Vegan leather offers a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative to genuine leather, crafted from synthetic materials or plant-based sources that mimic the texture and appearance of real leather. Genuine leather, derived from animal hides, is prized for its durability, natural breathability, and unique aging properties that develop character over time. While vegan leather is easier to maintain and often more affordable, genuine leather remains preferred for its authentic feel and exceptional longevity.
Table of Comparison
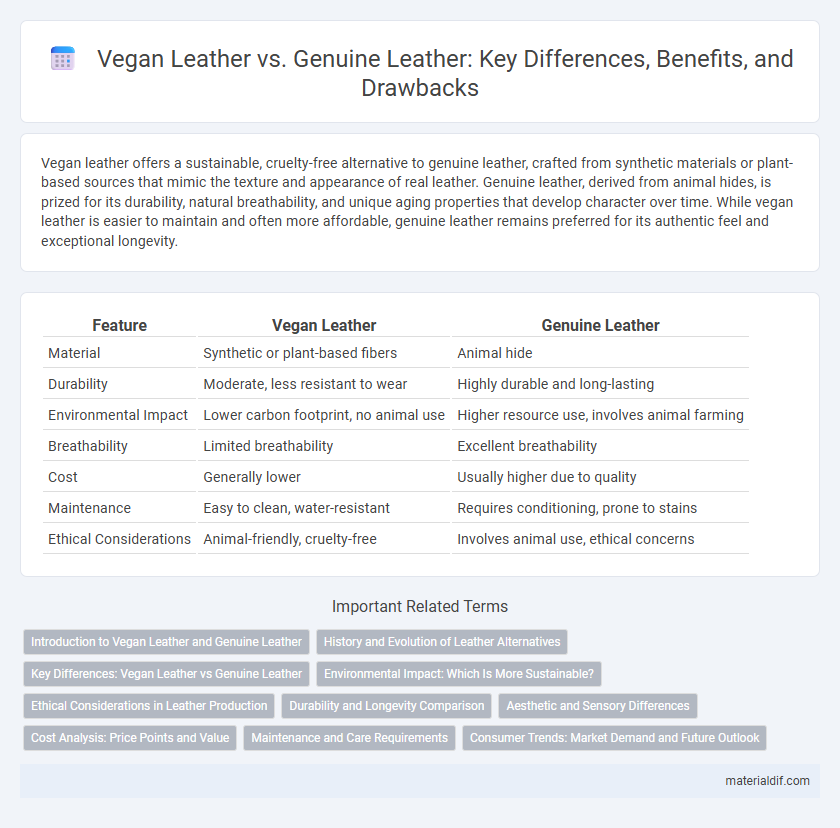
| Feature | Vegan Leather | Genuine Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Synthetic or plant-based fibers | Animal hide |
| Durability | Moderate, less resistant to wear | Highly durable and long-lasting |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, no animal use | Higher resource use, involves animal farming |
| Breathability | Limited breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Cost | Generally lower | Usually higher due to quality |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, water-resistant | Requires conditioning, prone to stains |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-friendly, cruelty-free | Involves animal use, ethical concerns |
Introduction to Vegan Leather and Genuine Leather
Vegan leather, crafted from synthetic materials such as polyurethane or natural alternatives like cork, offers a cruelty-free and environmentally conscious option with water-resistant and durable properties. Genuine leather, derived from animal hides through tanning processes, is valued for its natural texture, breathability, and longevity, often developing a unique patina over time. The choice between vegan leather and genuine leather depends on ethical considerations, maintenance preferences, and desired material characteristics.
History and Evolution of Leather Alternatives
Vegan leather, developed in the early 20th century as a response to ethical and environmental concerns, has evolved from synthetic plastics like polyurethane to innovative plant-based materials such as pineapple leaves and mushroom mycelium. Genuine leather, with origins dating back over 5,000 years, has traditionally been crafted from animal hides through tanning processes that have advanced from ancient vegetable tanning to modern chrome tanning techniques. The evolution of leather alternatives reflects a growing demand for sustainable, cruelty-free materials while maintaining the durability and aesthetics associated with traditional leather.
Key Differences: Vegan Leather vs Genuine Leather
Vegan leather is made from synthetic materials like polyurethane or natural plant-based sources, offering cruelty-free and more sustainable alternatives to genuine leather, which is derived from animal hides through tanning processes. Genuine leather is prized for its durability, breathability, and natural aging characteristics, while vegan leather often lacks the same longevity and develops wear differently over time. Environmental impact also varies, with genuine leather involving resource-intensive animal farming and tanning chemicals, whereas vegan leather production can rely on petrochemicals or renewable materials, influencing biodegradability and carbon footprint.
Environmental Impact: Which Is More Sustainable?
Vegan leather, often made from polyurethane or plant-based materials like pineapple leaves and apple peels, generally has a lower carbon footprint and uses fewer natural resources than genuine leather, which involves cattle farming known for high greenhouse gas emissions and deforestation. However, synthetic vegan leather production relies on non-biodegradable plastics that contribute to microplastic pollution, whereas genuine leather is biodegradable and can last longer if well-maintained, reducing frequent replacements. Evaluating sustainability requires considering factors such as raw material sourcing, chemical usage in tanning or fabrication, biodegradability, and overall lifecycle emissions.
Ethical Considerations in Leather Production
Vegan leather offers a cruelty-free alternative to genuine leather, eliminating animal suffering and reducing reliance on livestock farming, which significantly impacts greenhouse gas emissions. Genuine leather production involves animal slaughter and raises ethical concerns regarding animal welfare, but it tends to be more durable and biodegradable compared to many synthetic vegan leather options made from plastics. Consumers prioritizing sustainability and animal rights often choose vegan leather for its lower environmental footprint and avoidance of animal exploitation despite some trade-offs in material lifespan.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Vegan leather, typically made from polyurethane or plant-based materials, offers moderate durability but often lacks the long-term resilience of genuine leather, which is known for its natural strength and ability to develop a unique patina over time. Genuine leather resists wear and tear more effectively, making it a preferred choice for products requiring extended use and lasting appeal. While vegan leather may withstand daily use, genuine leather generally outperforms in terms of longevity and durability under heavy or prolonged usage.
Aesthetic and Sensory Differences
Vegan leather often mimics the smooth, uniform texture of genuine leather but lacks its natural grain patterns and subtle imperfections, which contribute to the unique aesthetic appeal of real leather. Genuine leather offers a rich, supple feel with a distinctive aroma that deepens over time, providing a sensory experience unmatched by synthetic alternatives. While vegan leather tends to have a consistent, sometimes plastic-like touch, genuine leather's breathability and warmth enhance its tactile quality and overall luxury.
Cost Analysis: Price Points and Value
Vegan leather typically costs less than genuine leather, with prices ranging from $10 to $50 per yard compared to $50 to $200 per yard for real leather, reflecting differences in material sourcing and manufacturing processes. Although genuine leather often offers superior durability and aging qualities, vegan leather provides a budget-friendly alternative with lower maintenance costs. Consumers must weigh initial price points against longevity and desired aesthetic when evaluating value between these two materials.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Vegan leather requires less intensive maintenance compared to genuine leather, as it is more resistant to stains and water damage, making it ideal for easy cleaning with just a damp cloth. Genuine leather demands regular conditioning with specialized leather creams to prevent drying and cracking, alongside protection from excessive moisture and direct sunlight to maintain its durability and appearance. The maintenance frequency and care products needed for genuine leather make it a higher-commitment choice compared to the low-maintenance, synthetic alternatives of vegan leather.
Consumer Trends: Market Demand and Future Outlook
Consumer trends reveal a rising demand for vegan leather driven by environmental concerns and animal welfare awareness, with the global vegan leather market projected to grow at a CAGR of over 48% from 2023 to 2030. Genuine leather maintains a loyal consumer base valuing durability and luxury, but faces challenges due to sustainability issues and shifting regulatory landscapes. Future outlooks indicate vegan leather innovation, such as plant-based and bio-fabricated materials, will significantly influence market dynamics and expand alternatives to traditional leather.
Vegan Leather vs Genuine Leather Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com