Indigo dyeing produces denim with a rich, deep blue color that fades uniquely over time, giving each garment a distinct, vintage look. Sulfur dyeing offers a wider range of colors, including black and shades of gray, with excellent colorfastness and resistance to fading. Choosing between indigo and sulfur dyeing depends on the desired aesthetic and durability for the denim pet products.
Table of Comparison
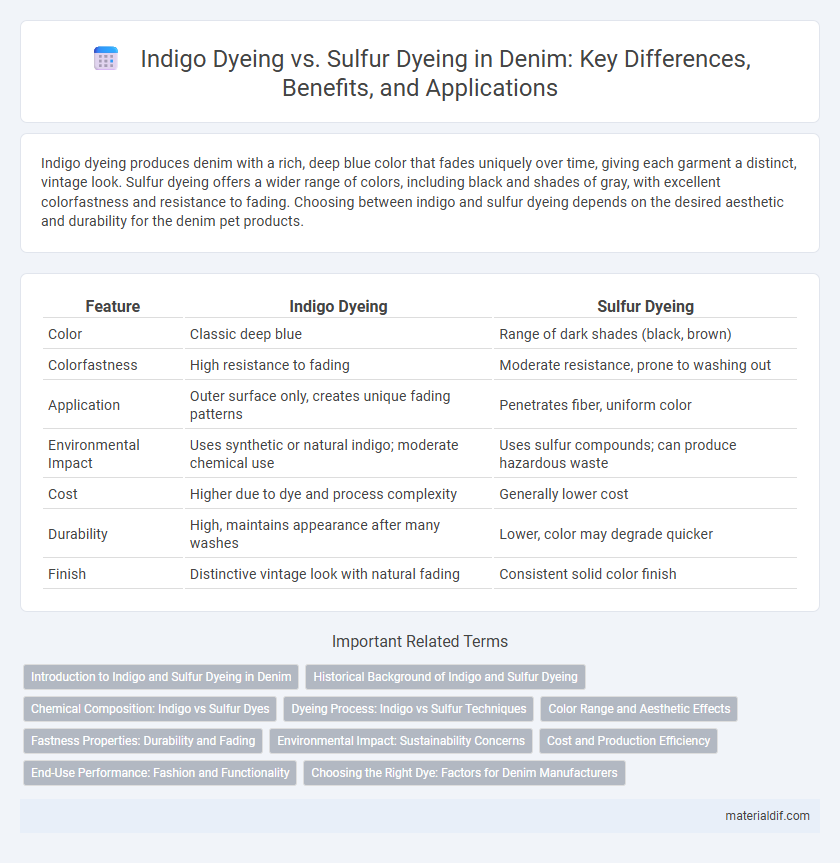
| Feature | Indigo Dyeing | Sulfur Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Classic deep blue | Range of dark shades (black, brown) |
| Colorfastness | High resistance to fading | Moderate resistance, prone to washing out |
| Application | Outer surface only, creates unique fading patterns | Penetrates fiber, uniform color |
| Environmental Impact | Uses synthetic or natural indigo; moderate chemical use | Uses sulfur compounds; can produce hazardous waste |
| Cost | Higher due to dye and process complexity | Generally lower cost |
| Durability | High, maintains appearance after many washes | Lower, color may degrade quicker |
| Finish | Distinctive vintage look with natural fading | Consistent solid color finish |
Introduction to Indigo and Sulfur Dyeing in Denim
Indigo dyeing is the traditional technique used in denim production, known for its unique fading characteristics and deep blue hue achieved through repeated dipping in indigo dye baths. Sulfur dyeing complements indigo by introducing black or other dark shades, enhancing the depth and diversity of denim colors. Combining both dyeing methods allows manufacturers to create varied denim finishes that cater to fashion trends and consumer preferences.
Historical Background of Indigo and Sulfur Dyeing
Indigo dyeing traces back over 4,000 years with origins in ancient India and Egypt, renowned for its vibrant, deep blue color derived from the indigofera plant. Sulfur dyeing emerged in the early 20th century as a cost-effective alternative, producing darker shades on denim with improved colorfastness using synthetic compounds. The shift from traditional indigo to sulfur dyes reflects technological advancements addressing mass production demands and durability in denim fabric.
Chemical Composition: Indigo vs Sulfur Dyes
Indigo dyeing relies on the chemical compound indigotin, a natural or synthetic molecule known for its vibrant blue color and poor water solubility, which requires reduction to leuco-indigo for fabric absorption. Sulfur dyes consist primarily of complex sulfur-containing organic compounds that form insoluble sulfide bonds in the fiber, producing a range of shades from black to brown with excellent wash fastness. The chemical stability of indigotin contrasts with the reactive sulfur compounds, influencing the denim's color intensity, durability, and environmental impact during the dyeing process.
Dyeing Process: Indigo vs Sulfur Techniques
Indigo dyeing involves a fermentation process where denim yarns are repeatedly dipped in indigo dye vats, creating the characteristic deep blue hue with a unique fading pattern due to surface dyeing. Sulfur dyeing uses sulfur-based dyes that penetrate the fiber more completely, resulting in colors like black, brown, or olive with higher wash-fastness and less fading. Indigo dyeing emphasizes the classic blue denim aesthetic with gradual wear effects, while sulfur dyeing offers a broader color palette and durability for varied denim styles.
Color Range and Aesthetic Effects
Indigo dyeing produces a signature deep blue hue with rich variation and a natural fading process that enhances denim's vintage appeal. Sulfur dyeing offers a broader color range including blacks, browns, and reds, providing versatility and a matte finish that complements contemporary styles. Combining both dyeing methods delivers unique aesthetic effects, balancing the classic indigo patina with diverse, modern shades.
Fastness Properties: Durability and Fading
Indigo dyeing offers superior durability with excellent fading characteristics that develop a unique patina over time, making it ideal for classic denim wear. Sulfur dyeing provides vibrant colors but generally exhibits lower fastness properties, resulting in quicker fading and less resistance to washing and abrasion. Denim treated with indigo dye maintains its aesthetic and strength longer, favored for long-lasting and iconic garment appeal.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Concerns
Indigo dyeing, traditionally used for denim, involves natural or synthetic indigo pigments that require large amounts of water and energy, raising concerns about water pollution and resource consumption. Sulfur dyeing uses sulfur compounds that can release harmful byproducts, including sulfur oxides and toxic sludge, posing significant risks to aquatic ecosystems and soil health. Sustainable alternatives emphasize closed-loop water systems and low-impact chemicals to minimize environmental footprints in denim production.
Cost and Production Efficiency
Indigo dyeing, known for its vibrant color and traditional appeal, involves a more complex, time-consuming process that can increase production costs and reduce efficiency compared to sulfur dyeing. Sulfur dyeing offers a more cost-effective and faster alternative, producing darker shades with simpler application methods, making it ideal for large-scale denim manufacturing. Manufacturers often balance the premium quality of indigo with the economical benefits of sulfur to optimize overall production efficiency and cost management.
End-Use Performance: Fashion and Functionality
Indigo dyeing offers denim a distinctive fading pattern and breathability, enhancing its appeal in fashion while maintaining comfort for everyday wear. Sulfur dyeing provides deep, rich colors with improved colorfastness, ideal for durable workwear and functional apparel that require long-lasting vibrancy. Combining both dyeing methods can optimize denim's aesthetic versatility and performance for various end-use scenarios.
Choosing the Right Dye: Factors for Denim Manufacturers
Denim manufacturers must consider factors such as colorfastness, environmental impact, and fabric texture when choosing between indigo dyeing and sulfur dyeing. Indigo dyeing provides the signature blue hue with excellent fade characteristics, ideal for traditional denim aesthetics. Sulfur dyeing offers a broader color palette with greater resistance to oxidation, enhancing durability and design versatility in denim production.
indigo dyeing vs sulfur dyeing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com