Pea gravel features smooth, rounded stones that provide excellent drainage and a comfortable walking surface, making it ideal for pathways and landscaping projects. Crushed granite consists of angular, sharp-edged particles that compact tightly, offering superior stability and load-bearing capacity for driveways and construction bases. Both materials are durable and visually appealing, but pea gravel suits decorative uses while crushed granite excels in structural applications.
Table of Comparison
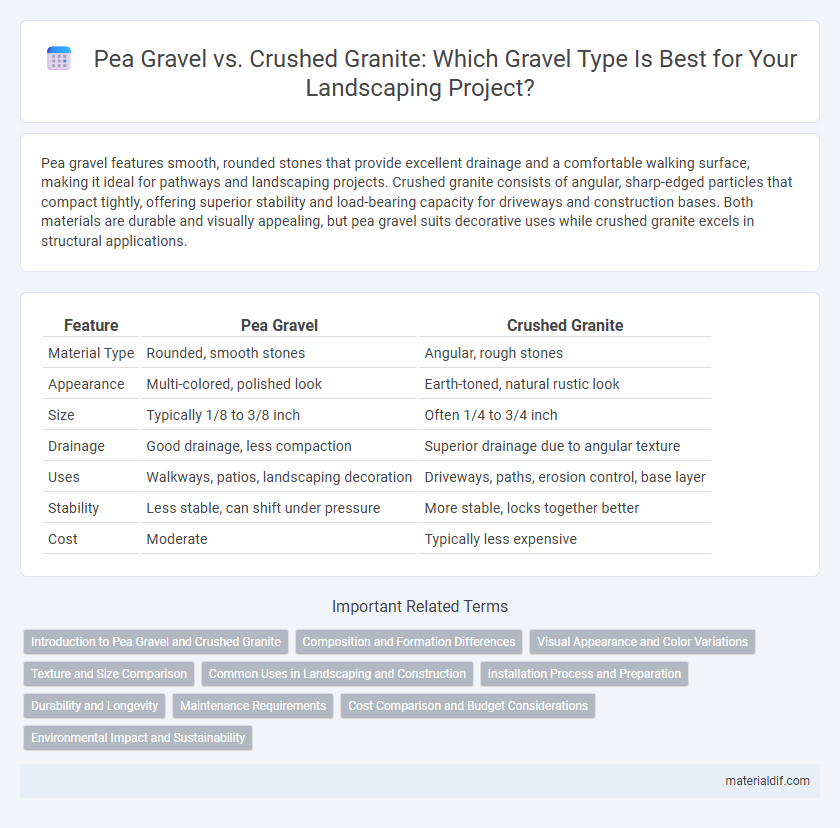
| Feature | Pea Gravel | Crushed Granite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rounded, smooth stones | Angular, rough stones |
| Appearance | Multi-colored, polished look | Earth-toned, natural rustic look |
| Size | Typically 1/8 to 3/8 inch | Often 1/4 to 3/4 inch |
| Drainage | Good drainage, less compaction | Superior drainage due to angular texture |
| Uses | Walkways, patios, landscaping decoration | Driveways, paths, erosion control, base layer |
| Stability | Less stable, can shift under pressure | More stable, locks together better |
| Cost | Moderate | Typically less expensive |
Introduction to Pea Gravel and Crushed Granite
Pea gravel consists of small, rounded stones typically measuring 3/8 inch or smaller, prized for its smooth texture and natural appearance in landscaping and pathways. Crushed granite features angular, jagged fragments ranging from fine dust to pieces about 3/4 inch, providing excellent drainage and stability in construction and erosion control projects. Choosing between pea gravel and crushed granite depends on the desired aesthetic, compaction properties, and application requirements.
Composition and Formation Differences
Pea gravel consists primarily of smooth, rounded river stones formed by natural water erosion processes, resulting in a polished appearance and uniform size typically ranging from 1/4 to 3/8 inches. Crushed granite is composed of angular fragments of granite rock, produced through mechanical crushing, which creates sharp edges and a rough texture ideal for compaction and stability. The distinct formation methods influence their composition: pea gravel's natural rounding contrasts with crushed granite's sharp, mechanically broken particles.
Visual Appearance and Color Variations
Pea gravel features smooth, rounded stones in a palette ranging from tan and brown to gray and white, offering a natural, polished look ideal for decorative landscaping and pathways. Crushed granite presents angular, jagged edges with a more uniform texture, available in earthy tones like reddish-brown, dark gray, and blue-gray, providing a rugged, modern appearance. These distinct visual and color variations influence design choices, where pea gravel enhances softness and warmth while crushed granite adds boldness and contrast.
Texture and Size Comparison
Pea gravel consists of small, smooth, rounded stones typically ranging from 1/8 to 3/8 inches in diameter, providing a softer texture underfoot compared to crushed granite. Crushed granite features angular, sharp-edged particles varying from fine dust up to 3/4 inches, creating a more compact and stable surface ideal for pathways and driveways. The distinct textural difference influences drainage, mobility, and aesthetic appeal in landscaping applications.
Common Uses in Landscaping and Construction
Pea gravel is commonly used in landscaping for pathways, garden beds, and decorative ground cover due to its smooth texture and rounded shape, which provides comfortable walking surfaces and aesthetic appeal. Crushed granite is favored in construction and heavy-duty landscaping projects such as driveways, drainage systems, and as a base material because of its angular edges that lock together for stability and excellent drainage. Both materials serve distinct purposes where pea gravel enhances visual appeal and comfort, while crushed granite emphasizes durability and structural support.
Installation Process and Preparation
Pea gravel installation requires minimal ground preparation, typically involving leveling and compacting the area, followed by laying a weed barrier fabric to prevent growth. Crushed granite installation demands more extensive preparation, including grading, compacting the sub-base, and adding a stabilizing base layer for durability and proper drainage. Both materials require edging to contain the gravel, but crushed granite often benefits from more precise base construction to maintain stability and prevent shifting.
Durability and Longevity
Pea gravel offers moderate durability and is less prone to compaction, making it suitable for decorative pathways but less ideal for heavy traffic areas. Crushed granite provides higher durability due to its angular edges, creating a more stable and long-lasting surface ideal for driveways and high-traffic zones. Over time, crushed granite maintains its structural integrity better than pea gravel, resisting displacement and wear more effectively.
Maintenance Requirements
Pea gravel requires minimal maintenance due to its smooth, rounded stones that resist compaction and allow for easy drainage. Crushed granite demands more frequent upkeep, including regular raking and occasional replenishment, as its angular edges tend to compact and settle over time. Maintaining optimal appearance and functionality for both materials involves periodic weeding and debris removal.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Pea gravel typically costs between $30 and $50 per ton, making it a more budget-friendly option compared to crushed granite, which ranges from $40 to $70 per ton depending on quality and location. Installation expenses for pea gravel are generally lower due to its rounded shape, reducing labor and compaction costs, whereas crushed granite requires more preparation and maintenance, increasing overall budget demands. When planning landscaping or driveway projects, selecting pea gravel can significantly reduce upfront and ongoing expenses, making it a preferred choice for cost-conscious homeowners.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pea gravel and crushed granite differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with pea gravel being a more natural, rounded material typically harvested from riverbeds, causing less habitat disruption. Crushed granite, produced by mining and mechanically crushing large rock deposits, often entails higher energy consumption and carbon emissions during extraction and processing. The natural sourcing and minimal processing of pea gravel generally result in a smaller ecological footprint compared to crushed granite, which may contribute to greater soil erosion and dust pollution.
Pea Gravel vs Crushed Granite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com