Suede leather features a soft, fuzzy texture created from the underside of animal hides, offering a luxurious feel but requiring careful maintenance to prevent stains and water damage. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of the hide, is less durable and more porous than full-grain leather, often coated or embossed to enhance appearance and resilience. Choosing between suede and split leather for pet products depends on balancing aesthetic preferences with durability and ease of cleaning.
Table of Comparison
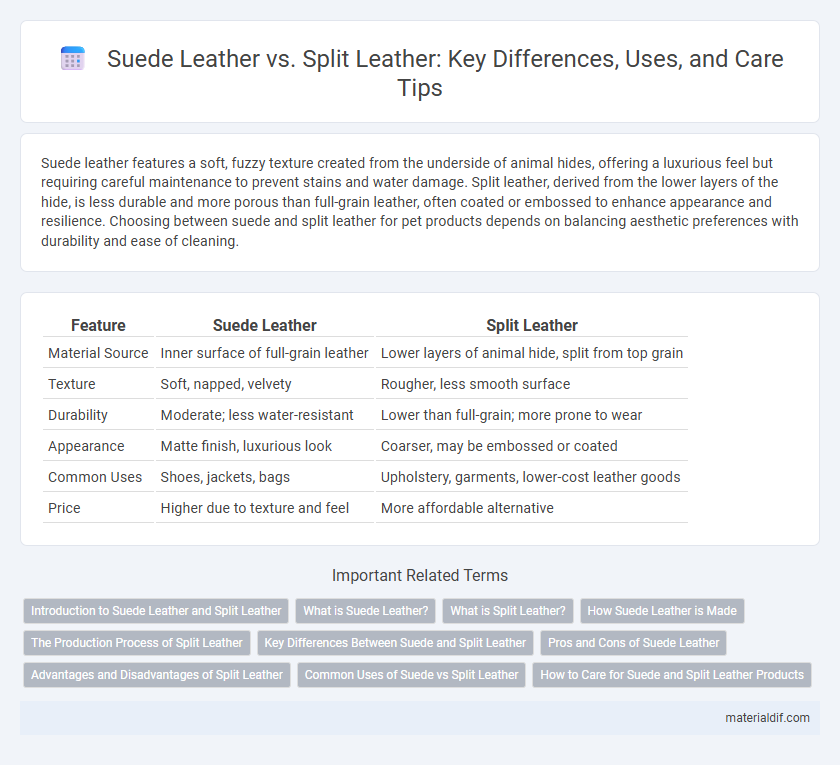
| Feature | Suede Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Inner surface of full-grain leather | Lower layers of animal hide, split from top grain |
| Texture | Soft, napped, velvety | Rougher, less smooth surface |
| Durability | Moderate; less water-resistant | Lower than full-grain; more prone to wear |
| Appearance | Matte finish, luxurious look | Coarser, may be embossed or coated |
| Common Uses | Shoes, jackets, bags | Upholstery, garments, lower-cost leather goods |
| Price | Higher due to texture and feel | More affordable alternative |
Introduction to Suede Leather and Split Leather
Suede leather originates from the underside of animal hides, characterized by its soft, napped finish and increased flexibility, making it ideal for fashion garments and accessories. Split leather derives from the fibrous lower layer after the top grain has been separated, offering durability but a rougher texture often enhanced through embossing or coating. Both types serve distinct purposes in leather goods, with suede valued for its appearance and comfort, while split leather is preferred for budget-friendly, rugged applications.
What is Suede Leather?
Suede leather is made from the underside of the animal hide, producing a soft, napped finish that distinguishes it from top-grain leather. Unlike split leather, which is derived from the lower layers of the hide and often lacks the fine texture of suede, suede is renowned for its velvety surface and flexible feel. This type of leather is commonly used in fashion items such as jackets, shoes, and accessories due to its unique texture and aesthetic appeal.
What is Split Leather?
Split leather is created by separating the fibrous layers from the hide's surface, resulting in a lower layer that lacks the tight grain and durability of full-grain leather. This type of leather is often used as a base for suede or coated with a synthetic finish to mimic more expensive leathers. Due to its porous texture, split leather is less resistant to wear and often more affordable than top-grain or full-grain leather varieties.
How Suede Leather is Made
Suede leather is created by sanding or buffing the inner surface of animal hides, primarily from cattle, to expose a soft, napped texture characterized by a velvety feel. This distinctive process differentiates it from split leather, which is made from the fibrous layer beneath the hide's surface without the sanding technique that produces suede's signature softness. Suede's production involves careful finishing to enhance its pliability and aesthetic appeal, making it prized for fashion and upholstery applications.
The Production Process of Split Leather
Split leather is produced by splitting the fibrous part of the hide after the top grain has been separated, creating a more porous and less durable material compared to full-grain leather. This production process involves mechanically separating the lower layers of the hide, which are often treated, embossed, or coated to mimic the appearance of higher-quality leather. Unlike suede, which is sanded from the inner flesh side to achieve its characteristic nap, split leather retains a rough, fibrous surface used in various applications like upholstery and footwear lining.
Key Differences Between Suede and Split Leather
Suede leather is made from the underside of the animal hide, offering a soft, napped finish with a delicate texture, whereas split leather comes from the fibrous part of the hide left after the top grain is separated, resulting in a tougher, less refined surface. Suede is more breathable and flexible, commonly used in fashion and accessories requiring a luxurious feel, while split leather is often utilized in industrial applications and lower-cost leather products due to its durability. The primary difference lies in texture, appearance, and typical usage, with suede prized for its softness and aesthetic appeal, contrasting split leather's emphasis on robustness and affordability.
Pros and Cons of Suede Leather
Suede leather offers a soft, velvety texture and enhanced flexibility, making it ideal for fashion items and accessories requiring a luxurious feel. Its porous nature provides excellent breathability but makes it more susceptible to stains, water damage, and wear compared to split leather. Maintenance challenges and lower durability when exposed to harsh conditions are notable drawbacks of suede leather.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Split Leather
Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a cowhide after the top grain is separated, offers advantages such as enhanced flexibility, increased affordability, and better suitability for upholstery and handbags due to its thickness. However, its porous nature makes it less durable and more prone to stains and water damage compared to top grain or suede leather. The lack of natural grain texture results in a rougher surface, which may require additional finishing treatments to improve appearance and longevity.
Common Uses of Suede vs Split Leather
Suede leather, known for its soft texture and elegant appearance, is commonly used in fashion items such as jackets, shoes, and accessories like gloves and handbags. Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layer of the hide, is often utilized in industrial applications, upholstery, and budget-friendly footwear due to its durability and lower cost compared to full-grain leather. Both materials offer unique advantages, with suede favored for aesthetic appeal while split leather excels in practicality and strength.
How to Care for Suede and Split Leather Products
Suede leather requires gentle care using a soft brush to remove dirt and a suede protector spray to maintain its texture and prevent stains. Split leather benefits from regular conditioning with leather cream to restore moisture and prevent cracking while avoiding excessive water exposure. Proper storage in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight extends the lifespan of both suede and split leather products.
Suede Leather vs Split Leather Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com