers are sustainable options, but flax remains the preferred choice for traditional linen due to its smooth finish and comfort.
Table of Comparison
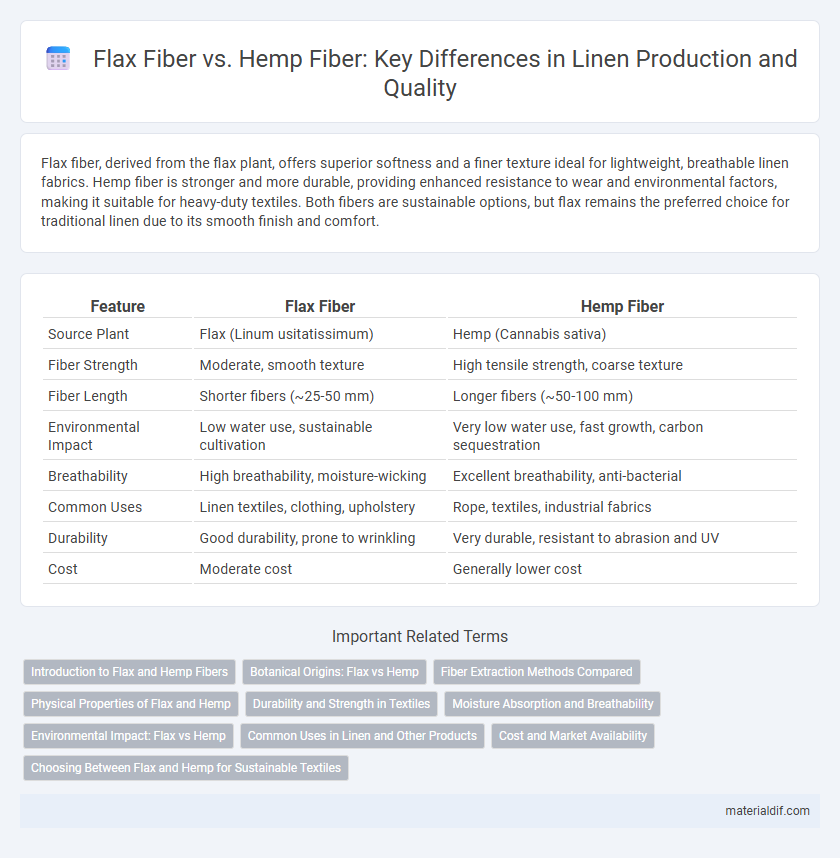
| Feature | Flax Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Flax (Linum usitatissimum) | Hemp (Cannabis sativa) |
| Fiber Strength | Moderate, smooth texture | High tensile strength, coarse texture |
| Fiber Length | Shorter fibers (~25-50 mm) | Longer fibers (~50-100 mm) |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, sustainable cultivation | Very low water use, fast growth, carbon sequestration |
| Breathability | High breathability, moisture-wicking | Excellent breathability, anti-bacterial |
| Common Uses | Linen textiles, clothing, upholstery | Rope, textiles, industrial fabrics |
| Durability | Good durability, prone to wrinkling | Very durable, resistant to abrasion and UV |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Flax and Hemp Fibers
Flax fiber, derived from the stalks of the Linum usitatissimum plant, is renowned for its strength, durability, and natural luster, making it a popular choice in linen production and textiles. Hemp fiber, obtained from the Cannabis sativa plant, offers superior tensile strength, moisture-wicking properties, and antibacterial qualities, positioning it as an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fibers. Both flax and hemp fibers are valued for their sustainability, biodegradability, and versatility in applications ranging from clothing to industrial materials.
Botanical Origins: Flax vs Hemp
Flax fiber originates from the flax plant (Linum usitatissimum), a member of the Linaceae family, renowned for its fine, strong fibers ideal for linen textiles. Hemp fiber comes from the stalks of the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa), belonging to the Cannabaceae family, known for its coarse and durable fibers used in various industrial applications. Both plants are bast fibers harvested from the outer stalk, but flax has a longer history in linen production while hemp is valued for its environmental sustainability and robustness.
Fiber Extraction Methods Compared
Flax fiber extraction involves retting, which relies on microbial decay to separate fibers, followed by scutching and hackling processes to refine the strands. Hemp fiber extraction uses similar retting methods but often employs mechanical decortication to efficiently strip the outer bark and separate fibers, resulting in higher yields and coarser fibers. Both fibers benefit from enzymatic retting techniques that enhance fiber quality and reduce environmental impact compared to traditional water or dew retting.
Physical Properties of Flax and Hemp
Flax fiber exhibits high tensile strength, excellent moisture absorbency, and a smooth texture, making it ideal for lightweight, breathable linen fabrics. Hemp fiber is coarser and thicker, with superior durability, resistance to UV light, and natural antibacterial properties, suitable for heavy-duty, long-lasting textiles. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives, but flax stands out for softness and fine weave, while hemp excels in strength and environmental resilience.
Durability and Strength in Textiles
Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is known for its exceptional strength and durability, making it a preferred choice in high-quality linen textiles. Hemp fiber surpasses flax in tensile strength and resistance to wear, offering enhanced durability for long-lasting fabric applications. Both fibers contribute to sturdy textiles, but hemp's robust structure provides superior resilience in demanding uses.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, exhibits superior moisture absorption properties, effectively wicking sweat and keeping the fabric dry, which enhances comfort in warm climates. Hemp fiber offers excellent breathability due to its porous structure, promoting air circulation and faster drying times, making it ideal for activewear and summer textiles. Both fibers provide natural antimicrobial benefits, but flax's moisture management combined with hemp's ventilation creates optimal conditions for breathable, moisture-regulating fabrics.
Environmental Impact: Flax vs Hemp
Flax fiber production requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to hemp, reducing its environmental footprint. Hemp fiber grows quickly and naturally suppresses weeds, minimizing the need for chemical inputs and enhancing soil health. Both fibers are biodegradable and renewable, but hemp's rapid growth and ability to improve soil carbon sequestration make it a more sustainable option overall.
Common Uses in Linen and Other Products
Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is predominantly used in producing high-quality linen fabric known for its softness, breathability, and durability, making it ideal for clothing, home textiles, and upholstery. Hemp fiber, valued for its strength and resistance to mold, is often utilized in producing textiles for industrial applications, ropes, canvas, and eco-friendly fashion items. Both fibers contribute significantly to sustainable fabric production but differ in texture and common uses, with flax favored in fine linens and hemp in heavy-duty textiles.
Cost and Market Availability
Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, generally commands a higher market price due to its established use in fine linen production and limited large-scale cultivation regions. Hemp fiber, while often more cost-effective because of its faster growth cycle and higher yield per acre, faces variable market availability driven by regulatory restrictions and less developed processing infrastructure. Both fibers compete in textiles, but flax's premium status contrasts with hemp's growing accessibility and competitive pricing in sustainable fabric markets.
Choosing Between Flax and Hemp for Sustainable Textiles
Flax fiber and hemp fiber both offer sustainable options for eco-friendly textiles, with flax providing a softer texture ideal for lightweight, breathable fabrics, while hemp delivers superior durability and resistance to pests without chemicals. Flax cultivation requires less water and fewer pesticides, making it environmentally efficient, whereas hemp's rapid growth and natural pest resistance contribute to higher yields and soil health benefits. Selecting between flax and hemp hinges on the desired fabric properties and sustainability goals, balancing softness, strength, and environmental impact for responsible textile production.
Flax Fiber vs Hemp Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com