Granite extraction involves quarrying large blocks of natural stone from the earth, requiring heavy machinery and precise techniques to minimize waste and preserve stone quality. Granite fabrication transforms these raw blocks into finished products through cutting, polishing, and shaping processes designed to meet specific design and functional requirements. Efficient coordination between extraction and fabrication ensures superior durability, aesthetic appeal, and cost-effectiveness in granite applications for construction and interior design.
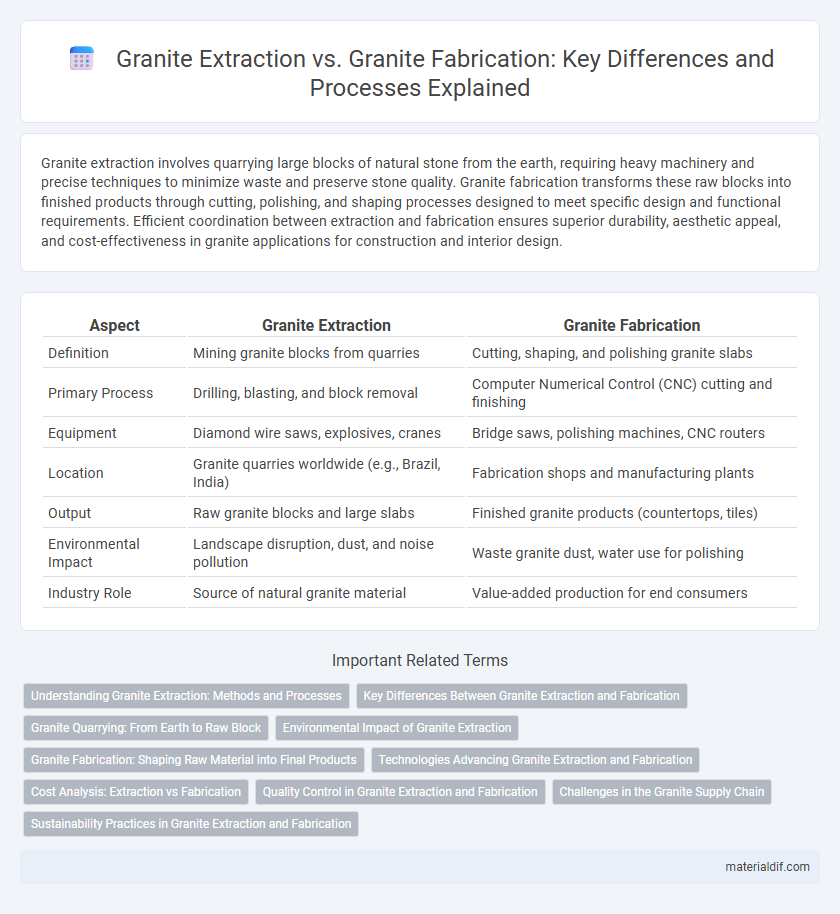
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Granite Extraction | Granite Fabrication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mining granite blocks from quarries | Cutting, shaping, and polishing granite slabs |
| Primary Process | Drilling, blasting, and block removal | Computer Numerical Control (CNC) cutting and finishing |
| Equipment | Diamond wire saws, explosives, cranes | Bridge saws, polishing machines, CNC routers |
| Location | Granite quarries worldwide (e.g., Brazil, India) | Fabrication shops and manufacturing plants |
| Output | Raw granite blocks and large slabs | Finished granite products (countertops, tiles) |
| Environmental Impact | Landscape disruption, dust, and noise pollution | Waste granite dust, water use for polishing |
| Industry Role | Source of natural granite material | Value-added production for end consumers |
Understanding Granite Extraction: Methods and Processes
Granite extraction involves quarrying large blocks of granite from open-pit mines using techniques such as drilling, blasting, and wire sawing to separate stone from the earth. Specialized machinery like diamond wire saws and hydraulic splitters ensures precise cutting while minimizing waste and damage to the rock. Understanding these extraction methods is essential for optimizing yield and maintaining the structural integrity required for subsequent granite fabrication.
Key Differences Between Granite Extraction and Fabrication
Granite extraction involves quarrying large blocks of granite from natural deposits using heavy machinery and controlled blasting, focusing on raw material removal and preservation of geological quality. Granite fabrication transforms these raw blocks into finished products through cutting, polishing, shaping, and assembling processes tailored to specific design requirements. While extraction centers on sourcing raw granite, fabrication emphasizes precision craftsmanship, surface finishing, and customization for functional and aesthetic applications.
Granite Quarrying: From Earth to Raw Block
Granite quarrying involves extracting massive blocks of granite directly from the earth, utilizing advanced diamond wire saws and drilling techniques to ensure precision and minimize waste. This raw block extraction process typically occurs in open-pit quarries where natural granite formations are exposed and systematically sectioned for transport. The quality and size of the granite blocks at this stage critically determine the efficiency and yield of subsequent fabrication processes.
Environmental Impact of Granite Extraction
Granite extraction involves quarrying large blocks from natural deposits, which significantly disrupts landscapes, causes habitat loss, and generates substantial amounts of waste material. The environmental impact includes dust emissions, water pollution from slurry runoff, and high energy consumption during blasting and transportation. In contrast, granite fabrication primarily focuses on cutting and polishing already extracted stone, resulting in comparatively lower environmental disturbances.
Granite Fabrication: Shaping Raw Material into Final Products
Granite fabrication transforms raw quarried granite into polished countertops, tiles, and architectural elements through cutting, grinding, and finishing processes. Skilled fabricators use advanced machinery like CNC routers and water jets to achieve precise shapes and customized designs, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal. Unlike granite extraction, which involves mining large blocks from quarries, fabrication focuses on converting these raw blocks into functional, market-ready products.
Technologies Advancing Granite Extraction and Fabrication
Diamond wire saws and advanced CNC machines have revolutionized granite extraction and fabrication, enabling precise cuts with minimal waste. Automation and laser-guided cutting systems enhance the efficiency and accuracy of fabricating granite slabs into countertops and tiles. Monitoring technologies such as drones and sensors optimize quarry operations by improving safety and reducing environmental impact.
Cost Analysis: Extraction vs Fabrication
Granite extraction involves high initial costs related to quarrying equipment, labor, and regulatory compliance, often resulting in expenses ranging from $15 to $75 per ton depending on location and quality. Granite fabrication costs are primarily driven by skilled labor, precision cutting, polishing, and installation, typically priced between $40 and $100 per square foot. The overall cost analysis reveals extraction as a capital-intensive process with variable operational costs, whereas fabrication focuses on value addition through craftsmanship and customization, influencing final market prices.
Quality Control in Granite Extraction and Fabrication
Granite extraction involves quarrying natural stone blocks with precision to minimize fractures, ensuring raw material integrity essential for high-quality end products. Quality control during extraction checks for structural consistency and absence of defects such as cracks or fissures that could compromise durability. In granite fabrication, stringent inspection of cutting, polishing, and finishing processes guarantees accurate dimensions and surface smoothness, enhancing aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
Challenges in the Granite Supply Chain
Granite extraction faces challenges such as high labor costs, environmental regulations, and limited quarry locations, impacting overall supply chain efficiency. Granite fabrication demands precision equipment, skilled labor, and timely delivery to meet construction and design specifications, often causing bottlenecks. Supply chain disruptions in transportation and raw material availability further complicate the balance between extraction and fabrication processes.
Sustainability Practices in Granite Extraction and Fabrication
Granite extraction emphasizes sustainable practices such as minimizing quarry waste, implementing water recycling systems, and restoring mined areas to reduce environmental impact. In granite fabrication, energy-efficient technologies and waste reduction techniques, including stone offcut recycling and low-emission polishing tools, contribute to sustainability. Both processes increasingly adopt green certifications and eco-friendly initiatives to ensure responsible sourcing and production.
Granite Extraction vs Granite Fabrication Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com