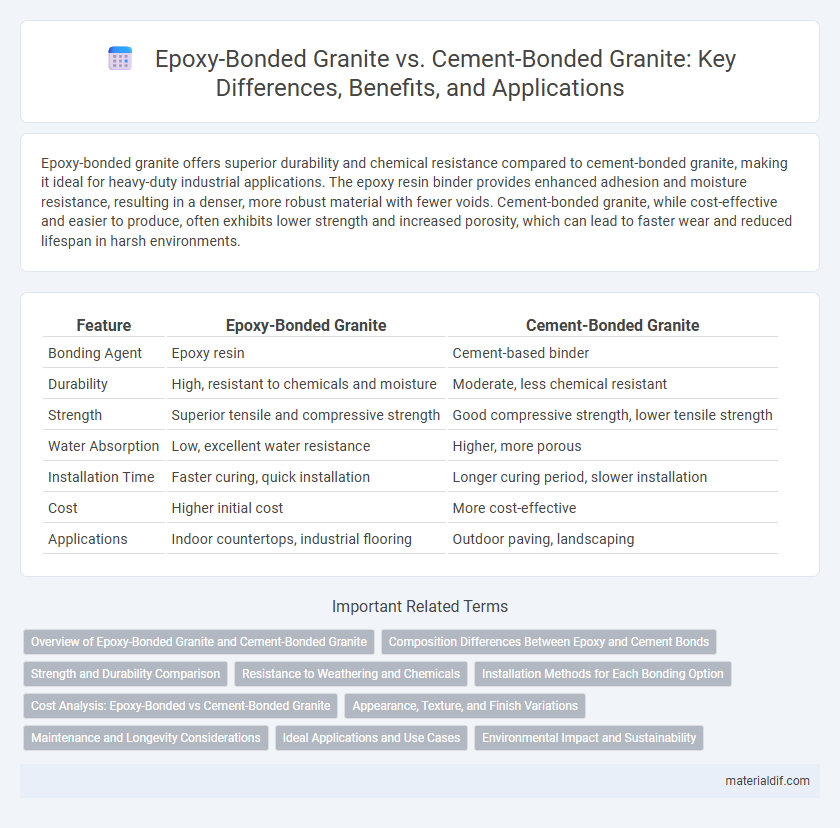
Epoxy-bonded granite offers superior durability and chemical resistance compared to cement-bonded granite, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. The epoxy resin binder provides enhanced adhesion and moisture resistance, resulting in a denser, more robust material with fewer voids. Cement-bonded granite, while cost-effective and easier to produce, often exhibits lower strength and increased porosity, which can lead to faster wear and reduced lifespan in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Epoxy-Bonded Granite | Cement-Bonded Granite |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding Agent | Epoxy resin | Cement-based binder |
| Durability | High, resistant to chemicals and moisture | Moderate, less chemical resistant |
| Strength | Superior tensile and compressive strength | Good compressive strength, lower tensile strength |
| Water Absorption | Low, excellent water resistance | Higher, more porous |
| Installation Time | Faster curing, quick installation | Longer curing period, slower installation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | More cost-effective |
| Applications | Indoor countertops, industrial flooring | Outdoor paving, landscaping |
Overview of Epoxy-Bonded Granite and Cement-Bonded Granite
Epoxy-bonded granite features a high-strength epoxy resin binder that enhances durability, chemical resistance, and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for precision machinery bases and industrial applications. Cement-bonded granite combines crushed granite with Portland cement, offering cost-effective solutions with good compressive strength but lower chemical resistance and flexibility compared to epoxy-bonded variants. Both materials utilize granite aggregates, but their bonding agents significantly influence performance characteristics and suitability for specific engineering uses.
Composition Differences Between Epoxy and Cement Bonds
Epoxy-bonded granite consists of crushed granite particles bonded with a high-strength epoxy resin, resulting in superior durability and chemical resistance compared to cement-bonded granite. Cement-bonded granite uses Portland cement as the binder, which provides a more porous structure and lower resistance to moisture and stains. The epoxy resin in epoxy-bonded granite creates a denser, non-porous surface, enhancing its performance in industrial and decorative applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Epoxy-bonded granite exhibits superior strength and durability due to the high adhesive properties of epoxy resin, which creates a stronger bond between granite particles and resists environmental degradation. Cement-bonded granite, while more cost-effective, tends to have lower tensile strength and is more susceptible to moisture penetration and cracking over time. The enhanced chemical resistance and rigidity of epoxy bonding make it ideal for applications requiring long-term structural integrity and resistance to wear.
Resistance to Weathering and Chemicals
Epoxy-bonded granite exhibits superior resistance to weathering and chemical exposure due to its dense, non-porous epoxy resin matrix that prevents water infiltration and chemical penetration. Cement-bonded granite, while durable, is more susceptible to degradation from freeze-thaw cycles and acidic environments because of its porous cementitious binder. The enhanced weathering and chemical resistance of epoxy-bonded granite makes it ideal for outdoor applications in harsh climates and industrial settings.
Installation Methods for Each Bonding Option
Epoxy-bonded granite installation involves applying a precise layer of epoxy resin adhesive that ensures strong bonding and minimal seam visibility, often requiring controlled temperature and humidity conditions for optimal curing. Cement-bonded granite installation uses a cementitious mortar mix applied to the substrate, providing a robust and durable bond but requiring longer curing times and allowing for some surface porosity. The choice between epoxy and cement bonding affects installation speed, surface finish quality, and environmental adaptability of the granite surface.
Cost Analysis: Epoxy-Bonded vs Cement-Bonded Granite
Epoxy-bonded granite typically incurs higher initial costs due to the price of epoxy resin and specialized application methods, but offers superior durability and resistance to chemicals, potentially lowering long-term maintenance expenses. Cement-bonded granite presents a more economical upfront investment with simpler installation processes, yet it may require more frequent repairs and sealant treatments, increasing lifecycle costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership for epoxy-bonded versus cement-bonded granite involves balancing upfront material and labor costs against longevity and maintenance demands specific to the installation environment.
Appearance, Texture, and Finish Variations
Epoxy-bonded granite offers a smoother, more polished surface with enhanced color depth and uniformity, resulting in a high-gloss finish that highlights intricate details and patterns. Cement-bonded granite exhibits a coarser texture with matte or semi-matte finishes, providing a more natural, rugged appearance that emphasizes the stone's organic grain and hues. The choice between epoxy and cement bonding directly influences durability, stain resistance, and aesthetic versatility of granite surfaces in architectural and design applications.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Epoxy-bonded granite offers superior resistance to moisture and chemical exposure, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and enhanced longevity compared to cement-bonded granite. Cement-bonded granite is more prone to cracking and degradation over time, necessitating more frequent repairs and surface treatments. Choosing epoxy bonding significantly extends the lifespan and durability of granite surfaces in industrial and precision applications.
Ideal Applications and Use Cases
Epoxy-bonded granite offers superior chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for precision industrial applications such as machine tool bases and heavy-duty countertops in laboratories where high stability and minimal vibration are crucial. Cement-bonded granite, being more economical and easier to produce, suits applications like flooring, paving, and decorative architectural elements where moderate strength and aesthetic appeal are required. Selecting epoxy-bonded granite ensures long-term structural integrity in high-stress environments, while cement-bonded granite serves well in cost-effective, large-scale construction projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Epoxy-bonded granite offers superior durability and resistance to chemicals, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste, which enhances its environmental sustainability. Cement-bonded granite, while generally more energy-intensive to produce due to cement manufacturing's high carbon footprint, utilizes more natural materials, potentially lowering long-term ecological impacts. Selecting epoxy or cement bonding depends on balancing immediate environmental costs with durability and lifecycle sustainability in construction projects.
Epoxy-Bonded Granite vs Cement-Bonded Granite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com