Natural granite is a durable, igneous rock formed over millions of years with unique patterns and natural variations that add distinct character to any surface. Synthetic granite, also known as engineered stone, combines crushed natural granite with resins and pigments to create a more uniform appearance and increased resistance to staining and scratching. While natural granite offers unmatched authenticity and heat resistance, synthetic granite provides greater customization options and consistent quality for countertops and flooring.
Table of Comparison
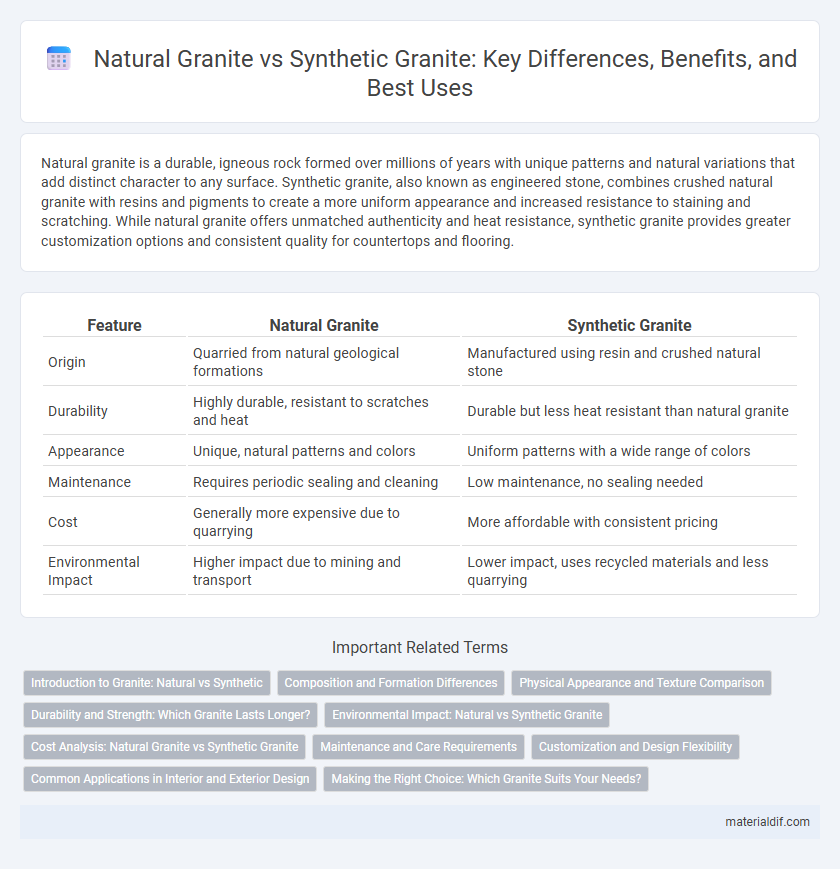
| Feature | Natural Granite | Synthetic Granite |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Quarried from natural geological formations | Manufactured using resin and crushed natural stone |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to scratches and heat | Durable but less heat resistant than natural granite |
| Appearance | Unique, natural patterns and colors | Uniform patterns with a wide range of colors |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing and cleaning | Low maintenance, no sealing needed |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to quarrying | More affordable with consistent pricing |
| Environmental Impact | Higher impact due to mining and transport | Lower impact, uses recycled materials and less quarrying |
Introduction to Granite: Natural vs Synthetic
Natural granite is an igneous rock formed through the slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth's surface, characterized by unique mineral compositions and natural variations in color and texture. Synthetic granite, also known as engineered or composite granite, is manufactured using a blend of crushed natural granite, resins, and pigments, offering more consistent patterns and enhanced durability. Both materials serve as popular choices for countertops and architectural elements, with natural granite prized for its authenticity and synthetic granite favored for its uniformity and resistance to staining.
Composition and Formation Differences
Natural granite is an igneous rock composed primarily of quartz, feldspar, and mica, formed through the slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth's surface. Synthetic granite, also known as engineered stone, is made from crushed natural granite mixed with resins and pigments, allowing for controlled color and pattern consistency. The key difference lies in natural granite's complex mineral structure and formation over millions of years versus synthetic granite's manufactured composition designed for uniformity and enhanced physical properties.
Physical Appearance and Texture Comparison
Natural granite showcases a unique, irregular pattern with a wide range of colors and veining due to its mineral composition, creating a one-of-a-kind surface. Synthetic granite often mimics natural stone but tends to have a more uniform texture and consistent color distribution, lacking the deep, complex veining and natural imperfections found in natural granite. The tactile feel of natural granite is typically cooler and denser, while synthetic granite may feel smoother and less textured due to its manufactured composition.
Durability and Strength: Which Granite Lasts Longer?
Natural granite exhibits superior durability due to its formation under intense heat and pressure, resulting in a dense, hard stone resistant to scratches and heat damage. Synthetic granite, while engineered for uniformity and enhanced stain resistance, often lacks the inherent toughness and long-term strength of natural stone. Over extended periods, natural granite typically outlasts synthetic alternatives, maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal in high-traffic or demanding environments.
Environmental Impact: Natural vs Synthetic Granite
Natural granite is a durable and eco-friendly material, as it requires minimal processing and is sourced directly from quarries, reducing chemical use and energy consumption. Synthetic granite, often made from resins and crushed stone, involves more intensive manufacturing processes that generate higher carbon emissions and potentially harmful waste. Choosing natural granite supports sustainable quarrying practices, whereas synthetic granite's production may contribute more significantly to environmental degradation.
Cost Analysis: Natural Granite vs Synthetic Granite
Natural granite typically incurs higher upfront costs due to quarrying, extraction, and transportation expenses, reflecting its unique and durable qualities. Synthetic granite offers a more budget-friendly alternative with lower production and installation costs, often making it preferable for large projects or tight budgets. When evaluating cost-effectiveness over time, natural granite's longevity and resistance to wear may offset initial investment compared to synthetic options, which can require more frequent maintenance or replacement.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Natural granite requires periodic sealing to prevent stains and moisture penetration, maintaining its durability and aesthetic appeal over time. Synthetic granite, often made from resins and fillers, offers lower maintenance as it resists staining and does not require sealing, making it more convenient for busy households. Both materials benefit from mild cleaning agents, but synthetic granite's non-porous surface reduces the risk of bacterial growth compared to natural granite.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Natural granite offers unique patterns and color variations formed by geological processes, providing one-of-a-kind aesthetics but limited customization due to its fixed natural structure. Synthetic granite allows for greater design flexibility with controlled pigmentation and consistency, enabling tailored color schemes, patterns, and sizes to meet specific design requirements. Manufacturers can incorporate additives and adjust textures in synthetic granite, enhancing customization options beyond the constraints of natural stone.
Common Applications in Interior and Exterior Design
Natural granite, prized for its unique patterns and durability, is commonly used in kitchen countertops, bathroom vanities, flooring, and exterior cladding, offering a timeless aesthetic that withstands weathering. Synthetic granite, engineered from crushed natural stone and resin, provides a more uniform appearance and is often chosen for commercial countertops, wall panels, and outdoor furniture due to its enhanced stain resistance and ease of maintenance. Both materials serve vital roles in interior and exterior design, balancing natural beauty with functional performance in various architectural applications.
Making the Right Choice: Which Granite Suits Your Needs?
Natural granite offers unparalleled durability and unique, organic patterns formed through millions of years of geological processes, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and luxury applications. Synthetic granite, composed of engineered materials like quartz and resins, provides consistent color and pattern options with lower maintenance and greater stain resistance. Choosing between natural and synthetic granite depends on prioritizing authenticity and longevity or uniformity and ease of care for your specific project needs.
Natural Granite vs Synthetic Granite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com