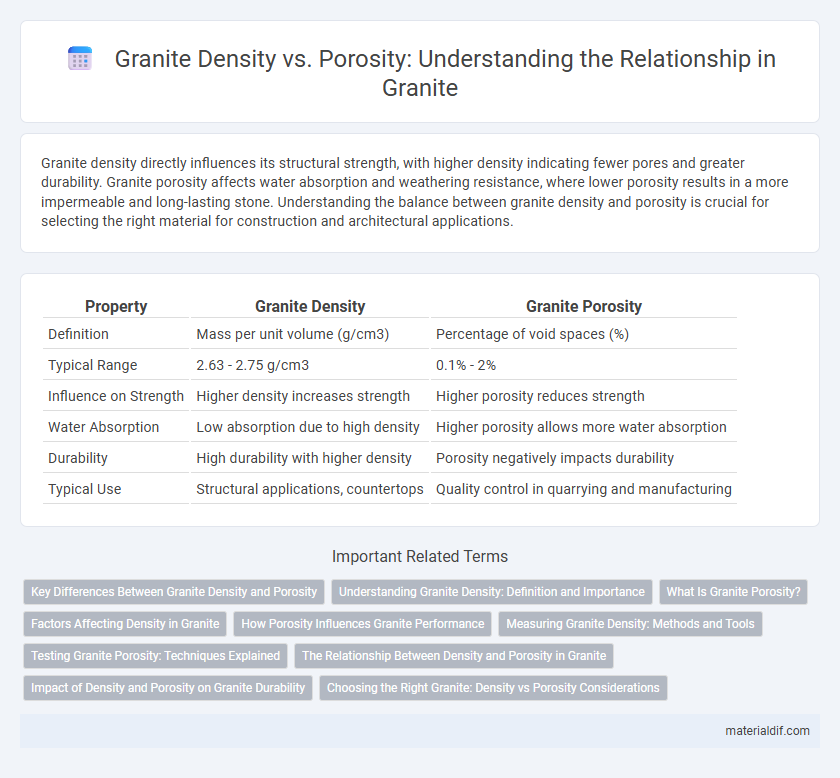
Granite density directly influences its structural strength, with higher density indicating fewer pores and greater durability. Granite porosity affects water absorption and weathering resistance, where lower porosity results in a more impermeable and long-lasting stone. Understanding the balance between granite density and porosity is crucial for selecting the right material for construction and architectural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Granite Density | Granite Porosity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mass per unit volume (g/cm3) | Percentage of void spaces (%) |
| Typical Range | 2.63 - 2.75 g/cm3 | 0.1% - 2% |
| Influence on Strength | Higher density increases strength | Higher porosity reduces strength |
| Water Absorption | Low absorption due to high density | Higher porosity allows more water absorption |
| Durability | High durability with higher density | Porosity negatively impacts durability |
| Typical Use | Structural applications, countertops | Quality control in quarrying and manufacturing |
Key Differences Between Granite Density and Porosity
Granite density measures the mass per unit volume, typically ranging from 2.63 to 2.75 grams per cubic centimeter, indicating compactness and strength. Granite porosity refers to the percentage of void spaces within the rock, usually less than 1%, affecting water absorption and durability. The key difference lies in density reflecting structural mass, while porosity determines permeability and resistance to weathering.
Understanding Granite Density: Definition and Importance
Granite density, typically ranging between 2.63 to 2.75 grams per cubic centimeter, reflects the compactness of its mineral composition, primarily quartz, feldspar, and mica. Porosity in granite, usually less than 1%, indicates the volume of void spaces that affect its strength, durability, and permeability. Understanding granite density is crucial for applications in construction and engineering, as it directly influences the stone's load-bearing capacity and weather resistance.
What Is Granite Porosity?
Granite porosity refers to the volume percentage of void spaces within the granite rock, affecting its ability to absorb and transmit fluids. While granite density typically ranges from 2.63 to 2.75 g/cm3, indicating its compact mineral structure, porosity values are much lower, often below 1%, due to its tightly interlocked crystals. Understanding granite porosity is crucial for its use in construction and geological studies, as even slight variations can influence durability, permeability, and weathering behavior.
Factors Affecting Density in Granite
Granite density primarily depends on its mineral composition, with quartz, feldspar, and mica concentrations influencing overall mass per unit volume. The porosity of granite, although generally low, affects density by introducing void spaces that reduce bulk density values. Temperature, pressure during formation, and geological processes such as fracturing also impact both the porosity and density of granite formations.
How Porosity Influences Granite Performance
Granite density typically ranges between 2.63 and 2.75 grams per cubic centimeter, while its porosity varies from 0.1% to 2%, significantly impacting its durability and structural integrity. Higher porosity increases water absorption, making granite more susceptible to weathering, freeze-thaw damage, and chemical degradation, which diminishes its long-term performance in construction and architectural applications. Low-porosity granite exhibits superior strength and resistance to environmental stressors, making it ideal for high-load-bearing and exterior applications.
Measuring Granite Density: Methods and Tools
Granite density is typically measured using the Archimedes principle, which involves determining the mass of a granite sample in air and its apparent mass when submerged in water, providing accurate results through water displacement methods. Advanced tools such as pycnometers and digital density meters enhance precision by accounting for pore spaces and surface irregularities that affect the apparent density. Understanding granite porosity is essential because higher porosity usually reduces density, influencing granite's structural properties and suitability for construction applications.
Testing Granite Porosity: Techniques Explained
Testing granite porosity involves techniques such as mercury intrusion porosimetry and helium pycnometry, which provide precise measurements of pore volume and connectivity. Granite density is inversely related to porosity, with higher porosity indicating lower bulk density due to increased void spaces within the rock matrix. Understanding the interplay between granite density and porosity is crucial for evaluating its durability and suitability for construction and geological applications.
The Relationship Between Density and Porosity in Granite
Granite density directly correlates with its porosity, where higher density indicates lower porosity due to reduced void spaces within the rock matrix. Typical granite density ranges from 2.63 to 2.75 g/cm3, while porosity usually falls below 1%, reflecting its compact crystalline structure. This inverse relationship impacts granite's strength, durability, and suitability for construction and engineering applications.
Impact of Density and Porosity on Granite Durability
Granite density, typically ranging from 2.63 to 2.75 g/cm3, inversely correlates with its porosity, where lower porosity enhances mechanical strength and reduces water absorption. Higher density granite exhibits increased durability due to fewer pores that limit chemical weathering and freeze-thaw damage. Porosity values below 1% significantly improve granite's resistance to environmental degradation, crucial for long-lasting construction and monument applications.
Choosing the Right Granite: Density vs Porosity Considerations
Granite density typically ranges from 2.63 to 2.75 g/cm3, indicating its compact mineral composition, while porosity usually falls below 1%, reflecting minimal pore space within the stone. Higher density granite often corresponds to lower porosity, enhancing durability and resistance to water absorption, critical factors in construction and countertop applications. Selecting granite with optimal density and low porosity ensures strength, longevity, and reduced susceptibility to staining or weathering.
Granite density vs Granite porosity Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com