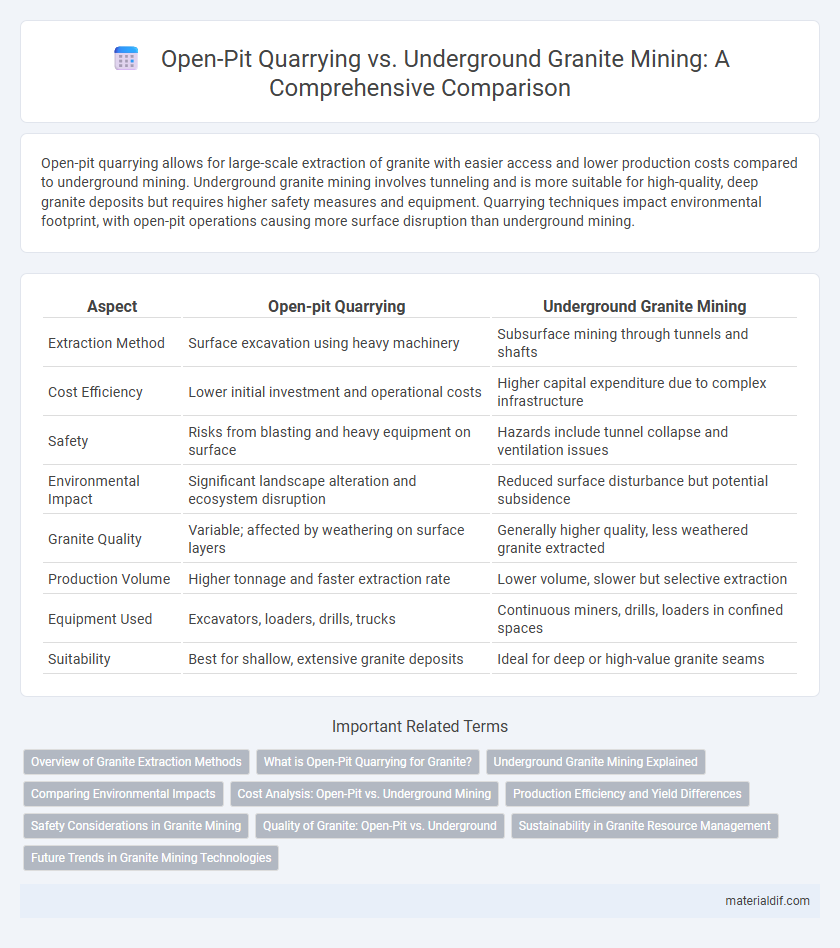
Open-pit quarrying allows for large-scale extraction of granite with easier access and lower production costs compared to underground mining. Underground granite mining involves tunneling and is more suitable for high-quality, deep granite deposits but requires higher safety measures and equipment. Quarrying techniques impact environmental footprint, with open-pit operations causing more surface disruption than underground mining.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Open-pit Quarrying | Underground Granite Mining |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction Method | Surface excavation using heavy machinery | Subsurface mining through tunnels and shafts |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial investment and operational costs | Higher capital expenditure due to complex infrastructure |
| Safety | Risks from blasting and heavy equipment on surface | Hazards include tunnel collapse and ventilation issues |
| Environmental Impact | Significant landscape alteration and ecosystem disruption | Reduced surface disturbance but potential subsidence |
| Granite Quality | Variable; affected by weathering on surface layers | Generally higher quality, less weathered granite extracted |
| Production Volume | Higher tonnage and faster extraction rate | Lower volume, slower but selective extraction |
| Equipment Used | Excavators, loaders, drills, trucks | Continuous miners, drills, loaders in confined spaces |
| Suitability | Best for shallow, extensive granite deposits | Ideal for deep or high-value granite seams |
Overview of Granite Extraction Methods
Open-pit quarrying involves extracting granite from an exposed surface by removing overburden and cutting large blocks directly from the rock face, which allows for efficient access to extensive granite deposits. Underground granite mining requires tunnel or shaft excavation to reach deeper granite layers, minimizing surface disturbance and enabling extraction in areas with limited surface exposure. Both methods utilize specialized cutting tools and explosives, with selection dependent on deposit depth, environmental impact, and economic feasibility.
What is Open-Pit Quarrying for Granite?
Open-pit quarrying for granite involves extracting large blocks of granite directly from the surface by removing overlying soil and rock layers. This method enables access to extensive granite deposits with minimal tunneling, offering cost-effective and efficient extraction. Open-pit operations facilitate the recovery of high-quality granite slabs ideal for construction, monuments, and architectural applications.
Underground Granite Mining Explained
Underground granite mining involves extracting granite from beneath the earth's surface through tunnels and shafts, minimizing environmental impact compared to open-pit quarrying. This method allows access to deeper granite deposits that are not feasible to reach by surface mining, ensuring high-quality stone with less surface disruption. Advanced techniques in underground mining enhance safety and efficiency while preserving surrounding ecosystems and reducing landscape alteration.
Comparing Environmental Impacts
Open-pit quarrying of granite results in significant landscape disruption, habitat destruction, and increased dust pollution, negatively affecting local ecosystems. Underground granite mining minimizes surface disturbance but poses risks like groundwater contamination and subsidence, impacting surrounding water quality and land stability. Overall, open-pit methods have more visible environmental footprints, while underground mining involves complex subsurface environmental challenges.
Cost Analysis: Open-Pit vs. Underground Mining
Open-pit quarrying generally incurs lower operating costs per ton of granite due to easier access, higher equipment productivity, and less labor-intensive processes compared to underground mining. Underground granite mining involves higher expenses from ventilation, underground support structures, and specialized machinery, significantly increasing capital and operational costs. Cost efficiency in open-pit quarrying is often optimized by economies of scale, whereas underground mining is preferable when surface deposits are depleted or environmental restrictions limit open-pit operations.
Production Efficiency and Yield Differences
Open-pit quarrying of granite typically results in higher production efficiency due to easier access to large, continuous granite beds, enabling the use of heavy machinery and faster extraction rates. Underground granite mining often yields less volume per operation but allows for selective extraction of premium-quality stone, reducing waste and increasing the value of the output. The overall yield in open-pit quarrying is generally higher, while underground mining provides more controlled extraction with potentially better material quality.
Safety Considerations in Granite Mining
Open-pit granite quarrying offers greater visibility and easier access, reducing risks related to confined spaces and ventilation issues commonly found in underground granite mining. Underground mining poses heightened safety concerns such as rockfalls, limited escape routes, and accumulation of hazardous gases, necessitating continuous monitoring and advanced ventilation systems. Implementing rigorous safety protocols and modern technologies is critical to minimizing accidents and ensuring worker protection in both mining methods.
Quality of Granite: Open-Pit vs. Underground
Open-pit quarrying typically exposes larger, more uniform granite blocks with consistent texture and color, yielding higher-quality stone for architectural and decorative purposes. Underground granite mining often encounters variable quality due to fractures and veining, which can compromise the integrity and aesthetic value of the extracted material. Consequently, open-pit methods generally provide superior granite quality essential for premium construction and design applications.
Sustainability in Granite Resource Management
Open-pit quarrying allows large-scale granite extraction with lower operational costs but often results in significant landscape disruption and increased carbon emissions due to heavy machinery use. Underground granite mining reduces surface environmental impact and preserves natural habitats, promoting better sustainability through minimal land footprint and reduced dust pollution. Implementing advanced waste management and water recycling techniques in both methods enhances resource efficiency and supports long-term granite sustainability goals.
Future Trends in Granite Mining Technologies
Future trends in granite mining technologies emphasize automation and sustainability, with open-pit quarrying adopting advanced drone surveying and AI-powered equipment for precision extraction. Underground granite mining is increasingly integrating real-time monitoring systems and robotic drilling to enhance safety and reduce environmental impact. Both methods are moving towards energy-efficient machinery and waste reduction techniques to meet stricter environmental regulations.
Open-pit quarrying vs Underground granite mining Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com