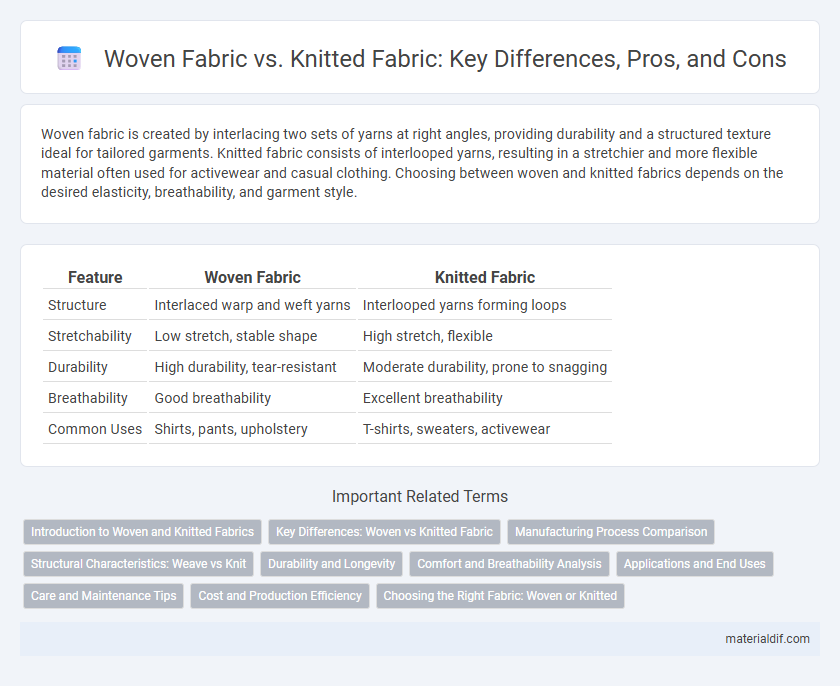
Woven fabric is created by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles, providing durability and a structured texture ideal for tailored garments. Knitted fabric consists of interlooped yarns, resulting in a stretchier and more flexible material often used for activewear and casual clothing. Choosing between woven and knitted fabrics depends on the desired elasticity, breathability, and garment style.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Woven Fabric | Knitted Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Interlaced warp and weft yarns | Interlooped yarns forming loops |
| Stretchability | Low stretch, stable shape | High stretch, flexible |
| Durability | High durability, tear-resistant | Moderate durability, prone to snagging |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Common Uses | Shirts, pants, upholstery | T-shirts, sweaters, activewear |
Introduction to Woven and Knitted Fabrics
Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles, resulting in a strong and stable textile commonly used for shirts, pants, and upholstery. Knitted fabrics consist of interlooped yarns, providing greater stretch and flexibility, ideal for t-shirts, activewear, and sweaters. Understanding the structural differences between woven and knitted fabrics is essential for selecting the appropriate material based on durability, elasticity, and intended use.
Key Differences: Woven vs Knitted Fabric
Woven fabric consists of interlaced yarns at right angles, creating a firm, stable structure ideal for garments requiring durability and shape retention. Knitted fabric features interlooped yarns, offering greater elasticity, softness, and breathability, making it suitable for stretchable, comfortable clothing like activewear and casual wear. Key differences include woven fabric's limited stretch and resistance to deformation, contrasted with knitted fabric's superior flexibility and tendency to snag or lose shape over time.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Woven fabric is produced by interlacing two sets of yarns at right angles using looms, resulting in a stable and durable textile structure. Knitted fabric is created by interlooping yarns with knitting machines, which offers greater elasticity and stretchability compared to woven fabrics. The manufacturing process for woven fabric involves higher tension and longer production times, whereas knitting allows faster production with enhanced flexibility and comfort properties.
Structural Characteristics: Weave vs Knit
Woven fabric consists of interlacing warp and weft yarns at right angles, creating a stable and firm structure that resists stretching. Knitted fabric is formed by interlooping yarns, resulting in a flexible and elastic material that adapts to body movements. The key structural difference lies in the rigid grid of woven fabrics versus the looped, stretchable configuration of knits.
Durability and Longevity
Woven fabric features tightly interlaced threads that provide superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and long-term use. Knitted fabric, created by interlooping yarns, offers greater flexibility and stretch but is generally less resistant to abrasion and may degrade faster under constant stress. The longevity of woven fabrics surpasses knitted ones due to their stable structure, which maintains integrity even after extensive washing and use.
Comfort and Breathability Analysis
Woven fabric offers a structured and durable texture with moderate breathability, making it suitable for formal wear but less ideal for high-movement activities. Knitted fabric excels in comfort and breathability due to its looped construction, allowing greater stretch and air circulation, which enhances moisture-wicking properties. The choice between woven and knitted fabrics significantly impacts garment performance, especially in terms of ventilation and flexibility.
Applications and End Uses
Woven fabric, characterized by its interlaced warp and weft threads, excels in applications requiring durability and structure, such as upholstery, denim jeans, and formal wear. Knitted fabric, formed by interlooping yarns, offers superior stretch and comfort, making it ideal for activewear, t-shirts, and hosiery. The choice between woven and knitted fabric directly impacts the performance and suitability of textiles in fashion, sportswear, and home furnishings.
Care and Maintenance Tips
Woven fabric, characterized by its interlaced yarns, typically requires gentle washing in cold water and air drying to maintain its structure and prevent shrinkage. Knitted fabric, known for its flexibility and stretch, benefits from hand washing or using a delicate cycle with mild detergent to avoid distortion and pilling. Both fabric types should be stored folded rather than hung to preserve their shape and prolong their lifespan.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Woven fabric typically incurs higher production costs due to its complex interlacing process and longer manufacturing time compared to knitted fabric, which benefits from faster machinery and fewer materials. Knitted fabric offers greater production efficiency with lower labor intensity and reduced waste, making it more cost-effective for large-volume orders. The choice between woven and knitted fabric often depends on balancing fabric durability with budget constraints and production speed requirements.
Choosing the Right Fabric: Woven or Knitted
Woven fabric, characterized by its interlaced yarns, offers durability and a structured feel ideal for tailored garments and home textiles requiring strength and stability. Knitted fabric, created by interlocking loops of yarn, provides superior stretch and comfort, making it suitable for activewear and casual clothing that demands flexibility and softness. Selecting between woven and knitted fabrics depends on the desired balance of durability, elasticity, and garment use, ensuring optimal performance and aesthetic appeal.
Woven Fabric vs Knitted Fabric Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com