Granite offers natural unique patterns and exceptional durability, making it a classic choice for countertops and flooring. Engineered stone, composed of crushed quartz and resin, provides more consistent color and pattern options while being non-porous and low-maintenance. Both materials are highly durable, but engineered stone resists staining better, whereas granite delivers a timeless, natural aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
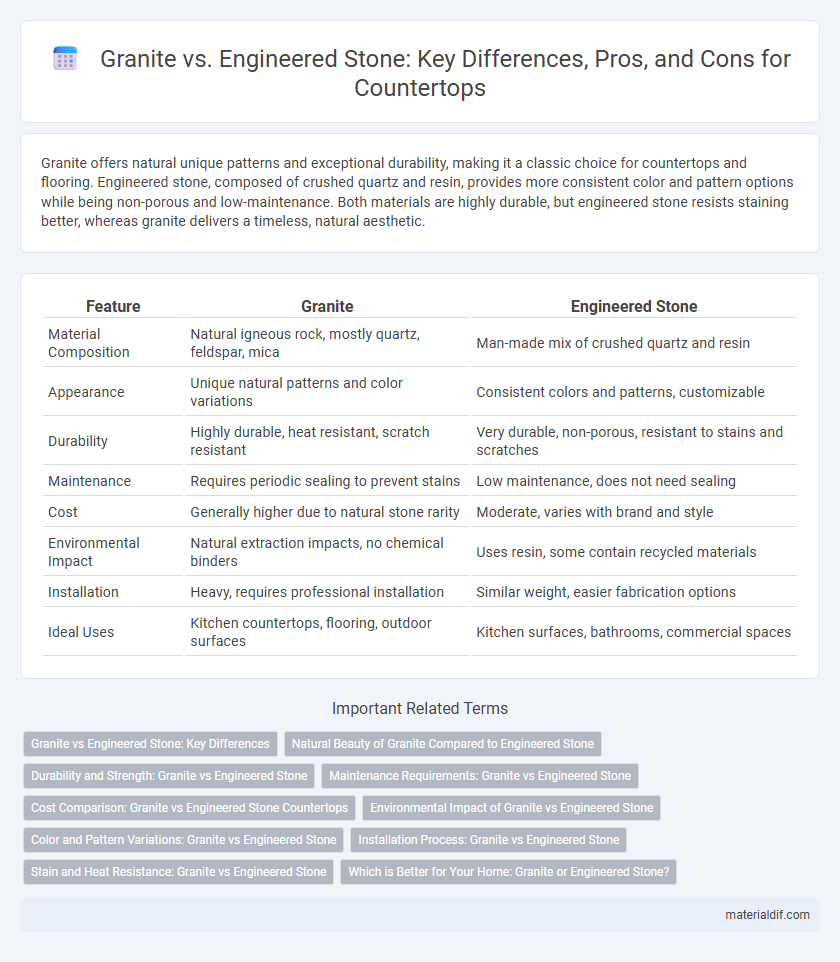
| Feature | Granite | Engineered Stone |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural igneous rock, mostly quartz, feldspar, mica | Man-made mix of crushed quartz and resin |
| Appearance | Unique natural patterns and color variations | Consistent colors and patterns, customizable |
| Durability | Highly durable, heat resistant, scratch resistant | Very durable, non-porous, resistant to stains and scratches |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic sealing to prevent stains | Low maintenance, does not need sealing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to natural stone rarity | Moderate, varies with brand and style |
| Environmental Impact | Natural extraction impacts, no chemical binders | Uses resin, some contain recycled materials |
| Installation | Heavy, requires professional installation | Similar weight, easier fabrication options |
| Ideal Uses | Kitchen countertops, flooring, outdoor surfaces | Kitchen surfaces, bathrooms, commercial spaces |
Granite vs Engineered Stone: Key Differences
Granite is a natural igneous rock composed primarily of quartz, feldspar, and mica, offering unique patterns and exceptional durability, whereas engineered stone is a man-made composite of crushed natural quartz bound with resin, providing consistent color and pattern. Granite's porous nature requires periodic sealing to prevent staining, while engineered stone is non-porous and resistant to bacteria and moisture without sealing. Cost-wise, granite typically has a higher initial price and installation complexity compared to more affordable and easier-to-maintain engineered stone surfaces.
Natural Beauty of Granite Compared to Engineered Stone
Granite boasts unique, naturally occurring patterns and color variations that result from its geological formation, offering unmatched authenticity and depth compared to engineered stone. Engineered stone, composed of crushed quartz and resin, often mimics granite's appearance but lacks the intricate mineral veining and texture found in natural granite slabs. The inherent durability and resistance to heat and scratches make granite a preferred choice for homeowners seeking both aesthetic appeal and long-lasting performance.
Durability and Strength: Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite offers exceptional durability and natural strength due to its dense crystalline structure, making it highly resistant to scratches, heat, and heavy impacts. Engineered stone, composed primarily of quartz and resins, provides comparable hardness and greater uniformity but may be more susceptible to heat damage and resin degradation over time. Both materials excel in kitchen and bathroom applications, yet granite's natural robustness often makes it the preferred choice for long-term durability.
Maintenance Requirements: Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite requires periodic sealing to maintain its resistance to stains and moisture, typically once a year depending on usage and exposure. Engineered stone, made from quartz and resins, is non-porous and does not need sealing, offering easier maintenance and higher stain resistance. Both materials are durable, but engineered stone's low maintenance makes it ideal for busy kitchens with frequent use.
Cost Comparison: Granite vs Engineered Stone Countertops
Granite countertops typically cost between $40 and $100 per square foot, while engineered stone countertops range from $50 to $120 per square foot, reflecting variations in material quality and installation complexity. Granite offers a natural stone aesthetic with unique veining and color patterns, which can affect price fluctuations depending on the rarity and quarry location. Engineered stone, composed of quartz and resins, provides more consistent patterns and greater stain resistance, often justifying its higher price point in terms of durability and maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact of Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite is a natural stone quarried directly from the earth, requiring minimal processing, which results in a lower carbon footprint compared to engineered stone composed of resin and crushed quartz, often involving synthetic materials and chemical adhesives. The extraction of granite, while energy-intensive, avoids the use of petrochemical resins found in engineered stone, reducing potential off-gassing of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in indoor environments. Engineered stone manufacturing generates more waste and consumes non-renewable resources, whereas granite's durability and recyclability contribute to its environmental sustainability over its lifespan.
Color and Pattern Variations: Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite offers unique color and pattern variations due to its natural formation, with each slab showcasing distinct mineral compositions and veining that cannot be exactly replicated. Engineered stone provides consistent color options and uniform patterns, created by blending natural quartz with resins and pigments for a more controlled aesthetic. Homeowners seeking one-of-a-kind designs often prefer granite, while those wanting predictable and matching surfaces lean toward engineered stone.
Installation Process: Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite installation requires precise cutting and sealing due to its natural composition, often necessitating professional expertise for a durable finish. Engineered stone offers a more uniform surface and easier installation with adhesive bonding, reducing the need for extensive sealing. The countertop choice impacts installation time and maintenance, with engineered stone typically allowing for quicker setup and less upkeep.
Stain and Heat Resistance: Granite vs Engineered Stone
Granite offers superior heat resistance, withstanding high temperatures without damage, making it ideal for kitchen countertops near stovetops and ovens. Engineered stone, composed of resin and natural quartz, provides excellent stain resistance due to its non-porous surface but can be vulnerable to heat damage from hot pots or pans. While engineered stone resists staining better, granite's natural thermal durability makes it more suitable for applications involving frequent exposure to heat.
Which is Better for Your Home: Granite or Engineered Stone?
Granite offers natural durability and unique, one-of-a-kind patterns ideal for homeowners seeking authentic stone surfaces, while engineered stone provides consistent color and pattern with enhanced stain and scratch resistance. Engineered stone, composed mainly of quartz resin, is non-porous, making it more resistant to bacteria and easier to maintain compared to granite's natural porous structure. Cost efficiency varies as granite tends to be more expensive upfront, whereas engineered stone can offer long-term savings due to lower maintenance requirements.
Granite vs Engineered Stone Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com